IAS UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 3rd March 2020
Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
World Wildlife Day
Part of: Prelims and GS-III-Environment
In news-
- The day is being celebrated on the 3rd of March every year to create awareness about the importance of protecting wildlife.
- In December 2013, UN General Assembly (UNGA) proclaimed 3 March – the day of signature of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) in 1973 – as UN World Wildlife Day.
- The UNGA resolution also designated the CITES Secretariat as the facilitator for the global observance of this special day for wildlife on the UN calendar.
About CITES
- It came into force in July 1975 and currently has 183 signatories
- Aim: Ensure that international trade in specimens of wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival.
- The CITES Secretariat is administered by UNEP and is located at Geneva, Switzerland.
- Although CITES is legally binding on the Parties, it does not take the place of national laws.
- Rather, it provides a framework to be respected by each Party, which has to adopt its own domestic legislation to ensure that CITES is implemented at the national level.
- The International Consortium on Combating Wildlife Crime (ICCWC), a consortium of the CITES Secretariat, INTERPOL, UN Office on Drugs and Crime, World Bank and the World Customs Organization has been established to tackle illegal wildlife trade.
Swathi Weapon Locating radar
Part of: Prelims and GS-III-Security
In news-
- Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) bags $40mn defence deal from Armenia for supplying four Swathi Weapon Locating Radars (WLR)
- Swathi WLR was indigenously developed by DRDO and manufactured by BEL.
- It is an electronically scanned phased array radar
- It automatically locates hostile artillery, mortars and rocket launchers and tracks friendly fire to locate the impact point of friendly artillery fire to issue necessary corrections.
- The radar is designed to detect projectiles with small cross section across the battle space horizon, and has the capability to handle simultaneous fire from weapons deployed at multiple locations.
- The radar uses advanced signal processing techniques for detection and tracking projectiles in the presence of ground, weather clutter and other forms of interference in Electronic Warfare scenario.
National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA)
Part of: Prelims and GS-III-Economy; GS-II- Governance
In news-
- NFRA was constituted in 2018 under section 132 (1) of the Companies Act, 2013.
- It is an independent regulator for enforcement of auditing standards and ensuring the quality of audits so as to enhance investor and public confidence in financial disclosures of companies.
- It can probe listed companies and those unlisted public companies having paid-up capital of no less than Rs 500 crore or annual turnover of no less than Rs 1,000 crore. (while ICAI retains jurisdiction of small listed companies)
- It can even investigate professional misconduct committed by members of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) for prescribed class of body corporate or persons.
Central Fraud Registry
Part of: Prelims and GS-III-Economy; GS-II- Governance
In news-
- There has been decline in frauds at Public Sector Banks from ₹50,329 crore in 2013-14 to just ₹3,781 crore in the first three quarters of 2019-20 (Finance Ministry)
- RBI has put in place a central fraud registry, which is a searchable database to help banks detect instances of fraud by borrowers early on.
- It also helps Banks in carrying out due diligence during the credit sanction process
- Frauds of below 5 Crore will be monitored by regional offices of RBI and above 5 Crore will be monitored by the Central Fraud Monitoring Cell (CFMC) of RBI
Dogra Dynasty
Part of: Prelims and GS-I- History
In news-
- Jammu Airport and the Jammu University to be renamed after Hindu Dogra monarchs Maharaja Hari Singh and Maharaja Gulab Singh, respectively
- Maharaja Gulab Singh founded the Dogra dynasty and became the first monarch of Jammu & Kashmir kingdom in 1846.
- J&K was annexed by the Sikhs in 1819 and Gulab Singh was made Raja of the state by Sikhs in 1820
- In the First Sikh War (1845–46), Maharaja Gulab Singh held aloof and then appeared as a mediator. As a reward, Jammu & Kashmir was given to him by the British for a cash payment
- Maharaja Hari Singh was the last Dogra monarch, who acceded to India in 1947. He contributed troops to British war effort in World War II and served on Churchill’s imperial War cabinet
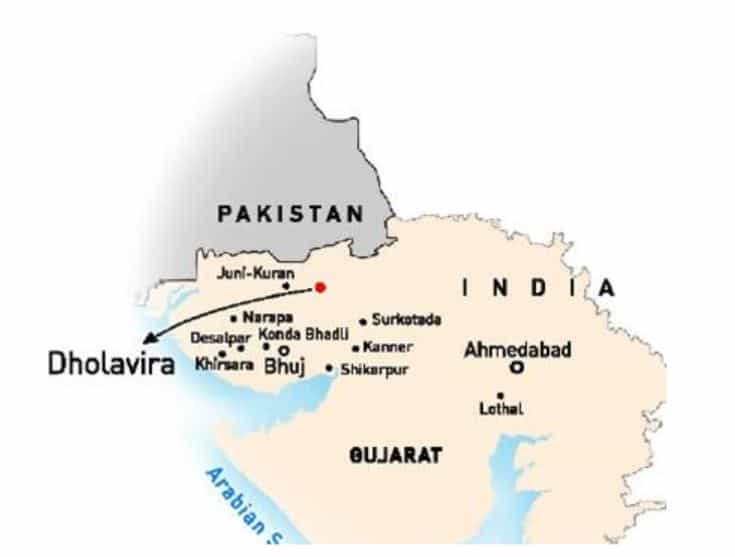
Dholavira
Part of: Prelims and GS-I- Art & Culture
In news
- Government of India has submitted nomination dossier of ‘Dholavira: A Harappan City’ for inclusion in the World Heritage List for the year 2020.
- Dholavira is an archaeological site at Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kutch District, in the state of Gujarat. Dholavira’s location is on the Tropic of Cancer.
- Also known locally as Kotada timba, the site contains ruins of an ancient Indus Valley Civilization/Harappan city.
- It is one of the five largest Harappan sites and most prominent archaeological sites in India belonging to the Indus Valley Civilization.
 Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 3rd March 2020[/caption]
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 3rd March 2020[/caption]
Per Capita Availability of Water
Part of: Prelims and GS-III- Economy
In news-
- The average annual per capita water availability in the years 2001 was 1816 cubic meters while it reduced to 1545 cubic meters in 2011
- This may further reduce to 1486 cubic meters in 2021 and 1367 cubic meters in 2031
- As per Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, 135 litre per capita per day (lpcd) has been suggested as the benchmark for urban water supply.
- For rural areas, a minimum service delivery of 55 lpcd has been fixed under Jal Jeevan Mission, which may be enhanced to higher level by states
- As per NCIWRD percentage of water used for irrigation out of the total water use for the year 1997-98 was 83.30%. The same is estimated to decrease to 72.48% by 2025.
- NCIWRD= National Commission for Integrated Water Resources Development
(MAINS FOCUS)
International Affairs
Topic: General Studies 3:
- India and its neighbourhood- relations.
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests
US-Taliban pact (Doha Agreement) – Part-II
Click here for Part-I of the article
The peace deal is expected to kick-off two processes- a phased withdrawal of US troops and an ‘intra-Afghan’ dialogue. The deal is a fundamental step to deliver a comprehensive and permanent ceasefire and the future political roadmap for Afghanistan peace process and the Central Asian region.
Challenges Ahead for the Deal:
- The deal deliberately excluded the Afghan government because the Taliban do not see the government as legitimate rulers. By giving in to the Taliban’s demand, the U.S. has practically called into question the legitimacy of the government it backs.
- U.S. has made several concessions to the Taliban in the agreement. The Taliban was not pressed enough to declare a ceasefire. Both sides settled for a seven-day “reduction of violence” period before signing the deal.
- Disunity within Afghan Government:
- President Ashraf Ghani (belongs to Pashtun- largest ethnic group) and his primary challenger Chief Executive Abdullah Abdullah (Tajiks- second largest ethnic group) threatening to set up parallel governments after conflict over 2019 election results.
- Concessions made by Mr. Ghani’s government to the Taliban will likely be interpreted by Mr. Abdullah’s supporters as an intra-Pashtun deal reached at the expense of other ethnic groups, especially the Tajiks and the Uzbeks, who formed the bulk of the anti-Taliban Northern Alliance from 1996 to 2001.
- Consequently, ethnic fissures may descend into open conflict.
- Disunity within Taliban
-
- Taliban is composed of various regional and tribal groups acting semi-autonomously.
- All of them may not be amenable to following the directions of its top leadership.
- It is, therefore, possible that some of them may continue to engage in assaults on government troops and even American forces during the withdrawal process thus threatening the deal
- Prisoner release: Afghan government is not on the same page with USA on the release of Taliban prisoners. It has stated the prisoners release can be on the agenda of Intra-Afghan talks and not a precondition to the talks.
- No promises on Civil Liberties and Democracy: Taliban, whose rule is known for strict religious laws, banishing women from public life, shutting down schools and unleashing systemic discrimination on religious and ethnic minorities, has not made any promises on whether it would respect civil liberties or accept the Afghan Constitution.
Taliban and India
- India and the Taliban have had a bitter past- IC-814 hijack in 1999,
- The Taliban perceived India as a hostile country, as India had supported the anti-Taliban force Northern Alliance in the 1990s.
- India never gave diplomatic and official recognition to the Taliban when it was in power during 1996-2001
- India has been backing the Ghani-led government and was among very few countries to congratulate Ghani on his 2019 contested victory.
- Indian foreign policy establishment has shied away from engaging with the Taliban directly, as it is viewed as a proxy of Pakistan. India has supported for enduring and inclusive peace and reconciliation which is “Afghan-led, Afghan-owned and Afghan-controlled”.
- India has consistently supported for an “independent, sovereign, democratic, pluralistic and inclusive” Afghanistan in which interests of all sections of society are preserved.
Implications of the deal on India
- The deal legitimises Taliban and its actions. This weakens India’s fight against all sorts of terrorism and violence adopted by such extremist groups.
- India has a major stake in the continuation of the current Afghanistan government in power, which it considers a strategic asset vis-à-vis Pakistan.
- As a result of the deal, Pakistan military (through its ally Taliban) will become dominant players in Kabul’s power circles, which is not aligned with India’s interests
- Although the pact mentions al-Qaeda, it is silent on other terrorist groups — such as anti-India groups Lashkar-e-Toiba or Jaish-e-Mohammed. India, not being an US ally, is not covered under this pact.
- Ghani government, which India has recognised as winner of the 2019 election, will only serve for an interim period as a result of this deal
- India will have to engage more directly with Taliban which already controls half of Afghanistan’s territory
- As Afghanistan is the gateway to Central Asia, the deal might dampen India’s interest in Central Asia.
- “The bottomline is that India cannot look at the agreements or the route to Kabul via Washington’s view” - Anand Arni (former Special Secretary in RAW)
Connecting the dots
- India’s projects in Afghanistan - Salma Dam
- Moral impact of deal on anti-India terrorist groups
Governance
Topic: General Studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources.
Top Three SDGs & India
Context: President Donald Trump applauded India’s achievements during his speech in Motera stadium in Ahmedabad.
The top three Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations are namely poverty elimination (SDG-1), zero hunger (SDG-2), and good health & well-being (SDG-3) to be attained by 2030
[caption id="attachment_57571" align="aligncenter" width="555"] Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 3rd March 2020[/caption]
Daily Current Affairs IAS | UPSC Prelims and Mains Exam – 3rd March 2020[/caption]
Pic Source: UNO
India’s Present status with regard to these three goals:
- The World Bank’s estimates of extreme poverty — measured as $1.9/per capita/per day at purchasing power parity of 2011 — show a secular decline in India from 45.9% to 13.4% between 1993 and 2015.
- If the overall growth process continues as has been the case since, say, 2000 onwards, India may succeed in eliminating extreme poverty by 2030.
- National Food Security Act (NFSA) that subsidises grains to the tune of more than 90% of its cost to 67% of the population can help India attain the goal of zero hunger before 2030
- The real challenge for India, however, is to achieve the third goal of good health and well-being by 2030
Poor Health condition in India (as per NFHS- In 2015-16)
- Almost 38.4% of India’s children under the age of five years were stunted
- 35.8% of children (below 5 years) were underweight (low weight for age)
- 21% of children (below 5 years) suffered from wasting (low weight for height)
- Also, the Global Hunger Index (GHI) ranks India at 102 out of 117 countries in terms of the severity of hunger in 2019.
- Slow Progress: The decadal decline in underweight children from 42.5% in 2005-06 to 35.8% in 2015-16 amounts to less than 1 per cent decline per year.
- Behind Other Nations: According to the Global Nutrition Report, 2016, at the present rates of decline, India will achieve the current stunting rates of China by 2055
What are the governments ambitions w.r.t malnutrition?
- The National Nutrition Strategy, 2017, aims to reduce the prevalence of underweight children (0-3 years) by 3% points every year by 2022 from NFHS 2015-16 estimates.
- Under National Nutrition Mission (renamed as POSHAN Abhiyaan), 2017, government aims to reduce
- Stunting by 2% per annum,
- Undernutrition by 2% per annum,
- Anemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) by 3% per annum
- Low birth weight by 2% per annum
In order to achieve good Health, government has to focus on below four areas
- Mother’s education.
- It is one of the most important factors that has a positive multiplier effect on child care and access to healthcare facilities.
- It also increases awareness about nutrient-rich diet, personal hygiene, etc.
- This can also help contain the family size in poor, malnourished families.
- Thus, a high priority to female literacy, in a mission mode through liberal scholarships for the girl child, would go a long way towards tackling this problem.
- Access to improved sanitation and safe drinking water.
- The Swachh Bharat Abhiyan should shift its focus from mere ODF declaration to ODF+ and ODF++ strategies which involves proper functioning of community toilets, efficient waste sludge management and recycling measures.
- Jal Jeevan Mission which aims to provide piped drinking water to all Households by 2024 needs to be implemented in mission mode
- Change in dietary patterns
- There is a need to shift dietary patterns from cereal dominance to the consumption of nutritious foods such as livestock products, fruits and vegetables, pulses, etc.
- But they are generally costly and their consumption increases only by higher incomes and better education.
- Diverting a part of the food subsidy on wheat and rice to more nutritious foods can help
- New agricultural technologies
- India must adopt new agricultural technologies of bio-fortifying cereals, such as zinc-rich rice, wheat, iron-rich pearl millet
- The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has to work closely with Farmer Producer Organisations and NGOs so as to make newer seeds and modern farm practices affordable and accessible to all farmers in the country.
Conclusion
- Global experience shows that with the right public policies focusing on agriculture, improved sanitation, and women’s education, one can have much better health and well-being for its citizens, especially children. India can certainly do better, but only if it focuses on this issue.
Connecting the dots
- 17 Sustainable Development Goals
- India’s achievements in Millennium Development Goals
- India’s Ayushman Bharat Programme
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1) Consider the following statements about Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES)
- It is legally binding on the Parties but it does not take the place of national laws
- India is a NOT a signatory to this convention
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Consider the following statements about Swathi Weapon Locating Radars (WLR)
- It is designed and developed by HAL in collaboration with USA post 1999 Kargil Conflict.
- The radar has the capability to handle simultaneous fire from weapons deployed at multiple locations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.3) Consider the following statements about National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA)
- It is a statutory body established by NFRA Act, 2018
- It is an independent regulator to oversee the auditing profession and accounting standards in India
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 Only
- 2 Only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.4) Central Fraud Registry was set up in 2016 by which body?
- Indian Banks Association
- Finance Ministry
- Reserve Bank of India
- NITI Aayog
Q.5) Dholavira, an Harappan Site, is located in which state of India?
- Rajasthan
- Gujarat
- Bihar
- Uttar Pradesh
ANSWERS FOR 02 March 2020 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | B |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | D |
Must Read
About Afghanistan -Taliban:
About Indo-US Nuclear energy deals:
About Economic Slowdown:
