Archives
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs – 1st April, 2016
INTERNATIONAL
TOPIC: General studies 2:
- Bilateral, regional , global groupings and agreement involving India and affecting its interest
- Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian Diaspora.
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate
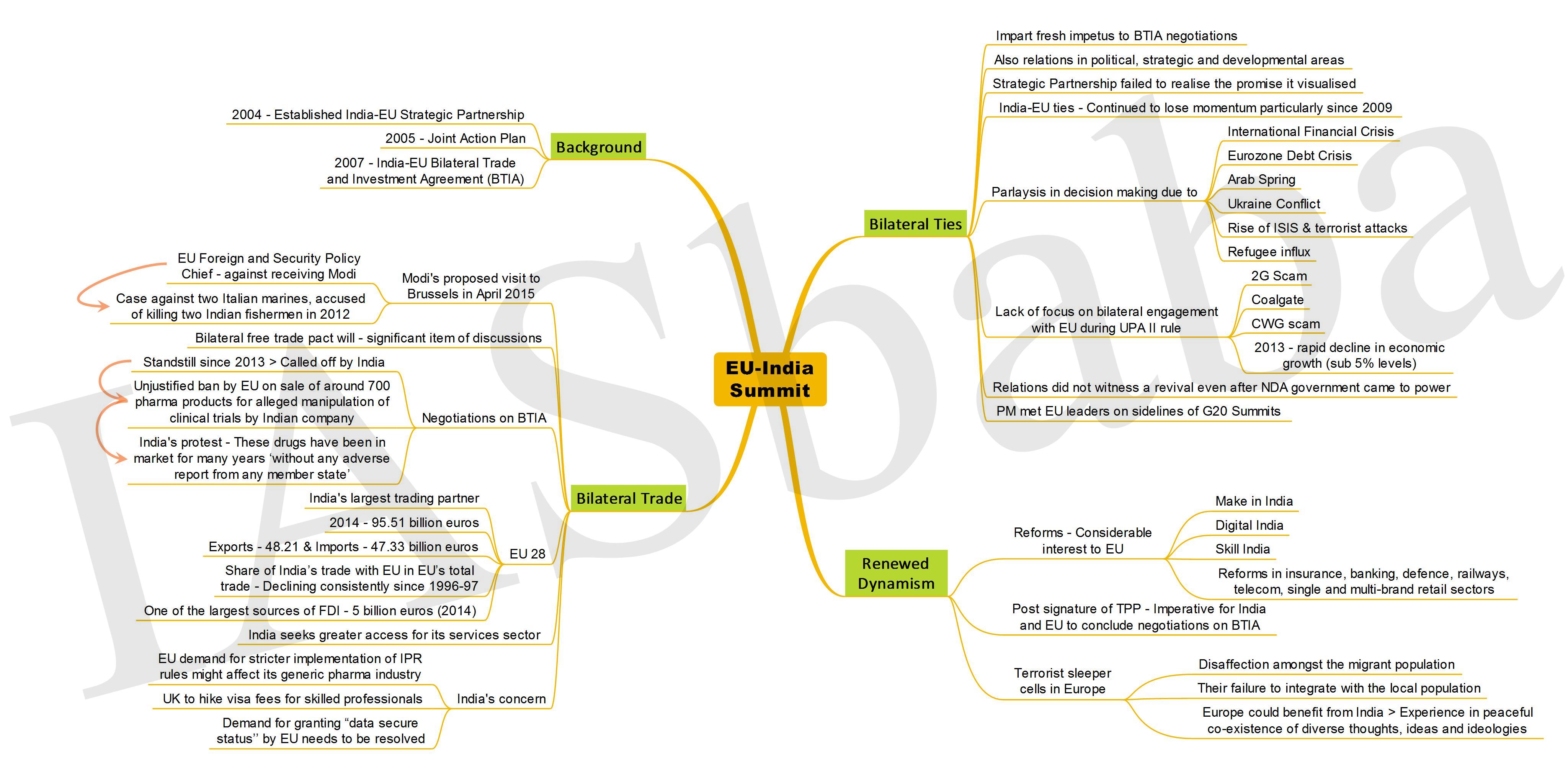
India, EU summit agrees on new agenda for strategic partnership
Background:
- India and the European Union (EU) have endorsed the 'EU-India Agenda for Action 2020' as a common road map for the strategic partnership in the next five years during 13th edition of India-European Union Summit which was held recently in Brussels, capital of Belgium. The EU-India strategic partnership was launched in 2004. The last summit i.e. 12th edition was held in 2012 in New Delhi.
- The summit laid out concrete priority actions for the strategic bilateral partnership in areas like trade and investment, climate, energy, water and migration in the next five years.
- The sectors of partnership range from foreign policy, counter terrorism and disarmament to transport and space.
- The Bilateral Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA) negotiations have remained deadlocked over growing differences regarding greater market access sought by both aides for merchandise exports
What is Strategic partnership all about?
- A strategic partnership is a long-term interaction between two countries based on political, economic, social and historical factors. Such a partnership manifests itself in a variety of relationships. India has signed “strategic partnerships” with more than 30 countries.
- India has strategic partnerships with the United States, Russia, China, Japan, UK, France and others.
- It is obvious that not all strategic partnerships are equally important. Some have a dominant political element, while others have a prominent economic dimension. In some cases, the security dimension may be the most important.
What were the key outcomes of the recently held summit?
EU-India Agenda for Action 2020: Both sides endorsed the agenda to concrete the road-map for the EU-India Strategic Partnership for the next five years.
EU-India Broad-based Trade and Investment Agreement (BTIA):
- The BTIA negotiations have remained deadlocked over growing differences regarding greater market access sought by both aides for merchandise exports.
- Point of contention is that EU has consistently sought lower import duties on a range of commodities. This time, the EU is seeking the lowering of tariffs on automobiles and wine products.
- Issues related to facilitation of greater movement of professionals from one country to another, arising out of the Mode 4 provisions of the 1995 General Agreement on Trade in Services is another point of contention between the two sides.
- Both sides agreed to further the negotiations on early conclusion of the BTIA.
- The new agenda pushes for a broad based approach to resolve trade irritants in particular concerning goods, services and investments, and strengthen trade and investment relations.
Terrorism:
- Both sides adopted a Joint Declaration on Counter-terrorism to step up cooperation to counter radicalization and violent extremism.
- It will also allow jointly countering the flow of sources of terrorist financing, Foreign Terrorist Fighters and arms supply.
- Also called for the early adoption of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism in the UN. They have also agreed to explore the possibility of India and EUROPOL, the EU’s law enforcement agency, to share intelligence.
Loan assistance:
- The European Investment Bank (EIB) agreed to lend loan of 450 million Euros for the construction of the first metro line in Lucknow.
Agenda for Action on environment issues: EU has agreed to help projects including the ‘Clean India’ initiative and the ‘Ganga Rejuvenation Initiative,’ in terms of developing a solution to clean up the river as well as developing legal and governance frameworks for managing the basin.
To control and organize migration:
- The Common Agenda on Migration and Mobility (CAMM), which was also adopted, is designed to control and organize migration – a pressing concern for the EU.
- Significantly for the EU, the Agenda for Action includes items on facilitating the return of irregular migrants and the possibility of exploring a ‘Readmission Agreement’ — returning visa over-stayers to their home countries.
- The Agenda also includes the prevention of human trafficking and promoting international protection as priority areas.
- Points of special interest to India on the agenda are easier visa procedures for skilled workers, IT professionals, and business travellers. For now, the CAMM is a political declaration and not a legal agreement.
Arbitration procedure on the Italian Marines: Both sides expressed their confidence in solving the marine case currently underway in the framework of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
Connecting the dots:
- What does strategic partnership mean? What are the key outcomes of recent held India-EU summit which help in strengthening strategic partnership?
NATIONAL
TOPIC: General studies 2:
- Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation
- Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources
India’s Drug Industry
Data fabrication and duplicity at Ranbaxy-
- Penalties of $500 million on Ranbaxy
- Increased scrutiny by the USFDA and other foreign regulators
- Heightened focus on quality-related issues within the Indian pharmaceutical industry
Dysfunctional System:
- An alarmingly high rate of substandard medicines being prescribed in publicly-funded programmes like the Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) and places like the Railway Hospitals and the Armed Forces Medical Stores Depots (AFMSD)
- Percentage of locally procured substandard drugs at a high 32 per cent in one year
- European companies were selling medicines in India that had not been approved in their home countries, or, for that matter, in any developed country.
- Ministry of Health had failed to investigate the officials who granted such ‘illegal’ approvals despite the Ministry giving a written commitment to Parliament.
- Recommendation making mandatory basic quality testing such as bioequivalence studies for all generic drugs was ignored (reason for rejection- India lacked the infrastructure) but encouraged such testing for exports because countries like the U.S. will not accept any drug formulation which is not proven bioequivalent.
- Only a minority cases results in a prosecution and even in those cases, judges wilfully ignore the mandatory sentencing provisions of at least one year of imprisonment, preferring instead a “simple imprisonment till the rising of the court”, thus allowing the convicted person to walk free as soon as the judge rose for the day.
Focus on improving quality-
- Targeted at only those manufacturing facilities that make products for export to lucrative Western markets
- Little done by either the industry or the government to improve the quality of medicines sold in less-regulated markets like India — and its poorer neighbours in Asia and in Africa.
Need of centralised licensing—
- Even when the drug inspectors are of a high calibre, very little can be done to stop the flooding in of substandard drugs from Himachal Pradesh or Uttarakhand- because only the governments in the respective States can cancel the licences of the erring drug manufacturers located there
- Two legislative efforts in 2007 and 2013 to centralise such regulations failed because of sabotage by the Indian pharmaceutical industry
Long-term Effects
- Growing antibiotic resistance: a growing serious worldwide public health problem which has a series of negative impacts such as prolonged morbidity, hospital stay and increased risk of mortality
- Birth of deathly superbugs
- Public health, especially to the poor and vulnerable, thereby, increasing health care costs and financial burden on the families
Related Articles:
Pharmaceutical Sector: India’s Drug Policy
MUST READ
Building with Brussels- PM Modi’s visit can help bring a necessary pragmatism into the India-EU relationship
For security’s sake-India must use the opportunity offered by the Nuclear Security Summit to pursue purposeful nuclear diplomacy.
Fertiliser imbalance-Policy changes are needed, not just advice to farmers
Related Articles:
Neem-coated truth: Urea policy isn’t a game-changer
An Act that hinders competitiveness- The provisions of the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, are more coercive than what were required to address market failure
Related Articles:
How bankruptcy code will save lenders- A key design focus in the proposed code is speed of resolution. Delay is disincentivized at various stages
Related Articles:
Dealing with Failure: Bankruptcy Code
Working through the bankruptcy maze
Aadhaar versus public goods- Aadhaar is exactly the kind of shiny new toy that further distracts attention from the core duty of government
Related Articles:
http://iasbaba.com/2016/03/iasbabas-daily-current-affairs-9th-march-2016/
http://iasbaba.com/2016/03/the-big-picture-legislative-backing-for-aadhaar-how-will-it-help/
How disabled friendly are India’s cities?-Hyderabad tops the list of India’s million-plus cities in terms of employment for disabled persons
Related Articles:
Disability Law & the Invisible People
Mental health Policy’ in India
MIND MAPS
1. EU - India Summit