Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims –ECONOMY
Context: India could soon see record imports of edible oil of over 16 to 16.5 million tonnes during the current oil year ending October 2023.
Background:-
- Low rainfall in the month of August, along with other factors, is driving the high demand.
- Data released on September 2023, showed the import of edible oil in August 2023 was 35 percent higher compared to imports in August 2022.
About Edible oil:-

IMAGE SOURCE: bestfoodfacts.org
- Oilseeds and edible oils are two of the most sensitive essential commodities.
- India is the world’s second-largest consumer and number one importer of vegetable oil.
- In terms of volumes, palm oil, soya bean oil, and mustard oil are the three largest consumed edible oils in India.
- India is one of the largest producers of oilseeds in the world. (Edible oil prices)
- India produces- rapeseeds, soybean, peanut, groundnut, copra, cottonseeds and sunflower seeds.
- In India, the Edible Oil industry is dependent on the vagaries of monsoons like other agricultural products.
- In order to cater to rising demand, India imports refined edible oil or crude stock to meet the demand-supply gap.
- India imported 0 million tonnes of edible oil in the year 2019, while the production is around 7.0 million tonnes.
- At present, India meets nearly 55% to 60% of its edible oil demand through imports.
- Palm oil (Crude + Refined) constitutes roughly 62% of the total edible oils imported and is imported mainly from Indonesia and Malaysia.
- Soyabean oil (22%) is imported from Argentina and Brazil.
- Sunflower oil (15%) is imported mainly from Ukraine and Russia.
India’s Export-Import Policy on Edible Oils:-
- To reduce the import of edible oils in the country, the Indian Government is focusing on increasing the production and productivity of oilseeds and area expansion under Oil Palm and tree-borne oilseeds to enhance the domestic availability of edible oils.
- National Mission on Oil Seed and Oil Palm (NMOOP) was launched by the Government from 2014-15 to increase the production and productivity of Oilseed crops including mustard and soybean in the country.
- The scheme is now merged with the National Food Security Mission from 2018-19 as NFSM-Oilseeds & Oil Palm. (National Food Security Act)
- It has also placed the import of refined palm oil in the ‘restricted’ category with effect from 8th January 2020.
MUST READ: National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm (NMEO-OP)
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements: (2023)
Statement-I:
India accounts for 3·2% of global export of goods.
Statement-II:
Many local companies and some foreign companies operating in India have taken advantage of India’s ‘Production-linked Incentive’ scheme.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The quantity of imported edible oils is more than the domestic production of edible oils in the last five years.
- The Government does not impose any customs duty on all imported edible oils as a special case.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –ART AND CULTURE
Context: Hindi Diwas was celebrated across country recently.
About Hindi Diwas:-
- “Hindi Diwas” is celebrated annually on September 14th in India.
- It commemorates the adoption of Hindi as one of India’s official languages.
- The Constituent Assembly of India, on September 14, 1949, formally recognized Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, as the official language of India for central government and Union purposes.
- This decision was enshrined in Article 343 of the Constitution of India.
- Article 351 pertains to the ‘Directive for development of the Hindi language’.
- World Hindi Day is observed on 10th January. (International Mother Language Day)
- About 425 million people speak Hindi as their first language and about 120 million people speak Hindi as their second language.
- The Hindi language is majorly spoken in states like Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Haryana, Bihar, Jharkhand etc.
- Hindi is also spoken in Mauritius, Nepal, Fuji, Suriname, Guyana, Trinidad and Tobago.
Other languages in India:-
- The Indian constitution recognizes 22 major languages of India in what is known as “the 8th Schedule” of the Constitution.
- These include Sanskrit, Assamese, Bangla, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kashmiri, Kannada, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Tamil, Telugu, Santali, Sindhi, and Urdu.
MUST READ: Languages of India
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) If a particular area is brought under the Fifth Schedule of the Constitution of India, which one of the following statements best reflects the consequence of it? (2022)
- This would prevent the transfer of land from tribal people to non-tribal people.
- This would create a local self-governing body in that area.
- This would convert that area into a Union Territory.
- The State having such areas would be declared a Special Category State.
Q.2) With reference to India, the terms ‘Halbi, Ho, and Kui’ pertain to (2021)
- dance forms of Northwest India
- musical instruments
- pre-historic cave paintings
- tribal languages
Syllabus
- Prelims –GOVERNMENT POLICIES
Context: Recently, the centre launched the Skill India Digital app.
Background:-
- The Skill India Digital app, brings together listings for upskilling courses and job listings.
- The app was soft launched in April 2023, and was announced by Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman during the Budget session of Parliament.
About Skill India Digital app:-
- Launched in 2023.
- Developed by: National Skill Development Corporation.
- Ministry: Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
- Skill India Digital app, brings together listings for upskilling courses and job listings.
- The app will be linked with DigiLocker and Aadhaar to issue verifiable certificates of course completion.
- It will generate digitally signed CVs for job applicants and people taking courses.
- The app would help in distributing courses on skills.
- It will use digital matchmaking to bring potential employers and employees together.
Skill India Digital:-
- Launched: September,2023.
- Ministry: Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship. (Schemes related to skill development)
- Skill India Digital is a state-of-the-art platform to bring all skilling initiatives together.
- It is the Digital Public Infrastructure for skilling, employment, and education.
- It engages and caters to learners, central and state ministries, employers, content providers, knowledge partners, sector skill councils, assessment bodies, and media.
- It is also a comprehensive information gateway for all government skilling and entrepreneurship initiatives.
- It is a go-to hub for citizens in pursuit of career advancement and lifelong learning.
- It is linked to the Udyam portal for the registration of micro, small, and medium enterprises.
- It is “the marketplace, the platform where all those who are interested — commercial or non-commercial stakeholders — can come together, plug in, deliver skills, gain skills, look for employment, and offer employment.
- It has a vision to make skill development more innovative, accessible, and personalized in its embodiment, focusing on digital technology and Industry 4.0 skills.( Skill Development in India)
- It will be a breakthrough in accelerating skilled talent hiring and facilitating lifelong learning and career advancement.
MUST READ: National Skill Development Mission
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following statements with reference to India: (2023)
- According to the ‘Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006’, the ‘medium enterprises’ are those with investments in plant and machinery between (15 crore and 25 crore).
- All bank loans to the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- Ministry of Labour and Employment
- NITI Aayog
- Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology/Geography
Context: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) recently, ordered the Madhya Pradesh government to stop the operation of cruise vessels as well as other motor-propelled boats in the Bhoj wetland.
About Bhoj wetland:-
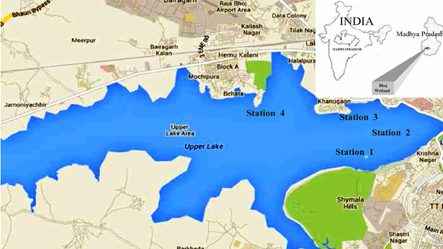
IMAGE SOURCE: ResearchGate
- Location: Bhopal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Bhoj Wetland consists of two contiguous human-made reservoirs.
- The upper and lower lakes are located in the city of Bhopal.
- Historical Background:-
- The Bhoj wetland was first conceived by the visionary king Paramara Raja Bhoj in 1005-1055 CE.
- He built the lake by raising an earthen dam across the Kolans.
- The Lower Lake was built much later in 1794 by Chhote Khan, a minister to Nawab Hayath Mohammad Khan.
- Bhadbhada dam was built on the southeast corner of Bhojtal in 1965.
- It was designated as the Ramsar site in 2002.
Threats to the Bhoj Wetland:-
- The Bhoj wetland faces various threats from urbanization and human settlements on all sides.
MUST READ: COP14 of Ramsar Convention on Wetlands
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Which one of the following is the best example of repeated falls in sea level, giving rise to present-day extensive marshland? (2023)
- Bhitarkanika Mangroves
- Marakkanam Salt Pans
- Naupada Swamp
- Rann of Kutch
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2023)
- Jhelum River passes through Wular Lake.
- Krishna River directly feeds Kolleru Lake.
- Meandering of the Gandak River formed Kanwar Lake.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Syllabus
- Prelims – ECONOMY
Context: Recently, India has become the 13th country in the world that issue Internationally Accepted OIML (International Organisation of Legal Metrology) Certificates.
About OIML (International Organisation of Legal Metrology) Certificates:-
- Established: 1955.
- HQ: Paris.
- OIML (International Organisation of Legal Metrology) is a renowned international standard-setting body in the field of legal metrology.
- Its primary role is to develop model regulations, standards, and related documents for use by legal metrology authorities and industries worldwide.
- These standards are crucial in harmonizing national laws and regulations concerning the performance of measuring instruments, such as clinical thermometers, alcohol breath analyzers, radar speed measuring instruments, ship tanks at ports, and petrol dispensing units.
- India became an OIML member in 1956.
- India signed the metric convention, emphasizing its commitment to international standards in metrology.
- The OIML-CS (Certificate System) is a globally recognized system for issuing, registering, and using OIML certificates, along with their associated OIML-type evaluation/test reports.
Advantages:-
- Indian manufacturers can now export their products with greater ease.
- The certification services provided by India will attract international manufacturers.
- To meet the growing demand for certification services, India is expected to witness a surge in employment opportunities in the legal metrology sector.
MUST READ: Legal metrology (packaged commodities) rules Amendment 2022
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following actions: (2023)
- Detection of car crash/ collision which results in the deployment of airbags almost instantaneously.
- Detection of accidental free fall of a laptop towards the ground which results in the immediate turning off
- of the hard drive.
- Detection of the tilt of the smartphone which results in the rotation of the display between portrait and landscape mode.
In how many of the above actions is the function of the accelerometer required?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q.2) Which one of the following is the context in which the term “qubit” is mentioned? (2022)
- Cloud Services
- Quantum Computing
- Visible Light Communication Technologies
- Wireless Communication Technologies
Syllabus
- Prelims –ECONOMY
Context: The onset of the Ukraine war has started fragmenting world trade as per the recent World Trade Report 2023.
About World Trade Report 2023:-
- Launched:12 September 2023.
- Published by: WTO. (India Challenges WTO verdict on sugar)
- It emphasizes policy goals beyond trade efficiency, including peace, security, poverty reduction, and sustainability.
- It features findings on how re-globalization or increased international cooperation and broader integration can support security, inclusiveness, and environmental sustainability.
Key Highlights:-
- The report addresses the shift in the narrative around globalization.
- It emphasizes policy goals beyond trade efficiency, including peace, security, poverty reduction, and sustainability.
- Re-globalization: The report advocates for “re-globalization,” expanding trade integration to more economies, people, and issues.
- Reorientation of Trade
- It states reorientation of Trade Trade is gradually aligning along geopolitical lines.
- It states Trade flows within hypothetical geopolitical “blocs” are growing faster than those between them, indicating a shift towards friend-shoring.
- Geopolitical Shifts
- It states that Geopolitical tensions, the Ukraine conflict, and the rise of China have impacted global trade dynamics.
- It states COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of resilient supply chains.
- It states that despite challenges, bilateral trade between China and the United States reached record highs. (China’s Developing Status at WTO)
- Inclusiveness: It states inclusiveness Trade integration has lifted millions out of poverty.
- Sustainability: It states Sustainability Trade can contribute to sustainability by providing access to green technologies.
MUST READ: 12th WTO Ministerial Conference
SOURCE: BUISINESS LINE
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Central Bank digital currencies, consider the following statements: (2023)
- It is possible to make payments in a digital currency without using the US dollar or SWIFT system.
- A digital currency can be distributed with a condition programmed into it such as a timeframe for spending it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) “Rapid Financing Instrument” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which of the following: (2022)
- Asian Development Bank
- International Monetary Fund
- United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
- World Bank
Syllabus
- Prelims –IMPORTANT PERSONALITIES
Context: Recently, Former Press Trust of India (PTI) journalist Walter Alfred passed away at the age of 103.
About Walter Alfred:-
- Birth: Mangalore, Karnataka.
- He covered India’s Independence.
- He also covered the days of Indira Gandhi’s Emergency.
- He also reported on the India-Pakistan and Vietnam wars.
- Three days after the 1971 India-Pakistan war, Alfred was arrested on espionage charges in Pakistan and imprisoned for a month in Rawalpindi.
- He was PTI’s Southeast Asia correspondent stationed in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, and Singapore.
- He featured leaders like Jawaharlal Nehru, Pakistani General Ayub Khan, and the former Indonesian premier Sukarno.
- Although he retired in 1980 after a 60-year career in journalism, he continued his profession.
- He taught journalism at New Delhi’s Indian Institute of Mass Communication.
- In 1997, he returned to Mumbai and continued to contribute articles for Indonesian and Malaysian newspapers for several more years.
- He traversed the globe as a PTI correspondent and witnessed some of the most historic moments of the 20th century.
MUST READ: Satyendra Nath Bose
SOURCE: AIR
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Madanapalle of Andhra Pradesh, which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
- Pingali Venkayya designed the tricolor Indian National Flag here.
- Pattabhi Sitaramaiah led the Quit India Movement of the Andhra region from here.
- Rabindranath Tagore translated the National Anthem from Bengali to English here.
- Madame Blavatsky and Colonel Olcott set up the headquarters of the Theosophical Society first here.
Q.2) Who among the following is associated with ‘Songs from Prison’, a translation of ancient Indian religious lyrics in English? (2021)
- Bal Gangadhar Tilak
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
- Sarojini Naidu
India-Brazil relations
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: Aiming for United Nations Security Council (UNSC) reforms, India and Brazil recently agreed to conduct regular bilateral meetings.
About India-Brazil relations:
Historical ties:
- Pedro Alvares Cabral, a Portuguese explorer landed on the East Coast of Brazil in 1500, two years after Vasco de Gama had landed in India.
- Between the 16th and 18th centuries, Brazil and Goa, both outposts of the Portuguese imperialist empire, had bilateral exchanges that are reflected in food and dressing as well as local traditions.
- The ‘Ongole’ strain from Andhra Pradesh led to the production of the zebu variety known in Brazil as ‘Nelore’.
Political:
- The strategic partnership established in 2006 between Brazil and India has deepened, with both countries cooperating closely within BRICS, IBSA, G4, G20, and the wider multilateral context of the United Nations.
- Brazil and India along with Germany and Japan jointly pursued aspirations of permanent seats in the UN Security Council and worked towards a multipolar world where large developing countries can frame global rules and democratise international institutions.
- Both countries played a pivotal role as leaders of the Global South or South-South cooperation.
- The Brazilian foreign policy of reciprocal multilateralism is in concurrence with India’s policy of strategic autonomy.
India-Brazil trade relation:
- Trade between Brazil and India increased to $7.02 billion in 2021, with Brazilian exports worth $4.8 billion and imports from India valued at $6.7 billion.
- In 2021, India became the world’s 5th largest trading partner of Brazil (2nd in Asia), and the 5th largest source of Brazilian imports and the 13th largest destination of Brazilian exports.
- Major Indian exports to Brazil includes processed Petroleum products, Agro-chemicals (insecticides, fungicides), Chemicals, Pharmaceutical, Textured filament yarn, and Unwrought Aluminum.
- Brazilian exports to India included Crude oil, soya oil, Gold (non-monetary), cane sugar, cotton, gum, wood and turpentine oils, chemicals (carboxylic acids) and iron ore and concentrates.
- Brazil played a crucial role in the India-MERCOSUR Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) that improves India’s access to the large South American market.
Defence and Security Cooperation:
- India and Brazil signed an agreement in 2003 for cooperation in defence.
- Meetings of Joint Defence Committee (JDC) are held as an institutionalized mechanism for defence cooperation.
- Brazilian firearms company Taurus Armas SA signed a joint venture with Jindal Defence (part of O P Jindal Group) to produce and sell small arms in India.
- An MoU on cooperation in the area of Cyber Security between CERT-In and its counterpart agency was signed during the State Visit of President Bolsonaro in January 2020.
Cultural Cooperation
- Brazil has a strong community of Yoga and Ayurveda
- The Brazilian Association of Ayurveda (ABRA) is a non-profit association with offices in 9 states of Brazil and has members all over Brazil.
- Mahatma Gandhi is highly regarded in Brazil and the government and NGOs are trying to inculcate the philosophy of non-violence among students, youth and police.
- A Cultural Exchange Programme (CEP) for the years 2020-2024 was signed during the State Visit of President Bolsonaro to India in January 2020.
Challenges in the bilateral relationship between India and Brazil:
- Trade competition: Both India and Brazil are major exporters of agricultural products such as sugar and meat, which can create competition and trade friction between the two countries.
- China’s trade dominance: Furthermore, there are concerns as China, which is Brazil’s largest trading partner, can have an impact on relations between India and Brazil.
- Sugarcane subsidy: Brazil’s complaint to the World Trade Organization about India’s subsidies to sugarcane farmers.
- This has led to tensions between the two countries due to Brazil’s concerns over India’s agricultural policies that could negatively impact its economic interests.
- Limited people-to-people contact: India and Brazil have a limited number of people-to-people contacts, including business, cultural, and educational exchanges.
- Differences in strategic priorities: India and Brazil are both emerging powers that seek to enhance their global influence, but their approaches to regional and global issues may differ.
Way Forward:
The decade long bilateral strategic partnership between India and Brazil is based on a common global vision, shared democratic values, and a commitment to foster economic growth with social inclusion for the welfare of the people of both countries. With their uniting stance on various multilateral and plurilateral forums, the two countries are considered to be important for the creation of new world order.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations)
Context: Recently the Prime Minister attended the 18th East Asia Summit (EAS) was held in Jakarta.
Key highlights of the 18th East Asia Summit (EAS):
- Leaders’ Declaration on ASEAN: At the 18th EAS, the Leaders’ Declaration on ASEAN as an Epicentrum of Growth was adopted.
- It was discussed on building resilience against emerging challenges and future shocks through cooperation on enhancing energy security and food security, maintaining financial stability, and strengthening regional health architecture.
- Plan of Action (POA): The Plan of Action (POA) for the next five years outlines the priorities that include efforts on the mainstreaming and implementation of the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP).
- It lays emphasis on strengthening partnerships, through cross-sectoral collaborations that includes efforts in furthering the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- Meet of ASEAN and non-ASEAN states: The meet provided an opportunity for ASEAN member states and the eight non-ASEAN countries to exchange views on issues concerning the region and the world at large.
Significance of East Asia:
- Regional Security: Considering tension on the Korean Peninsula, South China and in the Taiwan Strait, among others, it is vital for Japan, China and South Korea to maintain a common stance and to share a common concern for security in the East Asian region.
- Economic benefit: It represents nearly 50 per cent of the world’s population with 20 percent of global trade, and comprising 16 nations that are on a dynamic path of economic development.
- Global Implications: An East Asia community would play a big role in instilling a sense of responsibility in Asian countries and in leading them jointly in contributing to the resolution of global issues.
Challenges in the region:
- Regional challenges: While the EAS participating countries share a common perspective aimed at achieving peace and security in the Indo-Pacific, ongoing contestations like China with other countries issue limits cooperative and collaborative framework as envisaged originally.
- Complex geopolitical issues: Strengthening the EAS as a forum for dialogue and cooperation on a wide spectrum of strategic, political, and economic matters of common interest and concern, remains complex.
- This stems from the existing and ever-evolving multi-faceted threats and challenges which get compounded through the intense geo-political and geo-economic discourse being witnessed in the region.
- Concerns over the relevance: The deepening geo-political divide being witnessed today raises concern on the relevance of the EAS in addressing issues of human security challenges as a consequent of the socio-economic fallout from the COVID-19 and the ongoing Ukraine-Russia war.
- Hampering efficacy and effectiveness: The nature of the relations amongst the EAS participating countries, marked by confrontation and contestations, has had its impact on its efficacy and effectiveness.
Way Forward:
It was an attempt at the 18th EAS to strengthen the efficacy and effectiveness of the institution by emphasising on an international community, built on cooperation without division and confrontation. The EAS promotes adherence to international law and a rules-based order in the region which includes respecting maritime rights and territorial integrity and working towards peaceful conflict resolution.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1) Consider the following pairs:
| Ramsar Wetland | Location |
| 1.Kanwar Lake | Bihar |
| 2.Nalsarovar | Rajasthan |
| 3.Yashwant Sagar | Uttar Pradesh |
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Q2) Consider the following statements
Statement-I:
“Hindi Diwas” is celebrated annually on 10 January in India.
Statement-II:
The Indian constitution recognizes 22 major languages of India in what is known as “the 8th Schedule” of the Constitution.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
- Statement-I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
- Statement-I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Q3) With reference to the World Trade Report 2023, consider the following statements:
- It was launched in September,2022.
- It was Published by WTO.
- It shows that bilateral trade between China and the United States reached a record High.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Mains Practice Question
Q.1) Analyse the significance of East Asia Summit (EAS) as a premier forum for strategic dialogue in the Indo-Pacific. What are the geo-political and geo-economic challenges faced by the forum? (250 words)
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 15th September 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 14th September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – a
