Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Category: SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: Google recently launched a new computer chip, called Ironwood. It is the company’s seventh-generation TPU, or tensor processing unit, which has been designed to run artificial intelligence (AI) models.
Decoding the context: Processing units are essentially hardware units that are the brain of a computer. In this context, it is important to understand the difference between CPU, GPU and TPU.
Learning Corner:
About CPU (Central Processing Unit)
- Developed in the 1950s, a CPU is a general-purpose processor that can handle various tasks.
- A CPU has at least a single core — the processing unit within the CPU that can execute instructions. In the initial years, CPUs used to have just one core but today, they can contain from two to up to 16 cores. As each core of the CPU can handle one task at a time, the ability to multitask is determined by the number of cores in the hardware.
About GPU (graphics processing unit)
- Unlike a CPU, a GPU is a specialised processor (it is a type of application-specific integrated circuit, or ASIC) which has been designed to perform multiple tasks concurrently rather than sequentially (like in a CPU).
- Modern GPUs comprise thousands of cores which break down complex problems into thousands or millions of separate tasks and work them out in parallel, a concept known as parallel processing. This makes GPUs far more efficient than CPUs.
- Initially developed for graphics rendering in gaming and animation, GPUs today are far more flexible and have become the bedrock of machine learning.
About TPU (Tensor Processing Unit)
- A TPU is also a type of ASIC, meaning it is designed to perform a narrow scope of intended tasks. First used by Google in 2015, TPUs were specially built to accelerate machine learning workloads.
- TPUs are engineered to handle tensor — a generic name for the data structures used for machine learning — operations. They excel in processing large volumes of data and executing complex neural networks efficiently, enabling fast training of AI models.
- While AI models can take weeks to be trained with the help of GPUs, the same process can be executed within hours using TPUs.
Source : Indian Express
Category: GEOGRAPHY
Context: Recent findings reveal that the Indian Plate is splitting into two, a phenomenon that could reshape the region’s geological landscape.
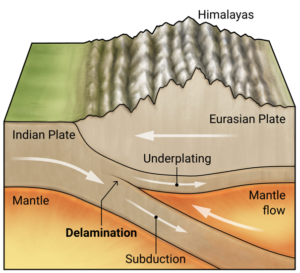
Decoding the context: Published in the American Geophysical Union, this groundbreaking discovery points to delamination, where the plate is peeling apart and sinking into the Earth’s mantle.
Learning Corner:
- The Indian Plate is a tectonic plate encompassing the Indian subcontinent, parts of the Indian Ocean, and regions of South China and western Indonesia, extending up to but excluding Ladakh, Kohistan, and Balochistan.
- Originally part of the supercontinent Gondwana, it broke away approximately 100 million years ago and began its northward journey, shaping the geological features of South Asia.
- Boundaries:
- North: Convergent boundary with the Eurasian Plate, forming the Himalayas.
- West: Transform boundary with the Arabian Plate (Owen Fracture Zone).
- Southwest: Divergent boundary with the African Plate (Central Indian Ridge).
- Southeast: Formerly fused with the Australian Plate as the Indo-Australian Plate, but recent studies suggest separation for at least 3 million years due to differing drift velocities.
- Movement: Currently moves northeast at 5 cm/year, while the Eurasian Plate moves north at 2 cm/year, causing compression at 4 mm/year and deformation of the Eurasian Plate.
- Thickness: Estimated at 100 km, half the thickness of other Gondwana-derived plates, possibly due to mantle plume activity that melted its lower part, enabling faster movement.
Historical Evolution
- Gondwana Breakup (140–100 Mya): The Indian Plate was part of Gondwana, alongside modern Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and Madagascar. Around 100 million years ago, it split from Madagascar, forming Insular India, an island continent.
- Northward Journey: Moving at up to 20 cm/year, one of the fastest plate movements recorded, it collided with the Eurasian Plate between 55–35 million years ago during the Eocene epoch, forming the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau.
- Deccan Traps: As it passed over the Reunion hotspot ~65 million years ago, massive volcanic activity formed the Deccan Traps, potentially contributing to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.
- Recent studies, reveal that the Indian Plate is undergoing delamination, a process where its dense lower layer (mantle rock) peels away from the buoyant upper layer (continental crust) and sinks into the Earth’s mantle. This phenomenon, observed beneath the Tibetan Plateau, is reshaping geological understanding.
Source : Science
Category: SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: China has reportedly suspended exports of vital minerals and magnets, triggering concerns of widespread disruptions for global industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to semiconductors and defense.
Decoding the context: The move is seen as retaliation for escalating US tariffs.
Learning Corner:
- Rare Earth Magnets are permanent magnets that generate a magnetic field without external power, using alloys of REEs like neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium, and samarium, combined with metals like iron, cobalt, or boron.
- They are the strongest permanent magnets available, with high magnetic strength, durability, and resistance to demagnetization.
- Types:
- Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) Magnets:
- Composition: Neodymium, iron, boron.
- Features: Highest magnetic strength, used in electric vehicles (EVs), wind turbines, hard disk drives, and drones.
- Limitations: Susceptible to corrosion, lower temperature resistance (up to 230°C).
- Samarium-Cobalt (SmCo) Magnets:
- Composition: Samarium, cobalt.
- Features: High-temperature stability, corrosion resistance, used in aerospace, military, and medical equipment.
- Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) Magnets:
- Key REEs Used:
- Neodymium (Nd): Most critical for NdFeB magnets, used in EVs and wind turbines.
- Praseodymium (Pr): Enhances magnet performance, often used with neodymium.
- Dysprosium (Dy): Improves high-temperature performance, critical for heavy REE applications.
- Samarium (Sm): Key for SmCo magnets, vital for defense systems.
Applications:
- Defense: Permanent magnets in missile guidance systems, radar, sonar, and underwater mine detection.
- Renewable Energy: NdFeB magnets in wind turbine rotors and EV motors.
- Consumer Electronics: Used in smartphones, hard disk drives, digital cameras, and audio equipment.
- Medical: SmCo magnets in MRI machines and surgical lasers.
- Strategic: Critical for space shuttle components, jet engines, and robotics.
Source : Times of India
Category: SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: In a major step to upgrade Mumbai’s suburban train travel, Union Minister for Railways Ashwini Vaishnaw announced that Kavach 5.0, the latest in the series of Automatic Train Protection (ATP) systems, will be implemented to increase the number of trains by 30 percent.
Decoding the context: Currently, Kavach 4.0 version is under implementation in the different parts of Indian Railways.
Learning Corner:
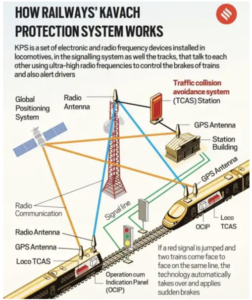
- Kavach is India’s very own advanced Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system developed by the Research Design and Standards Organisation in collaboration with the Indian industry to prevent train collisions by automatically activating the braking system of the train.
Key Features of Kavach:
- Collision Prevention: Automatically applies brakes if a train passes a red signal (Signal Passed at Danger, SPAD) or approaches another train on the same track, preventing head-on or rear-end collisions.
- Speed Regulation: Enforces speed restrictions by reducing train speed if the loco pilot fails to comply, e.g., slowing from 130 km/h to 30 km/h in restricted zones.
- On-Board Display of Signal Aspect (OBDSA): Provides real-time signal information in the loco pilot’s cab, reducing reliance on visual signals, especially in low-visibility conditions like fog.
- Emergency Response: Relays SoS messages during emergencies for swift coordination.
- Centralized Monitoring: Enables live tracking of train movements via the Network Monitor System for better operational oversight.
Source : Indian Express
Category: NATIONAL
Context: The government-backed Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) has announced that its MD and CEO, T Koshy, has stepped down following the completion of his three-year tenure at the company.
Decoding the context: ONDC offers small retailers an opportunity to provide their services and goods to buyers across the country through an e-commerce system, where buyers are able to purchase products that are sold on any platform. It is not an application, platform, intermediary or software but a set of specifications designed to foster open, unbundled, and interoperable open networks.
Learning Corner:
- The Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC) is an innovative, government-backed initiative launched by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce, to democratize e-commerce in India.
- Incorporated on December 31, 2021, as a Section 8 non-profit company, ONDC aims to shift e-commerce from a platform-centric model to an open-network model.
Key Features:
- Open-Source Protocols: Uses open specifications and network protocols, independent of specific platforms, similar to HTTP (web), SMTP (email), or UPI (payments).
- Interoperability: Allows a buyer on one platform (e.g., Amazon) to purchase from a seller on another (e.g., Flipkart) without needing to register on both.
- Network-Centric Model: Unlike platform-centric models, ONDC connects Buyer Applications, Seller Applications, and Gateways for seamless transactions.
- Standardized Operations: Protocols for cataloguing, inventory management, order fulfillment, and vendor discovery ensure uniformity.
- Inclusivity: Empowers small businesses by providing access to digital commerce without high platform commissions.
Objectives
- Democratize E-Commerce: Reduce dominance of large platforms (e.g., Amazon, Flipkart) and curb digital monopolies.
- Promote Inclusivity: Enable MSMEs, small retailers, and local businesses to compete in the digital marketplace.
- Enhance Consumer Choice: Allow buyers to access a wider range of sellers, products, and services across platforms.
- Cost Efficiency: Lower transaction costs by reducing platform fees (e.g., ONDC’s food delivery fees are ~20% of those charged by Swiggy/Zomato).
- Drive Innovation: Foster a competitive ecosystem through open-source collaboration.
Source : Business Standard
Practice MCQs
Q1. With reference to Rare Earth Magnets (REMs), consider the following statements:
- Neodymium-Iron-Boron (NdFeB) magnets are the strongest permanent magnets but have low resistance to corrosion.
- Samarium-Cobalt (SmCo) magnets work well even at very high temperatures and are used in defense and space technologies.
- Rare Earth Magnets are essential for making motors used in electric vehicles and wind turbines.
- India has large reserves of REEs but lacks advanced processing capabilities.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
A. 1, 2 and 4 only
B. 2, 3 and 4 only
C. 1, 2 and 3 only
D. 1, 2, 3 and 4
Q2.With reference to Kavach, India’s Automatic Train Protection (ATP) system, consider the following statements:
- Kavach can automatically apply brakes if a train passes a red signal or is on a collision course.
- It relies on RFID tags placed along railway tracks to determine the train’s location and direction.
- The system is imported from Japan and adapted to Indian Railways’ specifications.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 and 2 only
B) 2 and 3 only
C) 1 and 3 only
D) 1, 2 and 3
Q3.
Consider the following statements regarding the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC):
- ONDC aims to create an open and interoperable network for digital commerce similar to UPI in the payments sector.
- It is implemented by the Quality Council of India under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- ONDC functions as a profit-making public sector undertaking to promote e-commerce platforms in rural India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A. 1 and 2 only
B. 2 and 3 only
C. 1 only
D. 1, 2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 15th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – a
Q.2) – a
Q.3) – a
