Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus:
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: In a historic move to showcase India’s military heritage, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh unveiled the Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan on January 15, 2025, during the 77th Army Day celebrations in Pune.
Background: –
- This initiative is a joint effort between the Ministry of Defence and the Ministry of Tourism to highlight India’s rich military heritage and honor the sacrifices made by the armed forces
Key Aspects of Bharat Ranbhoomi Darshan:
- Historical Battlefield Sites: The initiative includes iconic war zones like Siachen (the world’s highest battlefield), Galwan (site of the 2020 India-China clash), and Longewala (highlighted in the 1971 India-Pakistan war), Kibithoo and Bum La Pass (locations in Arunachal Pradesh from the 1962 war with China) among others.
- Digital Tools: A dedicated app and website provide detailed insights into the historical significance of these sites, including virtual tours, historical narratives, and multimedia content. For those planning visits, the platform offers comprehensive travel information.
- Economic and Educational Benefits: By opening these regions to tourism, the initiative aims to boost local economies, provide educational opportunities, and inspire patriotism among visitors. The program aligns with the broader “Incredible India” campaign, merging tourism with educational experiences.
Additional Information
- Most of these sites fall along India’s borders with China (Line of Actual Control) and Pakistan (Line of Control) that have had a history of wars after independence and other clashes in recent times.
- What is the Line of Actual Control?
- The LAC is the demarcation that separates Indian-controlled territory from Chinese-controlled territory. India considers the LAC to be 3,488 km long, while the Chinese consider it to be only around 2,000 km. It is divided into three sectors: the eastern sector which spans Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim, the middle sector in Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh, and the western sector in Ladakh.
- How is the LAC different from the Line of Control with Pakistan?
- The LoC emerged from the 1948 ceasefire line negotiated by the UN after the Kashmir War. It was designated as the LoC in 1972, following the Shimla Agreement between the two countries. It is delineated on a map signed by DGMOs of both armies and has the international sanctity of a legal agreement. The LAC, in contrast, is only a concept – it is not agreed upon by the two countries, neither delineated on a map or demarcated on the ground.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Mains – GS 3
Context: As one of the oldest agrarian societies in the world, India’s farming practices have evolved over the years. However, agriculture today stands at a crossroads, with farmers grappling with challenges like climate change, shrinking arable land, depleting freshwater reserves, and rising input costs.
Background: –
- While there has been a major shift in agriculture’s contribution to the Gross Value Added in the economy from 61.7% in 1950 to 16.3% in 2020, the proportion of the workforce engaged in agriculture remains high at 46.5% as of 2020 compared to 69.2% in 1950-51.
From subsistence farming to market-oriented practices
- In subsistence farming, farmers usually raise crops or livestock to fulfil the needs of their families.
- Subsistence agriculture can be broadly classified into two types – Primitive subsistence agriculture and Intensive subsistence agriculture.
- Primitive subsistence agriculture or shifting cultivation involves clearing vegetation by fire and cultivating the land for 4-5 years before abandoning it. This practice is common in the northeastern states, where it is known as Jhuming, and Odisha and Telangana, where it is called Podu.
- Intensive subsistence agriculture is prevalent in densely populated regions with monsoon climates.
- Subsistence farming is labour-intensive as it lacks mechanization due to the small size of holdings. Organic manure is commonly used and fertilizers and pesticides are rare, resulting in low productivity. In addition, there is a high dependence on the monsoon.
Predominance of small and marginal land holdings and monsoon dependence
- According to the Agricultural Census 2015-16, small( 1-2 hectares) and marginal (<1 hectare) land holdings make up over 86% of the total agricultural land holdings in India. The average land holding size is just 0.38 hectares for marginal farmers and 1.4 hectares for small farmers.
- As per NITI Aayog, 55% of the net cropped area in India is under irrigation, while the rest is dependent on the monsoon for irrigation.
- There are various issues associated with the dependence on the monsoon. These include insufficient rainfall in the events of El Nino, excess rainfall (La Nina) causing destruction of crops and flooding, untimely rainfall, and dry spells during the monsoon season.
Shift to profit-driven agricultural practices
- Over time, there has been a gradual shift towards market-oriented agricultural practices, including diversification and the cultivation of high-value crops.
- Farmers are increasingly moving away from traditional food crops to non-food crops that offer higher returns, such as horticulture, floriculture, sericulture, viniculture, and apiculture. This shift reflects a structural change in the demand for high-value agricultural products like fruits, vegetables, and meat.
- Commercial farming in India is characterised by capital-intensive practices, the use of inorganic and modern inputs, advanced irrigation techniques, and larger landholdings. These trends indicate a move towards more specialised, profit-driven agricultural practices.
Challenges and the way forward
- The evolving nature of Indian Agriculture presents it with various challenges, such as the need for modern techniques, greater awareness, and better access to extension services.
- Overuse of fertilisers and inadequate soil conservation has resulted in soil degradation, underlining the potential and need for organic farming. Furthermore, the lack of adequate infrastructure, including storage facilities, cold chains, and poor road networks, causes substantial post-harvest losses.
- Another pressing issue is the lack of credit to small and marginal farmers, which limits their ability to invest.
- The government has introduced various measures to improve agriculture.
- Some of the initiatives are PM-KISAN, Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana, the formation and promotion of 10,000 FPOs scheme, the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund, the Soil Health Card scheme, the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana, Market Intervention Scheme, Micro Irrigation Fund, and Namo Drone Didi.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: During the inaugural event to celebrate 150 years of the India Meteorological Department (IMD), P M Modi launched ‘Mission Mausam’.
Background:
- Established in 1875, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) completed 150 years of service on January 15.
About Mission Mausam
- The mission aims to upgrade the capabilities of India’s weather department in forecasting, modelling, and dissemination.
- The primary objectives of Mission Mausam are:
- To enhance India’s capability in weather forecasting across various scales—short-term, medium-term, extended-range, and seasonal.
- To develop high-resolution models for improved accuracy in predicting monsoon behaviour.
- To strengthen observational networks with advanced radars, satellites, and automated weather stations.
- To provide actionable advisories for agriculture, water resources, energy, health, and disaster management sectors.
- To build capacity through research collaborations with national and international institutions.
- Mission Mausam will have a budget of Rs 2,000 crore for the first two years of its implementation.
- Mission Mausam adopts a multi-pronged approach to achieve its objectives:
- Infrastructure Development: Installation of Doppler Weather Radars (DWRs), Automatic Weather Stations (AWS), and rain gauges across the country.
- Supercomputing Power: Leveraging high-performance computing systems like Pratyush and Mihir for advanced climate modelling.
- Collaborative Research: Partnerships with global organizations like the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) to enhance forecasting techniques.
- Public Outreach: Dissemination of user-friendly advisories through mobile apps (e.g., Mausam app), SMS services, and media channels.
- The mission will also ‘manage’ certain weather events, and on-demand, enhance or suppress rainfall, hail, fog and, later, lightning strikes.
- For effective weather modification, one of the most important areas is cloud physics. Towards this end, India is establishing a first-of-its-kind cloud chamber at the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Pune.
- A cloud chamber resembles a closed cylindrical or tubular drum, inside which water vapour, aerosols, etc. are injected. Under the desired humidity and temperature inside this chamber, a cloud can develop.
- With Mission Mausam, India will build a cloud chamber with convection properties, as required to study Indian monsoon clouds.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus:
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Even as Tamil Nadu’s coastal communities continue to face challenges due to the regular arrests of fishermen by the Sri Lankan Navy, another group of ten fishermen from Thothoor village in the state has been allegedly arrested by the British Navy near Diego Garcia Island.
Background: –
- The fishermen were reportedly arrested for allegedly crossing the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL).
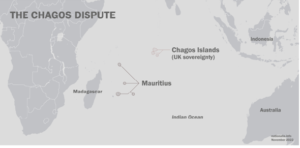
Key takeaways
- Diego Garcia is a coral atoll located in the central Indian Ocean, forming the largest and southernmost part of the Chagos Archipelago. It is part of the British Indian Ocean Territory (BIOT) and serves as a strategic military base jointly operated by the United Kingdom and the United States.
- Location: Approximately 3,535 km east of Tanzania, 2,984 km east-southeast of Somalia, and 726 km south of the Maldives
- Diego Garcia’s location along major international trade routes between Asia and Africa enhances its strategic importance. The joint UK-US military base supports various operations and serves as a logistical hub for forces operating in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The sovereignty of Diego Garcia has been a subject of international dispute. Mauritius claims the Chagos Archipelago, including Diego Garcia, as its territory.
- In October 2024, the UK announced plans to transfer sovereignty of the Chagos Islands to Mauritius, while retaining a long-term lease for the military base on Diego Garcia.
Source: NDTV
Syllabus:
- Prelims & Mains – GEOGRAPHY
Context: The wildfires that have devastated large parts of the Los Angeles city and surrounding areas in the United States since January 7 occurred due to rare meteorological conditions enhanced by global warming and consequent climate change, mainly due to a ‘hydroclimate whiplash’.
Background: –
- The blazes have already killed 24 people and burnt 12,000 structures to the ground over an area of 155 square kilometres as of January 13 and may intensify further due to fierce winds in the coming days.
Key takeaways
- Hydroclimate whiplash refers to rapid and extreme transitions between very wet and very dry conditions in a region. This phenomenon is becoming more frequent and severe due to climate change, leading to significant environmental and societal impacts.
Causes of Hydroclimate Whiplash:
- A primary driver is the increasing capacity of a warmer atmosphere to hold moisture. For every degree Celsius of warming, the atmosphere can hold about 7% more water vapor. This “expanding atmospheric sponge” effect results in:
- Intensified Precipitation: When the saturated atmosphere releases moisture, it leads to heavier and more intense rainfall events.
- Enhanced Evaporation: A warmer atmosphere also increases evaporative demand, drawing more moisture from soils and vegetation, which exacerbates drought conditions during dry periods.
- These dynamics contribute to more pronounced swings between wet and dry periods, characteristic of hydroclimate whiplash.
Impacts of Hydroclimate Whiplash:
- Wildfires: Periods of heavy rainfall promote vegetation growth, which, during subsequent droughts, becomes dry fuel, increasing wildfire risk. This sequence has been observed in regions like California, where wet winters followed by dry summers have led to severe wildfires.
- Flooding and Landslides: Intense rainfall can lead to flash floods and landslides, especially when occurring after prolonged dry spells that compromise soil stability.
- Agricultural Disruption: Crops may suffer from alternating flooding and drought conditions, affecting food production and security.
- Water Resource Management Challenges: The unpredictability of water availability complicates the management of reservoirs and water supplies, impacting both human consumption and ecological needs.
Source: Down To Earth
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to Diego Garcia, consider the following statements:
- Diego Garcia is a coral atoll located in the Atlantic Ocean.
- It serves as a strategic military base jointly operated by the United Kingdom and the United States.
- The sovereignty of Diego Garcia has been a subject of international dispute involving Mauritius.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q2.) Hydroclimate whiplash is characterized by which of the following?
- Rapid transitions between very wet and very dry conditions.
- Stable level of atmospheric pressure.
- Enhanced stability in water resource management.
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Q3.) Which of the following is/are objectives of Mission Mausam?
- Strengthening India’s capability in weather forecasting.
- Developing high-resolution models for improved accuracy in monsoon predictions.
- Enhancing collaborative research with World Health Organization (WHO).
Select the correct answer using the codes below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ Today’s – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 15th January – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – d
