Archives
(PRELIMS Focus)
Category: SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: CERN Collider Reveals Clue to Universe’s Bias Against Antimatter.
Key Finding:
For the first time, scientists have observed that the laws of physics differ between matter and antimatter in baryons (particles like protons and neutrons). This may help explain why the universe is dominated by matter despite both matter and antimatter being created in equal amounts during the Big Bang.
What Was Discovered?
- CP (Charge-Parity) violation observed in a particle called the Λb0 baryon (Lambda b zero).
- CP violation breaks the symmetry between particles and antiparticles, making them behave differently.
- This violation has been seen in mesons before, but never in baryons until now.
Experiment Details:
- Conducted by the LHCb collaboration at CERN using the Large Hadron Collider.
- Compared the decay rates of Λb0 baryons and their antimatter counterparts.
- Found a decay asymmetry of about 2.45%, with a statistical significance of 5.2 sigma (strong evidence).
Why Is This Important?
- It adds a missing piece to the puzzle of why there’s more matter than antimatter.
- Supports the idea that CP violation in baryons could have helped the universe evolve with more matter.
- Could lead to “new physics” beyond the Standard Model of particle physics.
Future Direction:
- More accurate measurement of the complex phase in baryon decays is needed.
- Researchers must determine whether the observed CP violation matches predictions or hints at unknown forces.
Historical Context:
- 1967: Physicists Sakharov, Andrei, and others proposed three conditions for matter to dominate antimatter, one of which was CP violation.
- Until now, CP violation was seen only in mesons, not in baryons.
Learning Corner:
CERN
CERN (Conseil Européen pour la Recherche Nucléaire), or the European Organization for Nuclear Research, is one of the world’s largest and most respected centres for scientific research in the field of particle physics.
Key Highlights:
- Established: 1954
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Members: 23 member states (India is an associate member since 2016)
Major Functions:
- Fundamental Physics Research: CERN studies the basic constituents of matter by colliding particles at high energy.
- Large Hadron Collider (LHC): World’s most powerful particle accelerator, used to discover the Higgs boson in 2012.
- Technological Innovation: Develops advanced detectors, computing infrastructure (e.g. GRID), cryogenics, and medical applications like cancer therapy.
India and CERN:
- India collaborates through institutions like TIFR, BARC, and IISc.
- Indian scientists contribute to detector development, grid computing, and engineering solutions.
- Indian companies have supplied cryogenics, precision mechanics, and electronics to CERN.
Source: THE HINDU
Category: Environment
Context: Climate Change is Fuelling Devastating Wildfires in Europe
Wildfire Situation in 2025:
- 227,000 hectares of land have burned in Europe so far this year — more than double the 20-year average.
- Not the worst year on record (2003 & 2017 saw over 1.1 million hectares burned annually).
- 1,118 fires reported till July 8, compared to 716 during the same period last year.
Role of Climate Change:
- Climate change is creating hotter and drier conditions, making wildfires more frequent and intense.
- Greenhouse gas emissions have warmed the Earth by 1.3°C since pre-industrial times.
- Europe is warming at twice the global average (WMO data).
Where are Fires Happening?
- Severe fires in Catalonia (Spain), Marseille (France), Greece (Evia and Crete), and Syria.
- Greek island fires have forced thousands to evacuate.
- Mediterranean fires have been the worst but relatively isolated.
Scientific Observations:
- Wildfires are worsened by early heatwaves and persistent dry spells.
- Once ignited, fires spread rapidly due to dry vegetation and wind.
- Climate change has caused earlier fire seasons and intensified fire behavior.
Learning Corner:
Wildfires
What Are Wildfires?
Wildfires are uncontrolled fires that rapidly spread across forests, grasslands, or other flammable vegetation.
Causes of Wildfires
- Natural Causes:
- Lightning strikes (major cause in remote forests)
- High temperatures and dry conditions
- Anthropogenic Causes:
- Campfires, discarded cigarettes
- Agricultural burning
- Power lines, sparks from machinery
Favourable Conditions (Fire Triangle)
- Fuel – Dry vegetation, trees, shrubs
- Heat – High temperatures, drought
- Oxygen – Abundant in the atmosphere
Effects of Wildfires
- Loss of biodiversity and wildlife habitats
- Increased carbon emissions
- Degradation of air quality (PM2.5, CO, NOx)
- Soil erosion and desertification
- Threat to human lives and infrastructure
- Disruption of ecosystem services
Global Hotspots
- USA – California, Oregon
- Australia – Bushfires (e.g., Black Summer 2019–20)
- Amazon Rainforest
- Siberia
- Mediterranean regions – Greece, Spain
- Canada – Record-breaking wildfires in 2023
Wildfires and Climate Change
- Rising temperatures and frequent droughts are increasing wildfire frequency and intensity.
- Wildfires contribute to climate change feedback loops by releasing stored carbon.
- Melting permafrost and peat fires are becoming more common in high-latitude regions.
India and Wildfires
- States with frequent forest fires: Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand
- Western Ghats and North-Eastern states are also vulnerable
- Major cause: man-made fires for shifting cultivation and poaching
Important Reports/Initiatives
- Forest Survey of India (FSI): Releases forest fire reports
- MODIS & VIIRS Satellites: Used for real-time fire detection
- National Action Plan on Forest Fires (2018) by MoEFCC
- Fire Alert System (FAS) by FSI and ISRO
- Global Forest Watch Fires: Tracks global forest fires
- RED-Alert System: Pre-wildfire alerts for vulnerable forest areas
Source: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
Category: Polity & Governance
Context : The Indian government has launched the PM-DDKY, an ambitious umbrella scheme that merges 36 existing agricultural schemes to revitalize farming in 100 low-performing districts across India.
Key Features:
- Integration of 36 Schemes across 11 departments with involvement from states and private partners.
- Focus Areas include:
- Increasing crop productivity through sustainable practices.
- Promoting crop diversification toward climate-resilient and high-value crops.
- Expanding irrigation and water-use efficiency.
- Boosting rural credit and strengthening storage at panchayat/block levels.
Implementation Details:
- Target Districts: 100 districts selected based on low crop productivity, cropping intensity, and weak credit flow. Each state/UT has at least one district.
- District Committees: Local “Dhan-Dhaanya Samitis” will design and monitor farm-level plans with support from progressive farmers.
- Monitoring: A digital dashboard will track progress across 117 indicators, guided by NITI Aayog and central nodal officers.
Scheme Highlights:
| Key Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Scheme Name | PM Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana (PM-DDKY) |
| Schemes Merged | 36 |
| Duration | 6 years (starting FY26) |
| Annual Budget | ₹24,000 crore |
| Target Coverage | 100 districts, 1.7 crore farmers |
| Key Goals | Productivity, sustainability, credit, storage |
| Monitoring Framework | 117 indicators, digital dashboard |
Objectives:
- Enhance agricultural productivity and farmer incomes
- Promote natural and organic farming
- Strengthen water and soil conservation
- Develop district-level agricultural resilience
Learning Corner:
Major Agricultural Schemes in India
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)
- Launched: 2019
- Objective: Provides ₹6,000 per year in three installments to all landholding farmer families for income support.
- Implementing Ministry: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare
Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY)
- Launched: 2016
- Objective: Crop insurance scheme that provides financial support in case of crop failure due to natural calamities, pests, or diseases.
- Premium: Farmers pay 2% for Kharif, 1.5% for Rabi, and 5% for commercial/horticulture crops.
- Implementing Agency: Ministry of Agriculture & State Governments
Soil Health Card Scheme
- Launched: 2015
- Objective: Provides soil health reports to farmers with recommendations on nutrient management for better crop yield and soil sustainability.
Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)
- Launched: 2015
- Objective: Promotes organic farming through the adoption of traditional practices and cluster-based certification.
- Support: Up to ₹50,000 per hectare for 3 years, including inputs and certification.
National Mission on Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Under: National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Objective: Promotes climate-resilient farming, soil and water conservation, and efficient resource use.
Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY-RAFTAAR)
- Launched: 2007 (revised in 2017 as RAFTAAR)
- Objective: Assists states in boosting agriculture development, marketing infrastructure, and value chains.
- Flexible funding model for innovation and entrepreneurship.
E-NAM (National Agriculture Market)
- Launched: 2016
- Objective: Digital platform to create a unified national market for agricultural commodities.
- Integrates mandis (APMCs) across India to enable transparent price discovery.
PM-Kisan Maandhan Yojana
- Launched: 2019
- Objective: Voluntary pension scheme for small and marginal farmers (age 18–40).
- Benefit: Monthly pension of ₹3,000 after the age of 60.
Agri-Infra Fund (AIF)
- Launched: 2020
- Corpus: ₹1 lakh crore
- Objective: Provides medium-long term debt financing for post-harvest infrastructure like cold storage, warehouses, etc.
- Interest subsidy: Up to 3% per annum
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY)
- Launched: 2015
- Objective: “Har Khet Ko Pani” – expands irrigation coverage and improves water use efficiency.
- Components: Accelerated Irrigation Benefits Programme, Watershed Development, and Per Drop More Crop.
Source : THE HINDU
Category: ECONOMICS
Context: India’s actions on dumping and import surges (2025)
Anti-Dumping Measures
- Duties Imposed: India imposed or extended anti-dumping duties on goods like:
- Plastic injection moulding machines (27–63% for 5 years)
- Chemicals such as PEDA, Acetonitrile, Vitamin A Palmitate, Insoluble Sulphur
- Aluminium foil and selected agricultural chemicals
- Focus Areas:
Over 60% of actions target Chinese imports, protecting sectors like chemicals, plastics, and industrial goods. - Criteria:
Duties are imposed based on proof of dumping, injury to domestic producers, and causation, with adjustments to protect downstream users when necessary.
Monitoring Import Surges
- Real-time Surveillance:
The Commerce Ministry and DGFT monitor unusual spikes in imports and alert concerned ministries. - World Trade Watch:
Monthly reports track country-wise and product-wise surges, helping formulate trade responses and export strategies. - Notable Trends:
Imports rose by 4.4% (April–June 2025). Major spikes were seen in electronics, machinery, and coal, while gold and petroleum imports stagnated or declined. - Specific Action – Liquid Gold:
Curbs were imposed on colloidal precious metals to prevent misuse and smuggling.
Institutional Mechanisms
- Import Monitoring Group:
A new inter-ministerial group tracks diverted imports—especially from China and Vietnam—to prevent India from becoming a dumping ground for globally rerouted goods. - Trade Remedies:
The DGTR (Directorate General of Trade Remedies) continues active investigations and recommendations, with an increased acceptance rate of its findings.
Learning Corner:
Duties on Foreign Trade
Foreign trade duties are taxes imposed on imports and exports to regulate international trade, protect domestic industries, and generate revenue.
Customs Duty
- Definition: General term for duties levied on goods when they are transported across international borders.
- Includes: Basic Customs Duty, Countervailing Duty, Safeguard Duty, etc.
Basic Customs Duty (BCD)
- Imposed on: All imported goods.
- Purpose: To protect domestic industries and generate revenue.
- Rates: Vary depending on product category and trade agreements.
Countervailing Duty (CVD)
- Imposed when: A foreign country subsidizes its exports, making them cheaper.
- Objective: Neutralize the unfair advantage and protect domestic producers.
- Legal Basis: WTO Agreement on Subsidies and Countervailing Measures.
Anti-Dumping Duty
- Imposed when: Foreign goods are sold in India at a price lower than their domestic price (dumping).
- Purpose: Protect Indian industry from predatory pricing.
- Authority: Directorate General of Trade Remedies (DGTR).
Safeguard Duty
- Imposed when: Sudden surge in imports threatens domestic industries.
- Temporary measure to allow the local industry to adjust to competition.
- WTO-compatible measure.
Protective Duty
- Recommended by: Tariff Commission.
- Purpose: To protect specific domestic industries against imports.
- Nature: Temporary and selective.
Social Welfare Surcharge (SWS)
- Rate: Usually 10% on the aggregate customs duties (excluding IGST).
- Objective: To finance education, health, and social welfare schemes.
Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST) on Imports
- Imposed under: GST Act.
- Applied on: Imports to bring them at par with domestic goods.
- Collected by: Central Government.
Source: THE HINDU
Category: POLITY
Context: Launched on 15 July 2025 by the Union Minister for Power, the ADEETIE (Assistance in Deploying Energy Efficient Technologies in Industries & Establishments) scheme aims to accelerate energy-efficient technology adoption in MSMEs across India. It is implemented by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
Key Objectives
- Reduce MSME energy consumption by 30–50%
- Promote green technologies and improve energy productivity
- Contribute to India’s climate goals: 45% emission intensity reduction by 2030, Net Zero by 2070
Scheme Details
- Total Outlay: ₹1,000 crore
- Duration: FY 2025–26 to 2027–28
- Interest Subvention: 5% for Micro/Small, 3% for Medium Enterprises
- Financial Allocation:
- ₹875 crore – interest subvention
- ₹50 crore – energy audits
- ₹75 crore – technical support & monitoring
- Investment Mobilization: Expected ₹9,000 crore, including ₹6,750 crore in MSME loans
Coverage & Support
- Targets 14 energy-intensive sectors (e.g. steel, textiles, food processing)
- Covers 60 industrial clusters initially, followed by 100 more
- Offers: interest subsidies, energy audits, DPR preparation, tech identification, and implementation support
- Dedicated portal launched: adeetie.beeindia.gov.in
Learning Corner:
Energy Efficiency Schemes in India
India has launched several initiatives to improve energy efficiency across industries, buildings, and appliances. These schemes are primarily implemented by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) under the Ministry of Power.
PAT Scheme (Perform, Achieve, and Trade)
- Objective: Improve energy efficiency in large energy-intensive industries.
- Mechanism: Provides energy saving targets to industries. Units exceeding targets can trade Energy Saving Certificates (ESCerts).
- Sectors Covered: Power, iron & steel, cement, aluminium, textile, pulp & paper, etc.
UJALA (Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All)
- Launch: 2015
- Implemented by: EESL (Energy Efficiency Services Limited)
- Objective: Promote widespread use of LED bulbs, tube lights, and energy-efficient fans.
- Impact: Over 36 crore LED bulbs distributed, saving energy and reducing carbon emissions.
Standards & Labeling Programme
- Started by: BEE
- Objective: Encourage energy-efficient appliances through star rating labels (1 to 5 stars).
- Appliances Covered: ACs, refrigerators, geysers, motors, fans, etc.
Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC)
- Target: New commercial buildings.
- Objective: Ensure design and construction of energy-efficient buildings.
- Versions: ECBC (Commercial), Eco-Niwas Samhita (Residential).
Street Lighting National Programme (SLNP)
- Implementing Agency: EESL
- Objective: Replace conventional street lights with energy-efficient LED lights.
- Impact: Significant energy savings and lower maintenance cost for urban local bodies.
DEEP Portal (Discovery of Efficient Electricity Price)
- Purpose: Facilitate transparent e-bidding for power procurement by DISCOMs.
- Promotes: Cost-effective electricity for end-users.
National Mission on Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE)
- Part of: National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC)
- Components:
- PAT (Perform, Achieve, and Trade)
- MTEE (Market Transformation for Energy Efficiency)
- EEFP (Energy Efficiency Financing Platform)
- FEEED (Framework for Energy Efficient Economic Development)
Source: PIB
(MAINS Focus)
Introduction (Context)
The recent earthquakes in Myanmar, Thailand, Tibet followed by recent in Delhi, exposing the nations vulnerability to it. With earthquake activity intensifying regionally and globally, the Government of India must lead a national dialogue to enforce seismic codes rigorously.
What is Earthquake?
- Earthquake is the sudden shaking of the ground caused by the passage of seismic waves through Earth’s rocks.
- Earth’s major earthquakes occur mainly in belts coinciding with the margins of tectonic plates.
Position of India
- India’s seismic risk arises from the northward drift of the Indian Plate, colliding with the Eurasian Plate at 4–5 cm per year
- This collision forms the Himalayas, a region overdue for a “Great Himalayan Earthquake” (magnitude 8 or higher).
- Examples:
-
- Bhuj earthquake (2001): Magnitude 7.7, over 20,000 deaths.
- Nepal earthquake (2015): Magnitude 7.8, widespread devastation.
India’s seismic zones
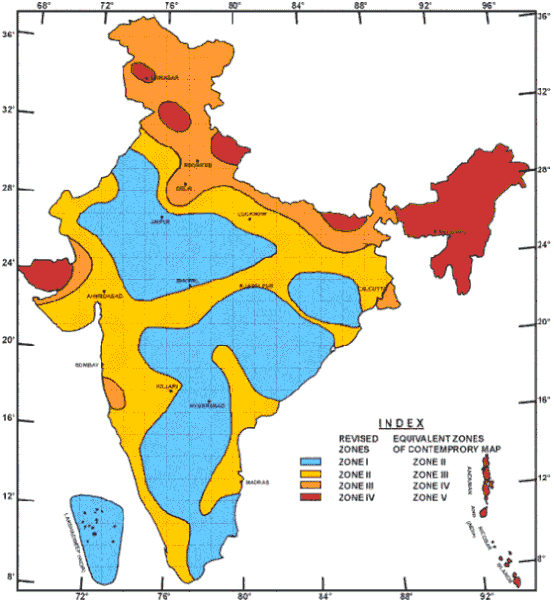
According to the seismic zoning map of the country, India is divided into four seismic zones.
Zone II – Low Risk
- Characterised by low seismic activity, with earthquakes rarely exceeding magnitude 4.9.
- Covers much of southern India, including Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and parts of central India such as Madhya Pradesh.
- This zone faces minimal earthquake hazards compared to other regions.
Zone III – Moderate Risk
- Experiences moderate seismic activity, with earthquakes typically between magnitude 5.0 and 6.0.
- Includes regions such as:
- Western and central India, including Mumbai, Pune, and nearby areas.
- Coastal states like Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
- Parts of the Indo-Gangetic plains, including Delhi and Bihar.
Zone IV – High Risk
- Marked by frequent and strong seismic events, generally ranging from magnitude 6.0 to 6.9.
- Major areas include:
- The Himalayan belt, covering Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- Delhi, highlighting its significant seismic vulnerability.
- Regions in Kashmir, Punjab, and western Uttar Pradesh.
Zone V – Very High Risk
- Identified as the most seismically active zone in India, where earthquakes often reach magnitude 7.0 or above.
- Comprises:
-
- The entire northeastern states, including Assam, Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram, and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Northern Jammu and Kashmir.
- The Kutch region in Gujarat, known for the devastating 2001 earthquake.
- Parts of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, which are also prone to tsunamis due to tectonic subduction activity.
Issues in Preparedness
- Rapid urbanisation exacerbates the risk.
- Construction of buildings in liquefaction-prone soils, and poorly designed high-rises without structural retrofitting.
- Lack of public awareness
- Poor enforcement of seismic codes. For example in the recent earthquake in Myanmar, enforced codes were not implemented which have worsened the quake toll in 2025.
Steps needed
- Rigorous enforcement of seismic codes for all new and existing structures.
- Retrofitting older buildings using steel jacketing, base isolation, and pile foundations. (Bangkok Uses high-strength concrete (30–40 MPa) and ductile detailing for earthquake resistance)
- Avoid construction on floodplains and liquefaction-prone zones. (example in Brahmaputra floodplain)
- Expand early warning systems to rural Zone V areas for timely evacuation.
- Public education campaigns on earthquake safety, kits, and drills.
- National dialogue involving urban planners, structural engineers, and local governments to mainstream seismic resilience in urban policy.
- Solutions must be tailored to regional conditions, e.g. Soft soil challenges in northeast and Sandy basin vulnerabilities in Kutch regions.
- Citizens should educate themselves about the need for emergency kits, safe building practices, and evacuation plans. The Bhuj disaster, where unpreparedness amplified casualties, remains a haunting lesson.
Conclusion
Earthquakes are inevitable natural events, but their devastation can be minimised through proactive governance, strict code enforcement, and public preparedness.
Mains Practice Question
Earthquakes are inevitable natural phenomena, but their impact on society is largely determined by human preparedness and policy measures. Discuss with reference to India’s seismic vulnerability and disaster management strategies. (250 words, 15 marks)
Introduction (Context)
Recently, the US Senate has passed the GENIUS Act, a landmark legislation that gives American banks and even large companies like Amazon and Walmart the legal green light to issue digital dollars known as stablecoins on public blockchains.
What are stablecoins?
- Stablecoins are digital tokens issued on blockchain platforms whose value is pegged to a stable reserve asset, such as a fiat currency or government bonds.
- The primary goal of stablecoins is to provide an alternative to the high volatility of popular cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC), which can make these digital assets less suitable for common transactions.
About USA Stablecoin
- In the US model, stablecoins are backed 1:1 by US Treasury Bills, ensuring price stability while leveraging the speed and transparency of blockchain technology.
- This means a bank in the US would be able to issue a digital version of the dollar, backed by government bonds, and it can be used for payments across the world.
Hence it is a combination of government securities and the speed and transparency of blockchain technology.
How do stablecoins work?
- Stablecoins are stored and exchanged on decentralized networks (known as blockchains) that serve as ledgers of all transactions.
- No single intermediary is required for two parties to transact in crypto assets.
- Instead, participants in a network receive small transaction fees for the computation expended to verify the validity of transactions
Usage
- Stablecoins are primarily used for trading crypto assets, transacting in goods and services, insulating against local currency instability, and sending payments across borders. Stripe allows stablecoin payments to US merchants with lower fees than cards.
- Used for hedging Currency Risks particularly popular in countries with volatile fiat currencies (Argentina, Nigeria, Turkey) to save in USD. According to 2024 Visa survey: 47% of users in Brazil, Turkey, Nigeria, India, and Indonesia use stablecoins for saving in dollars.
- Also used for Cross-Border Payments & Remittances.
India’s Position
In India, RBI has raised concerns about unregulated cryptocurrencies, particularly from a monetary policy and consumer protection standpoint. Hence it is using conventional tools like rate cuts.
However, stablecoins are different, as they are regulated, backed by government securities, and integrate blockchain with sovereign guarantees.
Where India lags?
- In India, there is no regulatory mechanism due to which legitimate fintech innovation remains stuck.
- Issues in digitising currency:
-
- Lack of regulatory clarity pushes Indian blockchain developers and fintech startups to relocate abroad.
- Risks of unregulated crypto turning into a “refined form of hawala”, demanding urgent regulation.
- Most Indian household savings remain in fixed deposits or gold, limiting formal financial market depth.
Steps needed
- Craft a balanced policy allowing stablecoins under RBI oversight, ensuring consumer protection, monetary stability, and legal clarity.
- Integrate blockchain-based products into the formal economy, supporting startups to build from India rather than relocating to Singapore or Dubai.
- Promote awareness on safe, regulated digital assets to deepen financial inclusion.
Conclusion
The stablecoin ecosystem isn’t just about finance — it’s about the future of fintech. It touches payments, digital wallets, eKYC, blockchain infrastructure, cybersecurity, tax compliance, and new forms of savings and investing. Hence, India should craft a framework that reflects Indian values — trust, transparency, and stability — while embracing the potential of fintech to create jobs, strengthen the rupee, and modernise our economy.
Mains Practice Question
“Stablecoins represent both an opportunity and a regulatory challenge for India’s fintech ecosystem.” Elaborate (250 words, 15 marks)
