Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Polity and Governance
Context: Recently, the Bar Council of India (BCI) has allowed foreign lawyers and law firms to practise law in India on a reciprocity basis.
About the Bar Council of India (BCI):-
- It is a statutory body established by Parliament under the Advocates Act, of 1961.
- It performs the regulatory function by prescribing standards of professional conduct and etiquette and by exercising disciplinary jurisdiction over the bar.
- It also sets standards for legal education and grants recognition to Universities whose degrees in law will serve as qualifications for enrolment as an advocate.
Historical Background:-
- In March 1953, the All India Bar Committee, headed by S. R. Das, submitted a report which proposed the creation of a bar council for each state and an all India bar council as an apex body.
- It was suggested that the all-India bar council would regulate the legal profession and set the standard of legal education.
- The Law Commission of India was assigned the job of assembling a report on judicial administration reforms.
- In 1961, the Advocates Act was introduced to implement the recommendations made by the ‘All India Bar Committee’ and ‘Law Commission’.
- The Bar Council was initially against allowing foreign lawyers and firms from practicing in India.
- However, based on the recommendations put forth in the Joint Consultative Conferences between BCI, State Bar Councils across the country and other stakeholders, the rules were changed.
New Rules:-
- The Bar Council of India has released new rules and regulations for the registration of foreign lawyers and international law firms in India.
- Through the Bar Council of India Rules for Registration and Regulation of Foreign Lawyers and Foreign Law Firms in India, 2022 these lawyers would be able to practice in non-litigious matters.
- The three major focus areas for these lawyers would be foreign law, international legal issues and arbitration matters.
Areas where foreign lawyers and firms can practice:-
- Transactional work, corporate work such as joint ventures, mergers and acquisitions, intellectual property manners, drafting of contacts
- Provide legal advice and appear as a lawyer for a person, company, firm, corporation, trust, etc. which has its address in a foreign country.
- Provide legal advice and appear as a lawyer at bodies other than courts, tribunals, and boards, who are not legally entitled to take evidence on oath.
- Provide legal advice concerning the laws of the country of primary qualification and diverse legal issues.
- Registered lawyers and firms can open offices in India
- Form a partnership with one or more registered foreign lawyers and firms
- Foreign lawyers and foreign firms would not be allowed to practice in India without registering with the council first.
- Exception: However, this rule can be relaxed for the foreign lawyer or foreign law firm who are coming to India on a “fly in and fly out basis” for the purpose of giving legal advice to a client on foreign law or international legal issues.
- These lawyers or firms cannot have an office in India and practice law for more than 60 days in any period of 12 months.
- The registration fee for a foreign lawyer is $25,000 (approximately Rs 20.64 lakhs) and for foreign firms, the registration fee stands at $50,000 (approximately Rs. 41.28 lakhs).
Significance:-
- This change in stance is expected to have significant implications for the Indian legal landscape.
- Foreign lawyers and law firms will now have the opportunity to offer their services in India.
- It will create competition and expose Indian law firms to global best practices.
MUST READ: Digitisation of Court Records
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Government law officers and legal firms are recognized as advocates, but corporate lawyers and patent attorneys are excluded from recognition as advocates.
- Bar Councils have the power to lay down the rules relating to legal education and recognition of law colleges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q.2) With reference to Indian Judiciary, consider the following statements. (2021)
- Any retired judge of the Supreme Court of India can be called back to sit by the Chief Justice of India with the prior permission of the President of India.
- A High court in India has the power to review its own judgement as the Supreme Court does.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity and International Relations
Context: Recently, a bipartisan resolution has been introduced in the upper chamber of the US Congress reiterating that the US recognises the McMahon Line as the international boundary between China and India in Arunachal Pradesh.
About McMahon Line:-
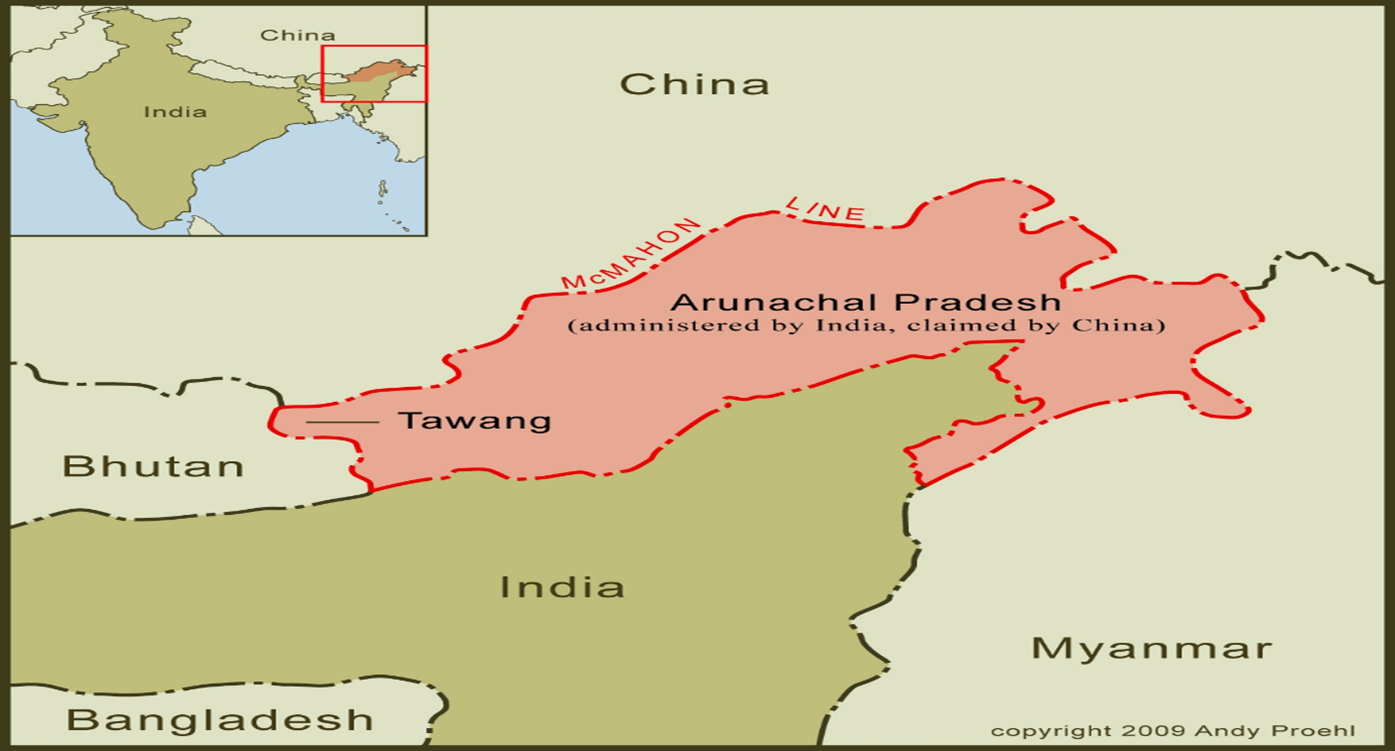
IMAGE SOURCE: http://chinamatters.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-myth-of-mcmahon-line.html
- The McMahon Line serves as the de facto boundary between China and India in the Eastern Sector.
- It specifically represents the boundary between Arunachal Pradesh and Tibet, from Bhutan in the west to Myanmar in the east.
- China has historically disputed the boundary and claims the state of Arunachal Pradesh as part of the Tibetan Autonomous Region (TAR)
Historical Background:-
- The McMahon Line was drawn during the Shimla Convention of 1914, officially described as the Convention Between Great Britain, China, and Tibet.
- The McMahon Line delimited the respective spheres of influence of Tibet and British India in the eastern Himalayan region in what is today India’s Northeast and northern Myanmar.
- The border in this region was undefined prior to the signing of the convention.
The Shimla Treaty:-
- According to the Shimla Treaty, the McMahon Line is the clear boundary line between India and China.
- On behalf of India, the British rulers considered the Tawang of Arunachal Pradesh and the southern part of Tibet as part of India and which was also agreed by the Tibetans.
- Due to this, the Tawang region of Arunachal Pradesh became part of India.
China’s stand on McMahon Line:-
- According to China, Tibet has always been a part of its territory, so the representatives of Tibet are not authorised to accept any agreement without Chinese consent.
- In 1950, China fully occupied Tibet.
- China neither approved nor accepted the McMahon Line.
- China argues that China was not involved in the Shimla Agreement, therefore the Shimla Agreement is not binding on it.
India’s stand on McMahon Line:-
- India believes that when the McMahon Line was established in 1914, Tibet was an independent country, so it has every right to negotiate a border agreement with any country.
- When the McMahon Line was drawn, Tibet was not ruled by China.
- Therefore, the McMahon Line is the clear and legal boundary line between India and China.
- Even after the Chinese occupation of Tibet in 1950, the Tawang region remained an integral part of India.
Current status of the McMahon Line:-
- India recognizes the McMahon Line and considers it to be the ‘Actual Line of Control (LAC)’ between India and China.
- China does not recognize the McMahon Line.
- This land dispute between India and China is in Tawang (Arunachal Pradesh), which China considers as the Southern part of Tibet.
- According to the Shimla Agreement, it is a part of the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh.
MUST READ: India-China Tawang clash and India-China relations, a year after Galwan
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement/ set-up Subject
- Alma-Ata Declaration – Healthcare of the people
- Hague Convention – Biological and Chemical Weapons
- Talanoa Dialogue – Global Climate Change
- Under2 Coalition – Child Rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
- 1 and 2 only
- 4 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 2,3 and 4 only
Q.2) Consider the following statements (2020)
- The value of Indo-Sri Lanka Trade has consistently increased in the last decade.
- “Textile and textile articles constitute an important item of trade between India and Bangladesh
- In the last five years, Nepal has been the largest trading partner of India in South Asia
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- 1,2, and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Environment and Ecology
Context: According to a recent report by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII), the Gujarat government has planned to translocate 40 adult and sub-adult lions to the Barda Wildlife Sanctuary.
About Barda Wildlife Sanctuary:
- Barda Wildlife Sanctuary area is located in the state of Gujarat.
- It falls into two districts Porbandar and Jamnagar.
- This area was declared a sanctuary in 1979.
- It is characteristically abundant in floral diversity, which consists of a good number of medicinal plants.
- A very high percentage of rare and endangered plants occurring in the area is an important component of the sanctuary.
- The area falls into two erstwhile princely states of history i.e. Rana Barda, where Ranas of Porbandar ruled once upon a time and Jam Barda, where the rule of Jamsaheb of Jamnagar prevailed.
- Ethnic races such as Maldharis, Bharvads, Rabaris and Gadhvis live in this region of Saurashtra.
- Flora: Gorad, Babul, Dhav, Rayan, Ber, Jamun, Amli, Dhudhlo, Bamboo etc.
- Fauna: Sambar, chital and chinkara were present in the Sanctuary in the recent past and therefore they can be re-introduced.
- This would create a good prey base for a big carnivore like a leopard.
MUST READ: Kambalakonda Wildlife Sanctuary
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements (2022)
- Wild animals are the sole property of the government.
- When a wild animal is declared protected, such animal is entitled to equal protection whether it is found in protected areas or outside.
- Apprehension of a protected wild animal becoming a danger to human life is sufficient ground for its capture or killing.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 and 2
- 2 only
- 1 and 3
- 3 only
Q.2) Which of the following Protected Areas are located in the Cauvery basin? (2020)
- Nagarhole National Park
- Papikonda National Park
- Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve
- Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Syllabus
- Prelims –Science and Technology
Context: Recently, Hyderabad-based Svaya Robotics has developed India’s first indigenous quadruped (four-legged) robot and exoskeleton for the defence sector.
About India’s first indigenous quadruped robot and exoskeleton:-
- It is part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
- It has been developed by the Hyderabad-based Svaya Robotics .
- It is India’s first indigenous quadruped (four-legged) robot and exoskeleton for the defence sector.
- India currently imports these robots from the US and Switzerland.
- The indigenous robots and wearable exoskeletons were developed in collaboration with the DRDO Labs, Research and Development Establishment (R&DE), Pune, and the Defence Bioengineering and Electromedical Laboratory (DEBEL), Bengaluru.
- Both are dual-use robots and have multiple use cases in industry and healthcare as well.
Quadruped robots:
- These are four-legged robots .
- They can walk or run on uneven and rough terrains.
- They can carry 25 kg in payload and walk along with the soldier.
Uses:-
- It is made for navigating in unstructured terrains to provide remote reconnaissance and inspection.
- Where soldiers have to navigate through unfavourable conditions, these robots can be used instead
Exoskeleton:
- It is developed to suit Indian soldiers’ anthropometry and augment soldier strength for walking long distances.
- These active exoskeletons, when worn by soldiers, can carry heavy loads without expending much effort.
MUST READ: Responsible Artificial Intelligence
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-speech conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
- 1, 3, and 4 only
- 2, 4, and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) In the context of wearable technology, which of the following tasks is/are accomplished by wearable devices? (2019)
- Location identification of a person
- Sleep monitoring of a person
- Assisting the hearing impaired person
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims – Environment and Ecology
Context: Recent findings state that the first photographic records of the semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal indicate that some stretches of the Neeru stream, a tributary of the Chenab river, are still unpolluted.
About Eurasian otter:-

- It is a semi-aquatic carnivorous mammal.
- Scientific Name — Lutra lutra
Distribution:-
- It’s range covers parts of three continents: Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Habitat: –
- It lives in a wide variety of aquatic habitats, including highland and lowland lakes, rivers, streams, marshes, swamp forests, and coastal areas.
- In the Indian sub-continent, Eurasian otters occur in cold hill and mountain streams.
- Smooth-coated are found all over India
- Asian small-clawed: found only in the Himalayan foothills, parts of the Eastern and southern Western Ghats
- Eurasian: Western Ghats and Himalayas.
Conservation Status:-
- IUCN: Near threatened
- Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule II
- CITES Appendix I
MUST READ: Conservation of species
SOURCE: THE HINDU
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) With reference to India’s biodiversity, Ceylon Frogmouth, Coppersmith Barbet, Gray Chinned Minivet and White-throated Redstart are (2020)
- Birds
- Primates
- Reptiles
- Amphibians
Q.2) Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Asiatic lion is naturally found in India only
- Double-humped camel is naturally found in India only
- One-horned rhinoceros is naturally found in India only
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Polity
Context: Recently, under the Smart Cities Mission, cities across the country were asked to submit proposals for projects to improve municipal services and to make their jurisdictions more liveable.
About The Smart Cities Mission:-
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme launched in 2015.
- It is under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- It covered 100 cities for the duration of five yearsstarting from the financial year (FY) 2015-16 to 2019-20.
- It aims to drive economic growth and improve the quality of life of peopleby enabling local development and harnessing technology as a means to create smart outcomes for citizens.
Objective: To promote cities that provide core infrastructure and give a decent quality of life to its citizens, a clean and sustainable environment and application of Smart Solutions.
Four pillars:-
- Social Infrastructure, Physical Infrastructure, Institutional Infrastructure, and Economic Infrastructure.
Significance:-
- India is the world’s second-most populous nation.
- Urban areas are anticipated to house 40% of India’s people and contribute around 75% of India’s GDP by the year 2030.
Status of the projects:-
- As of March 2023, the 100 cities have issued work orders for 7,799 projects worth Rs 1.80 lakh crore.
- Out of these, 5,399 projects worth Rs.1.02 lakh crore have been completed, and the rest are ongoing.
- Only around 20 cities are likely to meet the June deadline; the rest will need more time.
- Cities selected in January and June 2018 have achieved 44% of their targets.
- Cities selected in 2016 in the second round are not much farther ahead with 46% completion.
- Shillong has completed just one of its 18 proposed projects.
MUST READ: Smart cities and Academia Towards Action & Research (SAAR)
SOURCE: THE INDIAN EXPRESS
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
- Department of Science and Technology
- (b)Ministry of Labour and Employment
- (c)NITI Aayog
- (d)Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Q.2) Which of the following is/are the aim/aims of the “Digital India” Plan of the Government of India ? (2018)
- Formation of India’s own Internet companies like China did.
- Establish a policy framework to encourage overseas multinational corporations that collect Big Data to build their large data centres within our national geographical boundaries.
- Connect many of our villages to the Internet and bring Wi-Fi to many of our schools, public places and major tourist centres.
Select the correct answer using the code given below :
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Prelims –Art and Culture
Context: Recently, Bumchu Buddhist Festival was held in Sikkim.
About Bumchu Buddhist Festival:-
- Bumchu, the Tashiding holy water vase ritual, is a unique and important occasion that draws travellers from all over the world. Annual performances of this ancient ceremony are held at the Tashiding Monastery.
- The Bumchu festival commemorates a supernatural occurrence that took place in the 18th century under Chogyal Chakdor Namgyal.
- It is a time of intense delight and celebration in Sikkim.
- At the event, pilgrims travel to Tashiding from all around India as well as from close by nations like Bhutan, Nepal, and Sri Lanka.
About Tashiding Monastery:-
- The Tashiding Monastery is one of the most sacred Buddhist pilgrimage sites.
- It is located in the western part of Sikkim.
- It is located on a hilltop overlooking the Rangeet River in Sikkim.
- It is one of the most sacred Buddhist pilgrimage sites.
- Guru Padmasambhava, better known as Guru Rinpoche, the great Buddhist guru who brought Buddhism to Tibet, blessed the location of the monastery.
MUST READ: The Buddhist Circuit
SOURCE: THE PRINT
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) The Prime Minister recently inaugurated the new Circuit House near Somnath Temple Veraval. Which of the following statements are correct regarding Somnath Temple? (2022)
- Somnath Temple is one of the Jyotirlinga shrines.
- A description of the Somnath Temple was given by Al-Biruni.
- Pran Pratishtha of Somnath Temple (installation of the present-day temple) was done by President S. Radhakrishnan.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q.2) With reference to India, the terms ‘Halbi, Ho and Kui’ pertain to (2021)
- dance forms of Northwest India
- musical instruments
- pre-historic cave paintings
- tribal languages
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Recent studies show that Africa’s splitting plates could give birth to a new ocean, but with consequences.
About Tectonic Plates:
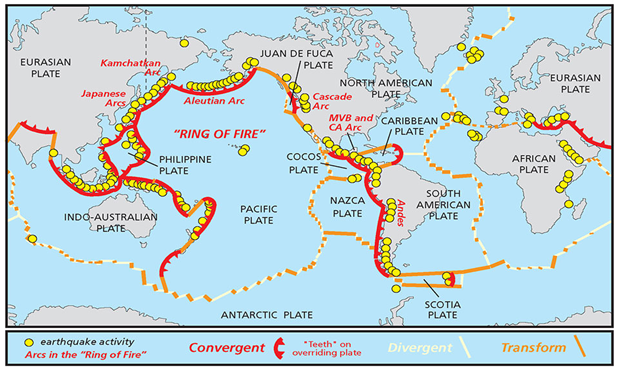
IMAGE SOURCE: https://oceanservice.noaa.gov/facts/tectonics.html
Plate tectonics was a theory developed in the 1960s.
- It explains how major landforms on earth were created as a result of Earth’s subterranean movement.
- A tectonic plate or a lithospheric plate is a massive, irregularly shaped slab of solid rock, generally composed of both continental and oceanic lithosphere.
- Tectonic plates are sometimes subdivided into three categories: major (or primary) plates, minor (or secondary) plates, and microplates (or tertiary plates).
Major plates of Earth:-
- African Plate
- Antarctic Plate
- Eurasian Plate
- Indo-Australian plate
- North American Plate
- Pacific Plate
- South American Plate
Minor Plates of the Earth:-
- Cocos plate: Between Central America and the Pacific plate
- Nazca plate: Between South America and the Pacific plate
- Arabian plate: Mostly the Saudi Arabian landmass
- Philippine plate: Between the Asiatic and Pacific plate
- Caroline plate: Between the Philippine and Indian plates (North of New Guinea)
- Fuji plate: North-east of Australia
- Juan De Fuca’s plate
About Rifting:-
- Major geomorphological features such as fold and block mountains, mid-oceanic ridges, trenches, volcanism, earthquakes etc. are a direct consequence of the interaction between various Tectonic Plates (lithospheric plates).
- There are three ways in which the plates interact with each other.
Divergence:
- In this kind of interaction, the plates diverge (move away from each other).
- Mid-ocean ridges (e.g. the Mid-Atlantic Ridge) are formed due to this kind of interaction.
- Here, the basaltic magma erupts and moves apart (seafloor spreading).
- Example: On continents, East African Rift Valley is the most important geomorphological feature formed due to the divergence of African and Somali plates.
Convergence:
- In this kind of interaction, two lithospheric plates collide with each other.
- The zone of collision may undergo crumpling and folding, and folded mountains may emerge (orogenic collision).
- Himalayan Boundary Fault is one such example.
- When one of the plates is an oceanic plate, it gets embedded in the softer asthenosphere of the continental plate, and as a result, trenches are formed at the zone of subduction.
Transcurrent Edge:-
- In this kind of interaction, two plates slide past each other.
- There is no creation or destruction of the landform but only the deformation of the existing landform.
- In oceans, transform faults are the planes of separation generally perpendicular to the mid-oceanic ridges.
- Example: San Andreas Fault (Silicon Valley lies dangerously close to the faultline) along the western coast of the USA
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH
PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
Q.1) Consider the following pairs: (2019)
Sea Bordering country
- Adriatic Sea Albania
- Black Sea Croatia
- Caspian Se Kazakhstan
- Mediterranean Sea Morocco
- Red Sea Syria
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
- 1, 2 and 4 only
- 1, 3 and 4 only
- 2 and 5 only
- 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Q.2) The Earth’s magnetic field has reversed every few hundred thousand years. (2018)
- When the Earth was created more than 4000 million years ago, there was 54% oxygen and no carbon dioxide.
- When living organisms originated, they modified the early atmosphere of the Earth.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 (International Relations) and GS 3 (Economy)
Context: Recently Reserve Bank India Deputy Governor emphasizes the need for better rupee volatility management to deal with risks of internationalization.
About Internationalisation of Indian Rupee:
- Currency internationalization is the widespread use of a currency outside the borders of its original country of issue.
- It refers to the process of making the Indian rupee a globally accepted currency, similar to other major currencies like the US dollar, Euro, and Japanese yen etc.,
- This process aims to promote India’s economic growth and development by increasing the use of the rupee in cross-border transactions, foreign investment, and global trade.
- It requires the liberalization of India’s capital account, which means allowing free flow of capital in and out of the country without any restrictions.
Present Status of Indian Rupee
- Currently, Indian rupee totals over 80 against USD.
- The first country to open a special Rupee Vostro account is Russia followed by Sri Lanka and Mauritius which are expected to use the Indian rupee trade settlement mechanism.
- A further assessment says that by 2040, the Rupee will challenge China’s Renminbi as the strongest global currency.
Advantages of Internationalization of rupee
- Currency risk is reduced for Indian businesses when using the Rupee in international transactions.
- Protection from currency volatility improves business growth and lowers operating costs, increasing the likelihood that Indian companies will expand internationally.
- The requirement for maintaining foreign exchange reserves decreases.
- Reserves have an impact on the economy even though they help control exchange rate volatility and project external stability.
- India becomes less susceptible to outside shocks by reducing its reliance on foreign currency.
- For instance, excessive foreign currency liabilities of domestic businesses result in a de facto domestic tightening during phases of monetary tightening in the US and a strengthening dollar.
- The discomfort of reversing capital flows would be significantly lessened by reduced exposure to currency risk.
- The bargaining power of Indian business would increase as the rupee’s use increased, adding weight to the Indian economy and raising India’s stature and respect internationally.
Challenges of Internationalisation of rupee:
- It requires integration with global financial markets, which can pose challenges in terms of regulatory compliance, market infrastructure, and investor protection.
- It is the primary challenge of internationalising the rupee as it can create risks for businesses and investors that operate in multiple currencies, leading to uncertainty and higher transaction costs.
- India’s financial markets are still relatively underdeveloped compared to other major economies, which can limit the range of products and services available to international investors.
- The rupee is not yet a widely traded currency, which means there is limited liquidity in global markets making it difficult for investors to buy and sell rupee-denominated assets, which can limit the attractiveness of the currency.
- It requires a supportive regulatory environment that balances the need for openness with the need for financial stability and regulatory oversight which is challenging to achieve, especially given the complexities of global financial markets.
Steps taken for the Internationalisation of the Rupee
- Recently the RBI has introduced a mechanism to facilitate international trade in rupees.
- Enabling external commercial borrowings in Rupees (especially Masala Bonds).
- The Asian Clearing Union is also exploring a scheme of using domestic currencies for settlement.
- An arrangement, bilateral or among trading blocs, which offers importers of each country the choice to pay in domestic currency is likely to be favoured by all countries, and therefore, is worth exploring.
- Promotion of offshore rupee markets: The RBI has allowed Indian banks to participate in the offshore non-deliverable market for rupee derivatives, which has facilitated the development of offshore rupee markets.
- Currency swap agreements: The RBI has signed currency swap agreements with several countries, which allow for the exchange of rupee and foreign currency between the central banks of the two countries.
- Bilateral trade agreements: The government has signed several bilateral trade agreements with other countries, which has facilitated greater cross-border trade and investment and increased the use of the rupee in international transactions.
Way Forward:
Therefore, Any possibility of conversation on rupee internationalization must be backed by a sustained and stable position of the Indian Rupee. Scale, stability and liquidity can be achieved through strong economic fundamentals and a process-driven regulatory environment. Overall, increase in the international use of the Indian rupee will go a long way in positioning India as a more attractive destination for foreign investment and trade.
Source: The Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3 (Environment)
Context: The Kochi landfill site around Brahmapuram that caught fire earlier this month was a stark reminder that Indian cities need to be prepared for more such incidents as summer approaches.
About Landfill:

- A landfill site, also known as rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. It is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal.
- US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established specific guidelines regarding creation and management of the Landfills.
- But in India, landfills are managed under the new Solid Waste Management Rules (SWM), 2016. However, many of the guidelines are not adhered to rules.
Landfill fires: Surface and Underground fires
- Surface fires: It involves recently buried or uncompacted refuse, situated on or close to the landfill surface in the aerobic decomposition layer.
- Surface fires generally burn at relatively low temperatures and are characterized by the emission of dense white smoke and the products of incomplete combustion.
- Underground fires: Underground fires in landfills occur deep below the landfill surface and involve materials that are months or years old.
- The most common cause of underground landfill fires is an increase in the oxygen content of the landfill, which increases bacterial activity and raises temperatures (aerobic decomposition).
- These so-called “hot spots” can come into contact with pockets of methane gas and result in a fire.
Reasons Landfills fire:
- India’s municipalities have been collecting more than 95% of the waste generated in cities but the efficiency of waste-processing is 30-40% at best.
- Indian municipal solid waste consists of about 60% biodegradable material, 25% on-biodegradable material and 15% inert materials, like silt and stone.
- The openly disposed waste includes flammable material like low-quality plastics, which have a relatively higher calorific value.
- In summer, the biodegradable fraction composts much faster, increasing the temperature of the heap to beyond 70-80° C.
- Higher temperature + flammable material = a chance for the landfill to catch fire.
Impact of Landfill Fires:
- Air Pollution: When a landfill fire burns, it releases harmful gases and particles into the air, including carbon monoxide, Sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- These pollutants can cause respiratory problems, exacerbate asthma and other lung conditions, and contribute to smog and acid rain.
- Health impact: It causes health ailments in residents living nearby the landfill like sore throat, itchy eyes and breathing problems.
- Groundwater Contamination: Landfill fires can release toxic chemicals and heavy metals into the groundwater, which can contaminate nearby water sources and potentially harm aquatic ecosystems.
- Soil Contamination: Landfill fires can also release harmful chemicals and heavy metals into the soil, which can harm plant growth and contaminate crops.
- Economic Impact: Landfill fires can result in significant clean-up costs for local governments, as well as economic losses for nearby businesses and property owners.
Landfill fire prevention
- Fire prevention can reduce property damage, injury, health, and environmental hazards of landfill fires.
- The cost of prevention is usually much less expensive than the cost of fighting and cleaning up a fire.
- Effective landfill management: Management measures include prohibiting all forms of deliberate burning, thoroughly inspecting and controlling incoming refuse, compacting refuse buried to prevent hot spots from forming, prohibiting smoking onsite, and maintaining good site security.
- Monitoring the emission of methane: If methane levels in or around the landfill become explosive, the landfill operator must take immediate steps to mitigate the danger.
- Converting Landfill Gas to Energy: The conversion of landfill gas to energy turns this landfill by-product into a marketable resource. The converted gas can be used to generate electricity, heat, or steam.
Govt Initiatives to prevent Landfill fires
- Swachha Bharat Mission – Urban (SBM-U).
- Swaccha Survekshan: An annual survey of cleanliness, hygiene and sanitation in cities and towns across India is undertaken. It has been launched as a part of the SBM-U under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- Swachhata Hi Sewa Campaign: It has been launched for ensuring cleanliness through the various stakeholders’ engagement in the ‘Jan Andolan’.
- Compost Banao, Compost Apnao Campaign: It is a multi-media campaign launched by MoHUA on waste-to-compost under SBM-(U).
Way Forward:
While these measures can help reduce the fires’ damage, they’re far from ideal and not long-term solutions. The 4 R’s philosophy of Reducing, Reusing, Recycling, and Recovering Resources should be actively encouraged. The permanent and essential solution is to ensure cities have a systematic waste processing system where wet and dry waste are processed separately and their byproducts treated accordingly.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q.1) Which of the following are minor tectonic plate boundaries?
- Antarctic Plate
- Eurasian Plate
- Arabian plate
- Cocos plate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 and 4 only
- 1 and 4 only
Q.2) Barda Wildlife Sanctuary is often mentioned in the news is in
- Rajasthan
- Assam
- Punjab
- Gujrat
Q.3) With reference to the Bar Council of India (BCI), consider the following statements:
- It is a constitutional body established under the Advocates Act, of 1961.
- It performs the regulatory function by prescribing standards of professional conduct and etiquette and by exercising disciplinary jurisdiction over the bar.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 17th March 2023 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 16th March – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – a
