Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2
Context: PM Narendra Modi proposed a human-centric “Global Development Compact,” during the Voice of the Global South Summit.
Background:-
- Global Development Compact will be inspired by the development priorities set by the countries of the Global South.
Key takeaways
- PM Narendra Modi, in his opening remarks at the virtually held India-hosted third summit, emphasized that global governance and financial institutions established in the last century have failed to address the challenges of the current century.
Global Development Compact:
- Debt-Free Development: PM Modi stated that under this new Compact, needy countries will not be burdened with debt in the name of development finance. Instead, the Compact will draw on India’s own development journey and its experiences in development partnerships.
- Focus Areas: The Compact will prioritize trade for development, capacity building for sustainable growth, technology sharing, project-specific concessional finance, and grants. To support trade promotion activities, India will initiate a special fund of USD 2.5 million, with an additional USD 1 million allocated to this cause.
- The prime minister said the compact will help in a balanced and sustainable development of the partner countries.
Closing the Global North-South Gap:
- Call for Unity: PM Modi urged the Global South to unite, speak with one voice, and strengthen one another by learning from each other’s experiences. He suggested that the upcoming Summit of the Future at the UN next month could be a significant milestone in this effort.
Understanding Global North and Global South:
- Global South: Refers to the countries of Asia, Africa, Latin America, and Oceania, where 88% of the world’s population lives. These countries often have a history of colonialism and have historically lagged in industrialization and development.
- Global North: Comprises the developed countries of North America and Europe, which have historically pursued imperial policies and are characterized by higher levels of development.
- Distinctions: The Global South typically exhibits lower development levels, higher income inequality, rapid population growth, agrarian economies, lower quality of life, shorter life expectancy, and significant external dependence. However, the term is more about political, geopolitical, and economic similarities than strict geographical location. For example, despite being in Asia, countries like Israel, South Korea, and Japan are considered part of the Global North due to their higher levels of development.
- In the last few years, India has been positioning itself as a leading voice, flagging concerns, challenges and aspirations of the Global South
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2
Context: The Union Service Public Commission recently sought applications for lateral entry for 45 posts of Joint Secretary, Director and Deputy Secretary across 24 Central ministries.
Background:
- Appointment to the posts will be on a contract basis for a period of three years, extendable to five years depending upon performance, and central government employees are not eligible for the posts as per advertisement.
Key takeaways
- Lateral entry into bureaucracy is a practice that involves recruiting individuals from outside the traditional government service cadres to fill mid and senior-level positions.
- Lateral entry into bureaucracy was formally introduced during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s tenure, with the first set of vacancies announced in 2018.
- The aim is to address complex governance and policy implementation challenges by tapping into external expertise.
- The concept of lateral entry has historical precedence. It was initially recommended by the Second Administrative Reforms Commission (ARC) established in 2005 during the United Progressive Alliance (UPA) government.
- The ARC, chaired by Veerappa Moily, advocated for lateral entry to fill roles requiring specialised knowledge unavailable within traditional civil services. These recommendations emphasised recruiting professionals from the private sector, academia and PSUs to improve policy implementation and governance.
Criticism
- Lack of Reservation: One of the primary criticisms is the absence of reservation for Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST), and Other Backward Classes (OBC) in these positions.
- Ambiguity in Recruitment Process: There are concerns about the transparency and clarity of the recruitment process. Critics point out that there is no clear policy on determining vacancies, shortlisting candidates, and evaluating their suitability.
- Political Allegations: Critics have accused the government of using lateral entry to appoint individuals loyal to specific political ideologies, thereby undermining the neutrality of the civil service.
- Impact on Career Civil Servants: Large-scale lateral induction may demotivate existing civil servants who have progressed through the traditional career path. It could potentially discourage talented officers from continuing in the service.
- Potential for Bias: There are fears that the selection process might be biased towards candidates from certain backgrounds or sectors, which could affect the diversity and inclusiveness of the bureaucracy
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT

Context: In July, the IMD’s forecasts for Mumbai were off nearly by 42 per cent. Also on at least four days in July, the IMD had changed its forecast and warnings twice within a 24-hour window.
Background:
- The IMD issues its daily forecast at 1 pm, for a 24-hour period starting 8.30 am that day to 8.30 am the following day. There are five-, two- and three-day advance forecasts as well, but the 24-hour forecasts are considered the most accurate.
Key takeaways
- On July 8, Mumbai woke up to severe flooding after 200 mm of rain overnight, far exceeding the India Meteorological Department’s (IMD) prediction. The IMD had issued a yellow alert, forecasting up to 115 mm of rain in 24 hours, but the city received 267 mm instead.
- Mumbai’s advanced Weather Radar Systems:
- Mumbai houses two sophisticated Doppler weather radars: an S-band radar at IMD’s Colaba observatory and a C-band radar in Veravali.
- Apart from tracking cyclones, radars are also useful for tracking other weather developments like thunderstorm activities. For thunderstorms, the radars undertake scanning every 10 minutes. Through the regular scans, the radars help in providing localised forecasts depending on the cloud developments and other factors.
- The metropolitan region also benefits from over 140 automatic weather stations operated by the BMC, in addition to IMD’s observatories at Santacruz and Colaba.
- Despite these resources, the IMD’s forecasts, especially city-specific ones, often lack accuracy and timeliness. The IMD acknowledges imperfections in its forecasts but notes that accuracy has improved by 40-50% in the last decade.
- The IMD’s observational network has expanded significantly, now operating over 400 weather stations, 1,000 automatic weather stations, and 1,300 automatic rain gauges.
- However, the unpredictability of weather systems, particularly in extreme weather events, exposes the limitations of current forecasting models.
- IMD models often fail to capture extremely localised weather systems which bring extremely heavy rain within a short span of time, making them difficult to forecast.
- Mumbai’s proximity to the sea and ghats adds complexity, making forecasting even more challenging due to dynamic weather changes.
- Factors like ocean and land temperatures, urban areas, and activities like irrigation can amplify convection, leading to unpredictable heavy rainfall.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – CURRENT EVENT
Context: OpenAI recently said that it has banned ChatGPT accounts linked to an Iranian influence operation that used the chatbot to generate content to influence the U.S. presidential election.
Background:
- OpenAI downplayed the impact of operation, noting that the content did not engage much with audiences and was not widely shared.
About Storm-2035 :
- Storm-2035 is a covert Iranian influence operation identified by OpenAI, involving four websites posing as news organizations to target U.S. voters.
- The websites exploited issues like LGBTQ rights and Israel-Hamas conflict and also used AI tools to plagiarise stories and capture web traffic
- Operatives used ChatGPT to generate long-form articles and social media comments, which were then posted on various X and Instagram accounts.
- AI chatbots such as ChatGPT can potentially assist foreign operatives fool internet users by mimicking American users’ language patterns, rehashing already existing comments or propaganda, and cutting down the time it takes to create and circulate plagiarised content meant to sway voters.
- Apart from the upcoming U.S. presidential election, the operation covered global issues like Venezuelan politics, Latin rights in the U.S., the situation in Palestine, Scottish independence, and Israel’s participation in the Olympic Games. It also exploited popular topics such as fashion and beauty.
Impact of Storm-2035:
- As per Brookings’ BreakoutScale, which measures the impact of covert operations on a scale from 1 (lowest) to 6 (highest), this operation was at the low end of Category 2, meaning it was posted on multiple platforms, but there was no evidence that real people picked up or widely shared their content.
Previous Incidents:
- In May, OpenAI posted a report revealing it had been working to dismantle covert influence operations that used its tools for generating comments on social media, articles in multiple languages, fake names and bios for social media accounts, and translating or proofreading text.
- A Russian outfit that OpenAI called ‘Bad Grammar,’ used the Telegram to target Ukraine, Moldova, the Baltic States and the U.S.
- Separately, another Russia-based operation titled ‘Doppelganger,’ an Israeli operation that OpenAI nicknamed ‘Zeno Zeno,’ a Chinese network called ‘Spamouflage,’ and an Iranian group called ‘International Union of Virtual Media’ or IUVM, used ChatGPT to write comments on social media platforms like X and 9GAG, and to post articles and news stories.
- Besides hunting down influence networks, OpenAI also found incidents of state-backed threat actors abusing AI to attack enemies.
OpenAI’s Response:
- OpenAI has developed AI-powered security tools to detect threats more quickly and has strengthened its safeguards against malicious use of its technology.
- The company is also collaborating with U.S. federal agencies and experts, including the U.S. AI Safety Institute, to enhance the security and reliability of its AI models.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY
Context: Recently, atleast 80 people killed in strike by Sudan paramilitary forces.
Background:
- This attack occurred despite recent U.S.-sponsored talks aimed at ending the 16-month-long war.
Key takeaways
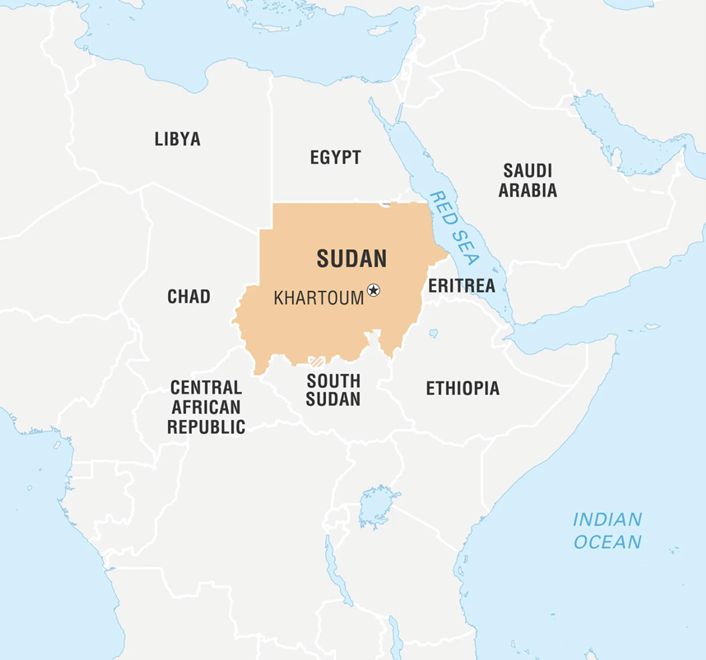
- Sudan is a country located in northeastern Africa.
- It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, and Libya to the northwest.
- Its capital is Khartoum, situated at the confluence of the Blue Nile and White Nile rivers.
- In modern times, it has experienced significant political and social upheaval, including civil wars and the secession of South Sudan in 2011.
- The country is currently under a transitional government following a military coup.
Main Causes of the Conflict in Sudan:
- Power Struggle: The primary cause is the power struggle between the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF). The leaders of these groups are vying for control of the country.
- Historical Tensions: Sudan has a history of political instability, marked by numerous coups and civil wars since its independence in 1956. The overthrow of longtime dictator Omar al-Bashir in 2019 led to a fragile transitional government, which was later disrupted by a military coup in 2021.
- Economic Factors: Sudan’s economy has been in crisis for years, exacerbated by corruption, mismanagement, and international sanctions. The competition over control of economic resources, particularly gold mines, has fuelled tensions between rival factions.
- Ethnic and Regional Divisions: Ethnic and regional divisions have also played a significant role. The RSF has its origins in the Janjaweed militia, which was involved in the Darfur conflict and accused of committing atrocities against non-Arab populations.
- External Influences: External actors and regional dynamics have further complicated the situation. Neighbouring countries and international powers have various interests in Sudan, influencing the conflict through support for different factions.
- Failed Peace Processes: Despite multiple attempts at peace talks and ceasefires, the lack of a comprehensive and inclusive peace process has hindered efforts to resolve the conflict.
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The UN General Assembly recently launched the Multidimensional Vulnerability Index (MVI).
Background:
- The MVI is a crucial tool in the global effort to address vulnerabilities and build a more resilient and sustainable future for all nations.
Key takeaways
- The Multidimensional Vulnerability Index (MVI) is a comprehensive tool developed by the United Nations to assess the vulnerability of countries, particularly small island developing states (SIDS) and other developing nations.
Purpose:
- It aims to provide a more nuanced understanding of the challenges these countries face, beyond traditional economic indicators.
- It designed to highlight the unique vulnerabilities of countries that are often overlooked by conventional metrics like GDP per capita.
- It helps in identifying the need for concessional financing and other support mechanisms.
- It helps policymakers identify areas of weakness and prioritize interventions to enhance resilience and sustainable development.
- The index can by international organizations and donors to allocate resources more effectively, ensuring that aid reaches the most vulnerable populations.
Dimensions:
- Economic Vulnerability: Includes indicators such as GDP per capita, debt levels, and trade dependency.
- Environmental Vulnerability: Factors in exposure to natural disasters, climate change impacts, and biodiversity loss.
- Social Vulnerability: Considers health care access, education levels, and income inequality.
Benefits:
- Targeted Interventions: By identifying specific vulnerabilities, the MVI enables more targeted and effective interventions, leading to better outcomes for affected communities.
- Enhanced Resilience: Countries can use the insights from the MVI to build resilience against future shocks, reducing the long-term impact of disasters and economic downturns.
- Informed Decision-Making: The index provides valuable data for decision-makers, helping them to allocate resources efficiently and implement policies that promote sustainable development.
Source: Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following countries:
- Egypt
- Chad
- Libya
- Eritrea
How many of the above-mentioned countries share border with Sudan?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Q2.) With reference to the Multidimensional Vulnerability Index (MVI), consider the following statements:
- The MVI is a comprehensive tool developed by the United Nations to assess the vulnerability of countries, particularly small island developing states (SIDS) and other developing nations.
- It aims to provide a comprehensive assessment of a country’s structural vulnerabilities, particularly focusing on factors like climate change, economic instability, and social challenges.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3.) Storm – 2035, recently seen in news is a
- Covert Iranian influence operation identified by OpenAI to target U.S. voters
- A high intensity thunderstorm which hit Caribbean islands
- An emerging form of AI technology
- None of the above
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 19th August 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 17th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – c
