Archives
(PRELIMS + MAINS FOCUS)
Sero Survey
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III- Governance
Key Findings of Fourth National Sero Survey
- Two-thirds of India's population have antibodies against the coronavirus.
- 67.6% of adults were seropositive, while more than 62% of adults were unvaccinated.
- About 400 million of India's 1.4 billion people did not have antibodies.
What is Sero Survey?
- Sero studies popularly known as sero survey examines how many people in a population have been infected with COVID-19
- Sero survey broadly indicates following things;
- The percentage of the population exposed to the virus.
- Which groups are more exposed or have had higher rates of infection
- How infection rates are progressing in a particular area.
- How far are we from herd immunity.
How is Sero Survey Done?
- The blood serum (fluid part of plasma) of a group of individuals is examined for antibodies (not the virus itself) that are developed in response to virus exposure.
- Seropositive=> Presence of antibodies => exposed to Coronavirus
- Everybody cannot be tested, only a few people chosen at random are tested. The results are an estimate of the proportion of people who have been infected in the past.
E-Aasthi
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III- E-Governance
In News: Bengaluru’s Municipal Corporation (BBMP) is set to extend the E-Aasthi project to all the wards in the three core zones – South, East and West.
Key Takeaways
- E-Aasthi Project aims to digitise property documents. Presently it is being implemented in 100 wards of BBMP Limits.
- E-Aasthi software was initially developed by the National Informatics Centre (NIC) for all urban local bodies. It was later customised by Karnataka State government.
-
- NIC, established in 1976 under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology provides network backbone and e-Governance support to Union/State/UT Governments.
- With the implementation of E-aasthi, updating different property transactions, such as sale, inheritance, partition, gift, will, land acquisition, khata amalgamation/ bifurcation can be done easily, without having to visit the BBMP offices.
- Since it is an end-to-end app, the E-Aasthi system was linked to property tax records under GIS-enabled Property Tax Information System (GEPTIS).
- Significance of E-Aasthi:
- Sanitises revenue records
- Bring in transparency and accountability in land transactions
- Stamps out illegal transactions and cutting out middlemen.
Supreme Court quashes part of Cooperative Amendment
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – II- Polity
In News: The Supreme Court on Tuesday struck down certain provisions of the Constitution (97th Amendment) Act, 2011
- Gujarat High Court in 2013 had struck down certain provisions of the 97th CAA by reasoning that Parliament cannot enact laws with regard to cooperative societies as it is a State subject. This was appealed by Centre in Supreme Court.
The Constitution (97th Amendment) Act, 2011 made following changes
- New Part IXB regarding the cooperatives working in India added
- Part IXB dictated the terms for running co-operative societies like the number of directors a society should have or their length of tenure and even the necessary expertise required to become a member of the society.
- In Art. 19(1)(c) the word “cooperatives” was added after “unions and associations”. This enables all the citizens to form cooperatives by giving it the status of fundamental right of citizens.
- A new Article 43B was added in the Directive Principles of State Policy (Part IV) regarding the “promotion of cooperative societies”
Key Takeaways of SC Judgement
- Upheld the validity of the 97th constitutional amendment
- However, dissenting judgement by Justice Nariman struck down the entire 97th CAA.
- Struck down part of Part IXB which dealt with cooperative societies confined to states. Court held that co-operative societies come under the “exclusive legislative power” of State legislatures and Centre can’t shrink State’s exclusive authority.
- However, Part IXB of the Constitution is operative only in so far as it concerns multi-State co-operative societies. This is because Multi-State Cooperatives comes under Union List.
- The court also took exception to the fact that the 97th Constitutional Amendment was passed without ratification from the States.
What is the significance of the verdict?
- It allays States’ fears that new Union Ministry of Cooperation would have dis-empowered them.
- Judgement reiterates State’s exclusive legislative power over cooperatives within their territories.
NEA Scout: NASA’s New Spacecraft
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III- Science & Technology
In News: National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) has announced that its new spacecraft, named Near-Earth Asteroid Scout or NEA Scout, has completed all required tests and has been safely tucked inside the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket.
About NEA Scout
- It is a miniaturized spacecraft, known as a CubeSat.
- Its main mission is to fly by and collect data from a near-Earth asteroid.
- It will take about two years to cruise to the asteroid and will be about 93 million miles away from Earth during the asteroid encounter.
- It is one of several payloads that will hitch a ride on Artemis I, which is expected to be launched in November, 2021.
- Artemis I is the first in a series of increasingly complex missions that will enable human exploration to the Moon and Mars.
- NEA Scout launches to the Moon in 2021 with a fleet of other small satellites aboard Artemis 1.
- At the Moon, NEA Scout will deploy its 86-square-meter solar sail and slowly spiral out of lunar orbit.
- It will travel to a near-Earth asteroid and perform a slow fly-by, capturing up-close images of the surface.
- The images gathered by NEA Scout will provide critical information on the asteroid’s physical properties such as orbit, shape, volume, rotation, the dust and debris field surrounding it, plus its surface properties.
What is unique about NEA Scout?
- It will also be America’s first interplanetary mission using a special solar sail propulsion.
- So far, spacecraft have been using solar energy to power them and execute critical functions. This will be the first time that a spacecraft uses solar energy as wind to generate thrust and move forward.
- The spacecraft will pave the way for the Solar Cruiser, which will use a sail 16 times larger when it flies in 2025.
External Benchmarks Lending Rate
Part of: GS Prelims and GS – III- Economy
In News: In a recent RBI report on ‘Monetary transmission in India’, the share of outstanding loans linked to External Benchmarks Lending Rate (EBLR - like repo rate), increased from as low as 2.4% during September 2019 to 28.5% during March 2021.
About Internal Benchmark Lending rate (IBLR)
- Lenders usually have an internal rate, which is the benchmark rate. Interest rates on all loans are linked to it.
- For example, a lender's benchmark rate is 6%.
- It would offer an auto loan 2% higher than the benchmark rate, which will be 8%.
- Similarly, it may provide personal loans at 8% higher than the benchmark rate or at 14%.
- Initially, RBI focused on making the benchmark rate transparent. It introduced different ways to calculate the benchmark rates which are as follows
| Benchmark Prime Lending Rate (BPLR) |
|
| Base Rate |
|
| Marginal Cost of Lending Rate (MCLR): |
|
What were the issues related to Internal Benchmark Lending Rates?
- The problem with the IBLR regime was that when RBI cut the repo and reverse repo rates, banks did not pass the full benefits to borrowers.
-
- Repo rate is the rate at which the RBI lends money to the banks for a short term. Here, the central bank purchases security.
- In the IBLR Linked Loans, the interest rate has many internal variables of Bank which prevented the smooth transmission of RBI’s Monetary Policy changes.
About External Benchmark Lending Rate (EBLR)
- RBI mandated the banks to adopt a uniform external benchmark within a loan category, effective 1st October, 2019.
- 4 external benchmarking mechanisms:
- The RBI repo rate
- The 91-day T-bill yield
- The 182-day T-bill yield
- Anny other benchmark market interest rate as developed by the Financial Benchmarks India Pvt. Ltd.
- Banks are free to decide the spread over the external benchmark. However, the interest rate must be reset as per the external benchmark at least once every three months.
- Significance: Faster Monetary Transmission + Transparency in Interest rates + Standardisation of fixing interest rate.
Concerns
- 28.5% of outstanding loans were linked to EBLR during March 2021.
- However, still 71.5% of outstanding loans are Internal Benchmark Lending Rate (IBLR- like base rate and MCLR) linked loans, which continues to impede the monetary policy transmission.
Miscellaneous
Places in News
Karlapat Wildlife Sanctuary
- Located in Kalahandi district, Odisha.
- It lies within the Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests ecoregion.
- Flora: Sal, Bija, Asan, Harida, Amala, Bahada and Bamboo and varieties of medicinal plants.
Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary
- Located in the Rajsamand District of Rajasthan, the sanctuary extends across the Aravalli Range.
- It is part of the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion.
- It was considered for the reintroduction of the Asiatic lion.
(Mains Focus)
SCIENCE & TECH/HEALTH
Topic:
- GS-3: General Science
Approaches to Vaccine Making
In News: The Centre is funding the development of four vaccines, which are currently in various stages of human trials
The four vaccines, being funded under Mission Covid Suraksha, were the
- DNA-based vaccine candidate by Cadila Healthcare, Gujarat
- Protein sub-unit vaccine by Biological E Ltd, Hyderabad
- Adenovirus intra-nasal vaccine by Bharat Biotech Ltd, Hyderabad
- m-RNA vaccine by Gennova Biopharmaceuticals, Pune.
There are three main approaches to making Vaccine
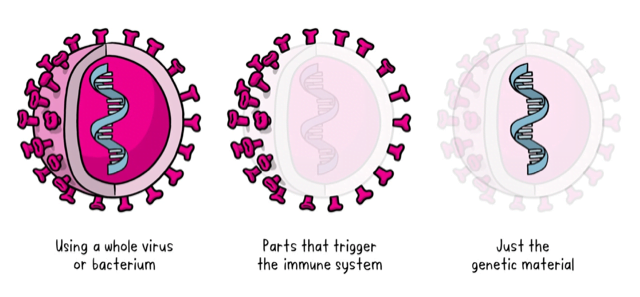
- The whole-microbe approach
- Inactivated vaccine: The first way to make a vaccine is to take the disease-carrying virus or bacterium, or one very similar to it, and inactivate or kill it using chemicals, heat or radiation Ex: Flu & polio vaccines. Also, Covaxin is an inactivated viral vaccine.
- A live-attenuated vaccine uses a living but weakened version of the virus or one that’s very similar Ex: measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) and the chickenpox vaccine.
Viral Vector Vaccine: This type of vaccine uses a safe virus (different from the one that caused disease) to deliver specific sub-parts – called proteins – of the germ of interest so that it can trigger an immune response without causing disease.
- Ex: COVISHIELD: A chimpanzee adenovirus – ChAdOx1 – has been modified to enable it to carry the COVID-19 spike protein into the cells of humans
- The subunit approach
- A subunit vaccine is one that only uses the very specific parts (the subunits) of a virus or bacterium that the immune system needs to recognize. It doesn't contain the whole microbe or use a safe virus as a vector. The subunits may be proteins or sugars.
- Ex: whooping cough, tetanus, diphtheria and meningococcal meningitis.
- The genetic approach (nucleic acid vaccine)
- A nucleic acid vaccine just uses a section of genetic material that provides the instructions for specific proteins, not the whole microbe.
- DNA and RNA are the instructions our cells use to make proteins.
- In our cells, DNA is first turned into mRNA (messenger RNA), which is then used as the blueprint to make specific proteins.
- A nucleic acid vaccine delivers a specific set of instructions to our cells, either as DNA or mRNA, for them to make the specific protein that we want our immune system to recognize and respond to.
- This is a new way of developing vaccines.
- Before the COVID-19 pandemic, none had yet been through the full approvals process for use in humans, though some DNA vaccines, including for particular cancers, were undergoing human trials.
ENVIRONMENT/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-3: Environment Conservation
- GS-2: Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Extreme weather events and Climate Change
Context: This year, people around the world have been doubly hit by the pandemic and extreme weather events which experts say have been fuelled by climate change.
Some of the extreme weather events across the world that were unusual:
- Unprecedented heat wave in Canada and parts of the USA
- It drove temperatures to a record high settling above 40°C for days and reaching 49.6°C — 4 degrees higher than the previous record, causing hundreds of deaths between June 25 to 30.
- Portland City in NW USA is known for its rainy weather and little sunshine, but the blistering heat caught many unawares this time and demand for air conditioners and fans soared
- Floods in Germany that killed over 180 people in the country
- Areas of Rhineland-Palatinate and North Rhine-Westphalia were hit by 148 liters of rain per square metre in just 48 hours in a part of Germany that usually sees about 80 liters in the entire month.
- Flooding at Köln-Stammheim station was the most striking as it broke more than a dozen records with 154mm of rain in over 24 hours, obliterating the city’s previous daily rainfall high of 95mm.
- Floods in New South Wales, Australia in March.
- The rainfall in March broke records, causing the worst flooding on the mid-north coast of Australia since 1929.
- Moreover, the floods came on the heels of other extreme weather events that happened in NSW over the recent years, including droughts, extreme heatwaves and the Black Summer bushfires.
Likewise, Cyclones Tauktae and Yaas that hit India’s west and east coasts, respectively.
Is climate change responsible for extreme weather?
- Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere averaged 419 parts per million in May this year, highest in 63 years.
- It is always difficult to determine forthwith the impact of climate change on extreme weather patterns, but scientific studies indicate that extreme weather events are likely to become more frequent or more intense with rising anthropogenic climate change.
- Climate scientists have also said that in general, the rising average global temperature is making heavy rainfall more likely. Warmer air carries more moisture, meaning that more water will be released eventually.
- Temperatures at the Earth’s poles are rising at two to three times the temperature at the equator
- This weakens the jet stream of the mid-latitudes, situated over Europe.
- During summer and autumn, the weakening of the jet stream has a causal effect resulting in slower-moving storms.
- This can result in more severe and longer-lasting storms with increased intensity.
- Indian Ocean is heating up at a faster pace in comparison to the Pacific or the Atlantic. And in fact, the western parts of the Indian Ocean are warming up even more.
- This is of particular concern as several studies have found that a rise in the temperature of the sea surface is related to the changes in the intensity and frequency of cyclones.
Conclusion
- Increasing temperatures mean more melting ice, higher sea levels, more heatwaves and other extreme weather.
- Rising temperatures can have far-reaching consequences, including an impact on food security, health, the environment and sustainable development. Therefore, all stakeholders have to come together to address the issue of Climate Change.
Connecting the dots :
WATER/ FEDERALISM/ GOVERNANCE
Topic:
- GS-2: Issues relating to development and management of Water
- GS-2: Issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure
Sharing during scarcity
Context: The Union Ministry of Jal Shakti’s gazette notification on the jurisdiction of the Krishna and Godavari River Management Boards over projects and assets in the fields of irrigation and hydropower.
Key Takeaways
- The two river boards can now administer, regulate, operate and maintain 36 projects in the Krishna Basin and 71 in the Godavari to ensure judicious water use in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- The arrangement is expected to leave the working of Water Resources or Irrigation Department in the States intact.
Critical Analysis
- Welcome Development:
- There was a seven-year delay to get the notification from Union government which reflects the tense equations between the two States over river water sharing.
- A gazette notification is a step in long term solution to the problem
- Avoids Competitive Water Projects:
- The States have been locked in a battle of sorts over the utilisation of Krishna water, with AP proposing a few projects, including a lift irrigation scheme for Rayalaseema, and Telangana coming up with half-a-dozen projects of its own.
- Empowering Krishna & Godavari River Board will ensure that such activities take place with approval of Board.
- Telangana’s Objection Addressed:
- Telangana had held the view that the notification should flow from finalisation by Krishna Water Dispute Tribunal (KWDT)-II through expanding the scope of reference.
- Telangana had even moved the Supreme Court but the Centre said it would consider Telangana’s request only if it withdrew its petition which it did.
- In the process, Telangana wanted its complaint to be referred to the current Tribunal to avoid duplication of inquiry.
Way Ahead
- Fair Functioning of Boards: The Centre must now see to it that the empowered Boards function in a fair manner, as the Union government’s decision will be final with regard to matters concerning jurisdiction of the two bodies
- Water Conservation: At the same time, the two States should instead focus on water and energy conservation and improving the efficiency of irrigation schemes and hydel reservoirs.
- River Basin Organisations: After studying the experiences of the revamped Boards, the Centre should look at turning the much talked-about concept of river basin organisations into a reality.
Connecting the dots:
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Note:
- Correct answers of today’s questions will be provided in next day’s DNA section. Kindly refer to it and update your answers.
- Comments Up-voted by IASbaba are also the “correct answers”.
Q.1 Karlapat Wildlife Sanctuary is located in which state?
- Andhra Pradesh
- Odisha
- Maharashtra
- Tamil Nadu
Q.2 External Benchmark Lending Rate can be based on which of the following
- RBI repo rate
- The 91-day T-bill yield
- The 182-day T-bill yield
Select the correct statements
- 1 and 2 Only
- 2 and 3 Only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
Q.3 Cooperative comes under which of the following lists?
- State List
- Union List
- Concurrent List
- Local Bodies List
ANSWERS FOR 20th July 2021 TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE (TYK)
| 1 | C |
| 2 | C |
| 3 | D |
Must Read
On Centrally Sponsored Schemes:
On Pegasus issue:
On Agri-Infrastructure:
