Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: A two-year-old child in Meghalaya has been infected with vaccine-derived polio.
Background:-
- Polioviruses are enteroviruses that are transmitted primarily by the faecal-oral route.
Vaccine-Derived Polio (VDPV):
- Vaccine-derived polio is a rare condition that occurs when the weakened (also called attenuated) strain of poliovirus used in the oral polio vaccine (OPV) mutates and regains the ability to cause paralysis.
- Mechanism:
- OPV contains a live, attenuated virus that is used for immunisation against the disease. This weakened virus triggers an immune response when administered, thus protecting people from the disease.
- The attenuated virus replicates in the intestines for a limited period and is excreted in the stool. In rare cases, the virus can mutate enough to cause the disease again, and circulate in areas where either immunisation is low, or where immunocompromised persons reside, or regions with poor sanitation and hygiene.
- Poliovirus Types: Three types – wild poliovirus type 1 (WPV1), wild poliovirus type 2 (WPV2) and wild poliovirus type 3 (WPV3).
About polio vaccines
- The first successful polio vaccine for poliovirus was made by Jonas Salk, in the early 1950s. Salk inactivated the virus using formaldehyde and injected it into the muscles of test subjects. This inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) induced systemic immunity in the subjects.
- After Salk, Albert Sabin developed another vaccine that contained live polio strains, weakened by growing them serially in macaque cells, making them unfit for human infection. Since this vaccine contained the live virus, it had to be administered through its natural mode of infection – in this case, oral. This is what we today know as the OPV.
- OPV is usually preferred over IPV because of its ease of administration & is inexpensive. However, the weakened virus in OPV can occasionally revert, causing the disease it is meant to prevent. IPV, on the other hand, is a less potent vaccine, but contains inactivated virus particles and hence no risk of causing vaccine-associated paralytic polio (VAPP) – a rare, adverse reaction to OPV. IPV is comparatively tougher to manufacture too.
- Vaccine-associated paralytic polio (VAPP) or vaccine-derived poliovirus (VDPV) are similar but different phenomena.
- On World Polio Day, October 24, 2019, the WHO declared that WPV3 has been eradicated worldwide. WPV2 was officially declared eradicated in 2015.
- However, more than 90% of vaccine-derived poliovirus outbreaks are due to the type 2 virus present in oral polio vaccines. VAPP constitutes 40% of cases caused by the type 2 oral polio vaccine. Many cases of VAPP from type 3 virus too occur in countries using OPV.
- The Indian government does not count VAPP as polio since these cases are sporadic and pose little or no threat to others.
- Even after the global switch from trivalent (containing all three variants) to bivalent (type 1 and type 3) oral polio vaccines in 2016 to prevent any more type 2 vaccine-derived poliovirus, the number of vaccine-derived type 2 poliovirus outbreaks have only increased sharply.
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2
Context: India and Japan recently stated that they reaffirmed their commitment to maintaining and strengthening rules-based international order founded on the principles of the UN Charter, respect for national sovereignty and territorial integrity, and peaceful settlement of disputes.
Background:
- This was stated in a joint statement released by both countries following the third Japan-India 2+2 Foreign and Defence Ministerial Meeting in New Delhi.
Takeaways from the third Japan-India 2+2 Foreign and Defence Ministerial Meeting
- The India-Japan partnership is set against a larger context of a free, open and rules-based Indo-Pacific amid China’s increasing military muscle-flexing in the region.
- Both countries agreed to explore discussions for coordination and cooperation in the field of defence and security assistance to third countries for peace and stability in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The ministers welcomed the Japan Maritime Self Defense Force and Indian Naval Force exploring future cooperation in the area of ship maintenance in India.
- They reiterated support for ASEAN’s unity and centrality and their full support for the ‘ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP)’ which upholds the principles such as openness, transparency, inclusivity, a rules-based framework and respect for international law.
- They agreed to continue working together on Security Council reform with a view to strengthening the UN.
- Ministers took note of the first air visit by Japanese fighters and their participation at Tarang Shakti—which is the first multilateral exercise hosted by the Indian Air Force.
- They also welcomed the conduct of the inaugural edition of the bilateral fighter exercise ‘Veer Guardian 2023’ between the Japan Air Self Defence Force (JASDF) and Indian Air Force (IAF) and conduct of the bilateral exercises of all the three services in one calendar year for the first time in 2023.
- Countries agreed to deepen bilateral cooperation in fields of space and cyber and reaffirmed the importance of multilateral defence cooperation and exchanges in the Indo-Pacific region, while expressing their commitment to continuing bilateral and multilateral exercises including Dharma Guardian, JIMEX and Malabar.
- The “2+2” dialogue with Japan was initiated to further deepen bilateral security and defence cooperation and bring greater depth to the special strategic and global partnership between the two countries.
- India has the “2+2” Ministerial format of dialogue with very few countries, including the United States, Australia, and Russia.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2 AND GS 4
Context: Ever since the infamous gang rape that rocked the country in December 2012 (Nirbhaya), much has been done to strengthen the laws on rape. But brutal incidents of rape continuing unabated should prompt us to ask several questions regarding existing laws.
Background:
- It is no surprise that the first accused apprehended in the Kolkata rape and murder case had a history of violent assault of his wife. Yet, there was no appropriate legal response at the time despite two complaints.
Where lies the malaise & Why is the law failing to act as a sufficient deterrent?
- One answer is that laws on rape cannot be examined in isolation and be expected to regulate men’s mentality.
- Men’s brutalising of women continues to be rampant because of the laxity in laws surrounding other equally heinous crimes, which warrant immediate and equal attention as rape.
Dowry Deaths in India:
- In 2022, India recorded 6,516 annual dowry deaths, with one victim every 90 minutes. Dowry deaths are the unnatural deaths of married women due to cruelty by their husbands or in-laws.
- The conviction rate in dowry death cases is low due to the common practice of the accused paying “blood money” to the victim’s family.
Domestic Violence:
- Domestic violence is one of the most underreported crimes against women across all socio-economic backgrounds.
- The law prescribes up to three years of imprisonment for domestic violence, making it difficult for police to arrest the accused.
- Victims often see their abusers released on bail quickly due to the “bail, not jail” rule for offenses with punishments under seven years.
Other Crimes Against Women:
- Crimes like stalking or harassment are also treated leniently, allowing perpetrators to continue their behavior. Women often hear dismissive remarks from their aggressors, who feel emboldened by the lax legal system.
- There are cases where previous violent behavior, such as in the Kolkata case, did not receive appropriate legal action, leading to more severe crimes later.
Need for Legal Reform:
- A serious legal response to women’s safety requires a review of all crimes against them in order to truly inculcate society’s intolerance to any form of abuse.
- Graded penal provisions should be introduced based on the severity of the crime. Forcibly disrobing a woman or stubbornly stalking her with the intention of committing sexual assault cannot be dealt at par with milder versions of harassment.
Bail and Judicial Reform:
- The current liberal bail system is problematic without broader judicial reforms.
- In 2022, of 3,449 dowry death cases disposed of by courts, 64% were disposed of without a trial, and only 35% of tried cases led to convictions.
- There is an urgent need to develop a criminal justice system that can fast-track cases of crimes against women.
- Where protracted trials remain a stubborn challenge, a long enough incarceration, depending on the severity of the particular crime, is the only available tool to instil a fear of the law.
- Courts should strictly prohibit extrajudicial compromises that are forced on victims due to the lengthy legal process or social pressures.
- Until significant reforms are made, abusers will continue to feel empowered and unafraid of the law, perpetuating violence against women.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi touched down in Poland on Wednesday, commencing his two-nation tour during which he will also travel to the Ukrainian capital Kyiv.
Background:
- Modi’s trip to Poland marks a significant milestone, as it is the first visit by an Indian Prime Minister to the nation in nearly half a century.
Key takeaways :
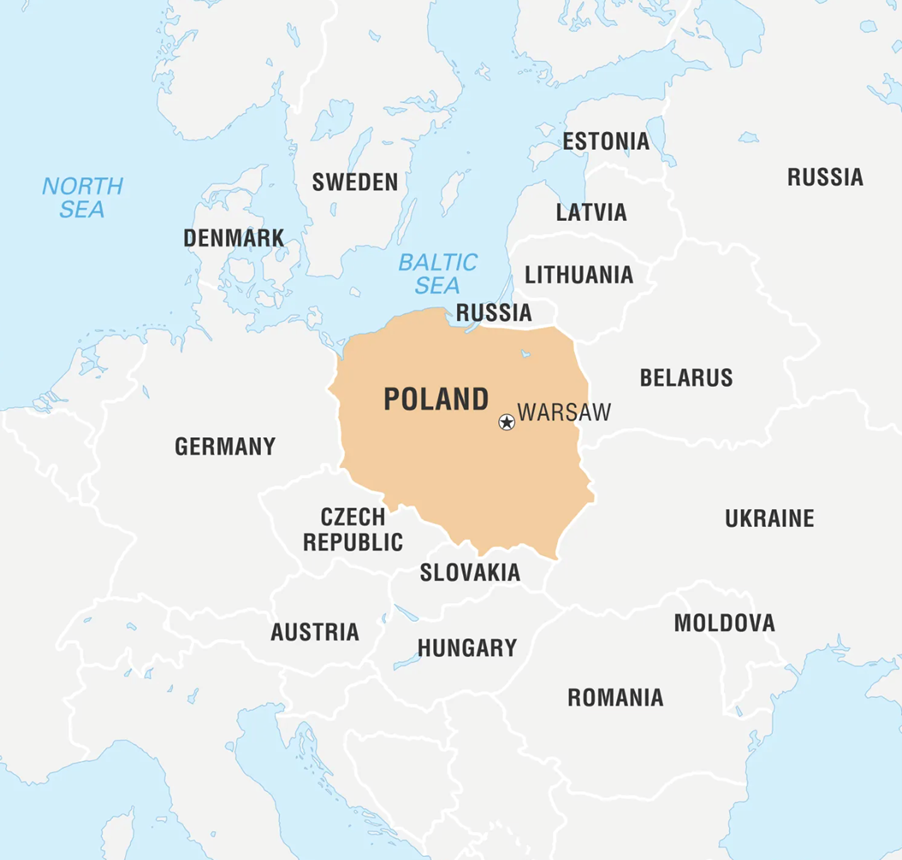
- Poland, officially known as the Republic of Poland, is a country located in Central Europe.
- It is bordered by Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south, Ukraine and Belarus to the east, and Lithuania and Russia to the northeast. The Baltic Sea lies to the north.
- It is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union with over 38 million people.
- Poland is a founding member state of the United Nations and a member of the World Trade Organization, OECD & NATO.
Key Facts about Poland:
- Capital and Largest City: Warsaw
- Official Language: Polish
- Currency: Polish złoty (PLN) ; Government: Unitary parliamentary republic
- Poland features a diverse landscape that includes the Baltic Sea coastline, the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains, and numerous lakes and rivers. The country has a temperate transitional climate.
- Poland has a rich history dating back over a thousand years. It was once one of the largest and most powerful states in Europe during the 16th century. However, it experienced partitions in the late 18th century, which led to its disappearance from the map until it regained independence in 1918.
- Poland has a mixed economy with a high-income status. It is one of the fastest-growing economies in the European Union, with key industries including manufacturing, mining, and agriculture.
Source: Times of India
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Indian Air Force (IAF) and Indian Army have successfully conducted their first precise para-drop operation of the Aarogya Maitri Health Cube at a high-altitude area near 15,000 feet.
Background:
- The operation aligns with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of delivering critical supplies to areas affected by humanitarian aid and disaster relief (HADR).
About Aarogya Maitri Health Cube
- The Arogya Maitri Disaster Management Cube is a state-of-the-art mobile hospital developed by the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- It is developed under the broader BHISHM initiative (Bharat Health Initiative for Sahyog, Hita, and Maitri).
- This innovative solution is designed to provide rapid medical assistance in disaster-stricken areas.
Key Benefits:
- Rapid Response: The cube can be deployed quickly, providing immediate medical assistance during the critical “golden hour” following mass casualty incidents.
- Advanced Medical Care: Equipped with state-of-the-art medical equipment, including operation theatres, X-ray machines, blood test equipment, and ventilators, ensuring comprehensive medical care.
- High Capacity: Capable of treating up to 200 casualties simultaneously, making it suitable for large-scale emergencies.
- Flexibility and Mobility: The 72 lightweight, transportable components can be easily moved by hand, cycle, or drone, allowing for deployment in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
- AI and Data Analytics Integration: Enhances coordination and real-time monitoring, improving the efficiency and effectiveness of medical response.
- Efficient Inventory Management: The BHISHM software ensures efficient inventory management, maintaining readiness for repeated use.
- Robust and Waterproof Design: Ideal for various emergency situations, including those in challenging environments.
- Enhanced Coordination: Facilitates better coordination among disaster response teams, ensuring timely and organized medical assistance.
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The US centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recently issued a health advisory due to concerning rise in cases of parvovirus B19.
Background:
- The advisory highlights the importance of screening high-risk patients and taking preventive measures to reduce the spread.
About parvovirus B19.
- Parvovirus B19 is a small DNA virus.
- Parvovirus B19, also known as “slapped cheek” disease or fifth disease, is a highly contagious virus that primarily affects children but can also impact adults.
- It known as “slapped cheek” disease due to the characteristic red rash on the cheeks, and fifth disease because it was historically the fifth disease identified with a rash in children.
Transmission
- Spread: The virus spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also be transmitted through blood transfusions and from a pregnant woman to her foetus.
- Contagiousness: Highly contagious, especially in environments like schools and daycare canters.
Symptoms
- Children: Bright red rash on the cheeks, sometimes accompanied by a lacy red rash on the body and limbs.
- Adults: Joint pain and swelling, particularly in the wrists, knees, and ankles. Some adults may also experience mild flu-like symptoms.
- Immunocompromised Individuals: Can suffer from severe anaemia due to the virus’s impact on red blood cell production.
- Pregnancy: Infection during pregnancy can lead to severe complications such as hydrops fetalis and miscarriage.
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis: Typically made based on clinical presentation and confirmed by serologic testing for Parvovirus B19-specific antibodies. PCR testing can also detect the virus’s DNA.
- Treatment: No specific antiviral treatment. Currently, there is no vaccine available for Parvovirus B19. Preventive measures focus on reducing transmission. Management focuses on alleviating symptoms, such as using antipyretics and analgesics for children and NSAIDs for adults.
Prevention
- Hygiene: Good hand hygiene practices, such as regular hand washing with soap and water.
- Avoiding Contact: Avoiding close contact with individuals who exhibit symptoms of the infection.
- Pregnancy Precautions: Pregnant women should take precautions to avoid exposure to infected individuals.
Source: CDC
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Consider the following countries
- Poland
- Turkey
- Lithuania
- Latvia
How many of the above countries are members of NATO?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 3 only
- All four
Q2.) With reference to the parvovirus B19, consider the following statements:
- Parvovirus B19 is a small DNA virus.
- It primarily affects children.
- There is no specific antiviral treatment for Parvovirus B19.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q3.) With reference to the Arogya Maitri Disaster Management Cube, consider the following statements:
- The Arogya Maitri Disaster Management Cube is a state-of-the-art mobile hospital developed by the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- It is designed to provide rapid medical assistance in disaster-stricken areas.
- The cube is equipped with advanced medical equipment and integrates AI and data analytics for effective coordination and real-time monitoring.
- It is developed under the BHISHM initiative.
How many statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- Only three
- All four
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 22nd August 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 21st August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – c
