Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: Today, India is celebrating its first National Space Day. This day commemorates the groundbreaking success of the Chandrayaan-3 mission, which achieved the safe landing of the Vikram Lander on the lunar surface on August 23, 2023.
Background:-
- With Chandrayaan-3 mission achievement, India became the fourth country to successfully land on the moon, making history as the first to land near the southern polar region.
Chandrayaan-3 Mission
- Mission Type: India’s third lunar mission and second attempt at a soft lunar landing.
- Launch Vehicle: Launch Vehicle Mark-III (LVM3).
- Primary Objectives:
- Demonstrate a safe and soft landing on the lunar surface.
- Demonstrate a rover roving on the Moon.
- Conduct in-situ scientific experiments.
- Chandrayaan-3 Components:
- Lander Module (LM)
- Rover
- Propulsion Module (PM)
Lander Payloads and Objectives
- Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE): Measures the thermal properties of the lunar surface near the polar region.
- Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA): Measures seismic activity around the landing site and analyzes the lunar crust and mantle structure.
- Radio Anatomy of Moon Bound Hypersensitive Ionosphere and Atmosphere (RAMBHA): Estimates plasma density and its variations.
- Laser Retroreflector Array (LRA): A passive experiment to understand the dynamics of the Moon’s system.
Rover Payloads and Objectives
- Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS): Determines the elemental composition of lunar soil and rocks.
- Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS): Analyzes elemental composition in the vicinity of the landing site.
Propulsion Module Payload
- Propulsion Module Payload: Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE) for studying Earth’s spectral and polarimetric measurements from lunar orbit.
- SHAPE will aid in the study of exoplanets to assess their potential habitability.
Significance of Chandrayaan-3
- International Standing: Positions India as a serious player in planetary exploration and space technology.
- Cost Efficiency: Demonstrates ISRO’s ability to achieve space missions cost-effectively (Mission cost: Rs 615 crore).
- Strategic Importance: Enhances India’s role in international space policy and resource extraction discussions.
- Technological Leadership: Establishes India among the few nations with the capability for planetary exploration, contributing to space-related decision-making.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 2
Context: Israeli security forces suspect Iran and Hezbollah’s role in the suicide bombing in Tel Aviv on Sunday.
Background:
- Israel believe that the terror attack could be Iran and its proxy’s bid to avenge the assassination of Ismail Haniyeh (leader of Hamas) in Tehran last month.
- Iran’s opposition to Israel is rooted in religious, ideological, and geopolitical factors, including its support for Palestine and its anti-American stance.
Israel-Iran Conflict Overview
- The formation of Israel in 1948 was a watershed moment in the history of the Middle East. It triggered an Arab-Israeli war and the long Israeli-Arab and Israeli-Palestinian conflicts.
- Iran, although opposed to the formation of Israel and voted against the Partition Plan (1947) and Israel’s admission into the United Nations (1949), was the second Muslim-majority country after Türkiye to recognize Israel in 1950.
- The friendly relations between the two states were not always reflected among the wider population in Iran who were sympathetic to the plight of the Palestinians and their struggle for a state.
The 1979 Islamic Revolution in Iran
- Israel and Iran have been in conflict since the 1979 Islamic Revolution in Iran, which led to a break in diplomatic relations.
- Post-revolution, Iran labeled Israel as the “Little Satan” and ceased all diplomatic and economic ties.
- Religious and Ideological Differences:
- Iran opposes Israel’s control over Jerusalem, which is considered holy in Islam.
- The ideological basis of Iranian opposition to Israel emanates from anti-imperialist and anti-Americanism rooted in the 1979 revolution.
- Besides Islam, these form the most important component of the revolutionary zeal of Khomeini (Irans supreme leader), who considered Israel as an American and imperial outpost in the Middle East.
- Geopolitical Tensions:
- Since the revolution, Iran has called for the expulsion of all external forces from the region and to form a regional security architecture through collaboration among the regional states. Iran, therefore, is considered a revisionist power that wants to replace the US-led regional order with an Iran-led order.
- Iran’s regional activities of creating, arming and supporting non-state actors, especially in the vicinity of Israel and its pursuit of nuclear energy, are viewed as a part of the Iranian plan to encircle Israel militarily and a preparation for a future war against Israel.
Recent Escalations:
- Before the current state of affairs, Iran and Israel had been engaged in a proxy war but had avoided attacking each other directly.
- The Israel-Hamas war has, however, started a new phase in the Israel-Iran war, with the two gradually moving to a direct confrontation.
- The Israeli attack on the Iranian diplomatic complex in Syria and killing of IRGC commanders and officers, its constant targeting of Hezbollah commanders in Lebanon and the killing of Haniyeh in Tehran are part of the pattern. Iran, too, is no longer satisfied with showing restraint and issuing verbal threats, as was visible during the 13 April rocket, missile and drone attacks.
- For Iran, the killing of Haniyeh was a serious provocation as it was a direct challenge to Iranian sovereignty and also to its military capacity and deterrence.
- Tehran nonetheless faces the dilemma because any reckless action can lead to an all-out war and might force the US to join Israel, which Iran would like to avoid at this point.
Implications for India
- India, with significant investments in the Middle East, is concerned about potential disruptions in hydrocarbon supplies and the impact on its diplomatic relations in the region. A peaceful Middle East is crucial for India’s strategic interests, but ongoing conflicts pose challenges to its diplomatic balancing act.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – POLITY
Context: The Election Commission of India (ECI) on Wednesday halted the announcement of results for the ongoing recruitments in Haryana till assembly poll process is over.
Background:
- Election Commission of India (ECI) plays a crucial role in ensuring transparent, free and fair elections.
Election Commission of India (ECI) Overview
- Purpose: A permanent, independent, and constitutional authority responsible for conducting free and fair elections in India.
- Jurisdiction: Supervises elections to Parliament, state legislatures, and the offices of President and Vice President of India.ECI does not oversee local body elections (e.g., municipalities, panchayats).
Constitutional Provisions (Articles 324–329):
- Article 324: Superintendence, direction, and control of elections.
- Article 325: Prohibits exclusion from electoral rolls based on religion, race, caste, or sex.
- Article 326: Establishes adult suffrage as the basis for elections.
- Article 327: Empowers Parliament to legislate on election-related matters.
- Article 328: Allows state legislatures to make laws related to state elections.
- Article 329: Prohibits courts from interfering in electoral matters.
Functions:
- Advisory:
- The Constitution grants the ECI advisory authority over the post-election disqualification of sitting members of Parliament and State Legislatures.
- The commission is also consulted in matters involving individuals found guilty of engaging in corrupt activities during elections that are brought before the Supreme Court and High Courts to determine whether or not they should be disqualified from contesting elections and, if so, for what period.
- Quasi-Judicial:
- A candidate who fails to submit an account of his election costs within the mandated time and format may be disqualified by the ECI.
- Along with other legal disqualifications, the commission also has the authority to eliminate or shorten the duration of such disqualifications.
- It also resolves conflicts pertaining to the recognition of political parties and the assignment of electoral symbols to them.
- The EC establishes a model code of conduct and ensures that all candidates and political parties follow it throughout the election season.
- Administrative:
- It is responsible for the delimitation of electoral constituencies. It is also responsible for the registration of all eligible voters and for producing and updating electoral rolls on a regular basis.
- It sends out election schedules and dates and reviews nomination documents.
- It recognises political parties and assigns them election emblems. EC confer upon them the status of national or state parties based on their polling performance.
- The ECI also invalidates voting in cases of violence, booth capture, tampering, or other anomalies.
- It controls, without bias, the amount of money each political party spends on a candidate’s campaign.
Composition:
- As of now, it consists of a Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) and two Election Commissioners. All commissioners are appointed by the President.
- Decisions are made by majority vote in case of differences in opinion.
- Tenure is up to six years or until age 65.
- The Chief Election Commissioner can only be removed by the same process used for removing a Supreme Court judge.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: At least one man died and six people are missing after a luxury yacht was hit by a violent storm off the coast of Sicily, Italy recently. Experts suggest the storm could have been a waterspout.
Background:
- A waterspout is a large column of air and mist rotating over a water body. It usually appearing as a funnel-shaped cloud in contact with the water.
Key takeaways :
- A waterspout is a column of rotating, cloud-filled wind that descends from a cumulus cloud to a body of water, such as an ocean or lake. Despite its name, a waterspout is not filled with water from the ocean or lake; instead, the water inside a waterspout is formed by condensation in the cloud.
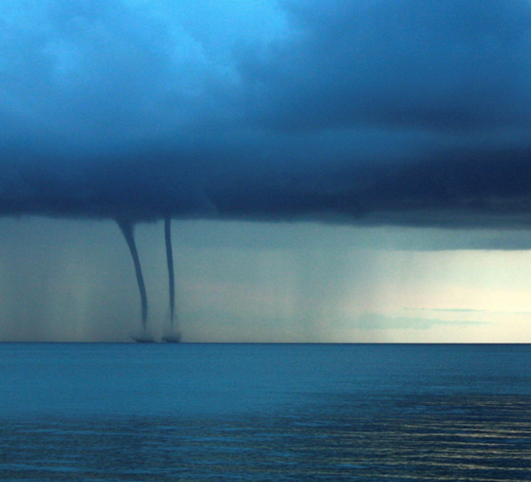

Formation
- Waterspouts form when winds blowing in different directions collide, creating a rotating column of air near the surface. This air rises, carrying water vapour high into the sky, where it forms rain showers, storms, and cumulus clouds. The process involves five stages:
- Dark Spot: The water surface darkens where the vortex reaches it.
- Spiral Pattern: Light and dark bands spiral out from the dark spot.
- Spray Ring: A swirling ring of sea spray forms around the dark spot.
- Mature Vortex: The waterspout reaches its most intense stage, visible from the water surface to the clouds.
- Decay: The waterspout collapses as the flow of warm air weakens.
- There are two main types of waterspouts:
- Tornadic Waterspouts: These start as true tornadoes influenced by severe thunderstorms and are the most powerful and destructive type.
- Fair-Weather Waterspouts: More common and less dangerous, these form in developing storm systems but not in storms themselves.
- Regions where Waterspouts are frequently occurred:
- Waterspouts are most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions. Here are some of the key areas where they frequently occur:
- Florida Keys and Gulf of Mexico: This region sees the highest number of waterspouts, with many forming during the late spring and summer months.
- Mediterranean Sea: Waterspouts are common off the coasts of Greece, Italy, and other Mediterranean countries.
- Great Lakes: Although less frequent, waterspouts can also form over the Great Lakes, especially during the late summer and early fall.
- Western Coast of Europe: This includes areas like the British Isles and the Baltic Sea.
- East Coast of Australia: Waterspouts are also observed off the eastern coast of Australia.
- These regions provide the warm, moist conditions that are conducive to waterspout formation.
Source: BBC
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) recently facilitated the first export of India’s ready-to-drink fig juice, made from GI-tagged Purandar Figs, to Poland.
Background:
- This milestone marks a significant achievement in promoting India’s unique agro-products on the global stage.
About APEDA
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) is an organization under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India.
- Established in 1985, APEDA is responsible for promoting the export of agricultural and processed food products from India.
Functions of APEDA
- Market Development: Identifying and developing new markets for Indian agricultural and processed food products.
- Quality Control: Ensuring products meet international standards and providing certification and quality assurance.
- Infrastructure Development: Supporting the development of infrastructure for export, including cold storage, packaging, and transportation facilities.
- Training and Capacity Building: Offering training programs for farmers, exporters, and other stakeholders to enhance their skills and knowledge.
- Financial Assistance: Providing financial assistance to exporters for market development, quality improvement, and infrastructure development.
- Promotion of GI Products: Promoting the export of Geographical Indication (GI) tagged products, which are unique to specific regions in India.
Purandar Figs:
- Purandar Figs are a unique variety of figs grown in the Purandar taluka of Pune district in Maharashtra, India. These figs have been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, which means they are recognized for their unique qualities and origin.
- Purandar Figs are known for their sweet taste and soft texture.
Benefits of GI Tagging
- Quality Assurance: The GI tag ensures that the figs are of high quality and are produced in a specific region using traditional methods.
- Market Recognition: It helps in gaining recognition in both domestic and international markets.
- Economic Benefits: Farmers and producers can command a premium price for GI-tagged products, leading to better income.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) and Australia’s CSIRO have launched a call for applications for the Climate Smart Agritech cohort of the India Australia Rapid Innovation and Start-up Expansion (RISE) Accelerator.
Background:
- The India Australia RISE Accelerator offers tailored support and opportunities for agritech startups and SMEs ready to scale their innovations across borders.
About India Australia Rapid Innovation and Start-up Expansion (RISE) Accelerator
- The India Australia Rapid Innovation and Start-up Expansion (RISE) Accelerator is a bilateral program launched by the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) and Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO).
- It was designed to support start-ups and small- to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in both India and Australia.
- RISE Accelerator targets to enable start-ups with mature tech-based innovations to fast-track their cross-border social, economic and environmental impact through cross-border innovation ecosystem.
The RISE Accelerator aims to:
- Foster Innovation: Encourage the development of cutting-edge technologies.
- Facilitate Cross-Border Collaboration: Enable start-ups to expand their impact across India and Australia.
- Address Shared Challenges: Focus on solutions for environmental and climate issues.
The program provides:
- Market Insights: Valuable information on market trends and regulatory landscapes.
- Partnerships: Connections with potential partners, investors, and customers.
- Mentorship: One-on-one guidance from industry experts.
- Validation and Adaptation: Support for adapting and validating technologies in new markets.
Benefits
- Participants in the RISE Accelerator can expect:
- Accelerated Growth: Fast-tracked connections to the right partners and customers.
- Credibility: Enhanced reputation and visibility in international markets.
- Funding Opportunities: Access to joint-innovation funds, grants, and investors.
- Comprehensive Support: Tailored assistance to navigate early steps in a new region and scale technology overseas
Source: PIB
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to the India Australia Rapid Innovation and Start-up Expansion (RISE) Accelerator, consider the following statements:
- RISE Accelerator is a bilateral program launched by the Atal Innovation Mission (AIM) and Australia’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation (CSIRO).
- RISE Accelerator targets to enable start-ups with mature tech-based innovations to fast-track their cross-border social, economic and environmental impact through cross-border innovation ecosystem.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2.) Consider the following statements:
- The Agricultural and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) is an organization under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India.
- APEDA is responsible for promoting the export of agricultural and processed food products from India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3.) With reference to the Waterspouts, consider the following statements:
- A waterspout is a large column of air and mist rotating over a water body.
- Waterspouts form when winds blowing in different directions collide, creating a rotating column of air near the surface.
- Waterspouts are most commonly found in equatorial region.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
- 1 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 23rd August 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 22nd August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – d
Q.2) – d
Q.3) – d
