Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims – Current Event
Context: Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) will conduct checks on products of spice brands MDH and Everest Group after authorities in Hong Kong and Singapore last week determined that four of their spice mixes contained high levels of carcinogen ethylene oxide.
Background:-
- FSSAI doesn’t permit use of ethylene oxide in any food product.
About Ethylene Oxide
- Ethylene oxide is a pesticide that has been classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, meaning there is sufficient evidence from human studies that it can cause cancer.
- It is used by the spice industry as a fumigant to reduce microbial contamination, such as E. coli and Salmonella.
- It is a colourless, highly flammable and very reactive gas that kills bacteria, viruses and fungi. It is an industrial chemical.
- Ethylene oxide can damage DNA during sterilisation procedures.
- While the risk from occasional, low-level exposure may be minimal, spices and spice blends like those flagged are commonly used in household cooking across multiple dishes. This can lead to chronic, persistent exposure over time, which has been linked to an increased risk of cancers like leukemia, stomach cancer and breast cancer.
- It can even lead to respiratory irritation and lung injury, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and shortness of breath.
- Ethylene oxide was banned by the European Union (EU) in 2011 for fumigation of food and animal feed during transport and storage. The use of ethylene oxide is now only permitted in disinfection and sterilisation of medical devices.
Additional information
- Escherichia coli (E.coli) is a bacterial strain that is commonly found in the intestines of people and animals, fecal waste of cattle and humans.
- Salmonella is a group of bacteria that can cause food-borne illnesses known as salmonellosis. The World Health Organisation (WHO) identifies Salmonella as one of four key global causes of diarrhoeal diseases.Individuals who develop salmonellosis may show symptoms such as nausea, diarrhoea, fever, and abdominal cramps 12-72 hours after contracting the infection.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – International Event
Context: Six months after the October 7 attack, Israel’s war to eliminate Hamas has resulted in the near-complete destruction of Gaza and a dire humanitarian crisis with the area on the verge of famine.Iran and its allies have militarily united behind the Palestinian cause and expanded the confrontation to other parts of the region.
Background:
- The dynamics of war have drastically changed following the massive Iranian drone and missile attacks on military targets in Israel on April 14. This was in retaliation to Israeli aerial strikes on an Iranian diplomatic compound in Damascus on April 1 in which top Iranian generals were killed. Israel had not seen direct attacks by a state on its soil since 1991 when Saddam Hussein fired 42 Scud missiles.
A volatile Middle East:
The geopolitics of the region has already undergone a sea change since October 7 in four substantive ways:
- First, thawing of the hitherto icy Shia-Sunni relationship, with Hezbollah, Houthis and Iran (all Shia entities) extending open support to “Sunni” Palestinians, presenting regional unity via the Axis of Resistance, opposing US-Israel domination. The first signs of the Resistance surfaced early on in the war, with conflict with Hezbollah in northern Israel leading to the displacement of thousands of Israeli civilians who are yet to return. This active front is likely to simmer.
- Second, the war has expanded across the region, pushing the US to become the fulcrum of efforts to contain expansion and making it a primary target.
- Third, the Saudi-aligned Sunni Arab States have adopted the political and diplomatic route, advocating a ceasefire, supporting humanitarian assistance, and calling for a two-state solution while remaining in line with US-led initiatives.
- Fourth, the Yemen-based Houthis — a non-state actor devoid of a navy — have managed to successfully disrupt a critical sea lane of communication for five months, impairing trade substantively.
Additional Information
- The expansion of the war has already caused economic distress to the Israeli economy .The Israeli economy has reportedly shrunk by 20 per cent in the last quarter of 2023.
- Two crucial Israeli ports, Eilat on the Red Sea and Haifa on the eastern Mediterranean have been sporadically attacked. The Eilat port is said to be down to a quarter of its business, while Israeli media reports an acute shortage of labour in Israel, primarily on account of military conscription and volunteerism.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – Economy & Environment
Context: National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) recently unveiled its Climate Strategy 2030 document which aims to address India’s need for green financing.
Background:
- NABARD’s Climate Strategy 2030 is structured around four key pillars which include accelerating green lending across sectors, playing a broader market-making role, internal green transformation and strategic resource mobilisation.
What is Green financing
- Green financing refers to any structured financial activity – a product or service – that has been designed to ensure a better environmental outcome.
- It encompasses a variety of loans, debt mechanisms, and investments aimed at promoting the development of green projects or minimizing the climate impact of regular projects.
Purpose and Importance:
- Green finance aims to align financial activities with environmental goals.
- It plays a crucial role in achieving several of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals by supporting sustainable development priorities.
Examples of Green Finance Projects:
- Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency: Funding projects related to clean energy sources and energy-saving technologies.
- Pollution Prevention and Control: Financing initiatives that reduce pollution and promote cleaner practices.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Supporting efforts to protect and preserve biodiversity.
- Circular Economy Initiatives: Investing in projects that promote resource efficiency and waste reduction.
- Sustainable Use of Natural Resources and Land: Financing projects that balance economic development with environmental conservation.
Green Bonds:
- Green bonds are a common green finance instrument.
- They adhere to specific criteria, including the use of proceeds, project evaluation, proper management, and detailed reporting.
- The United States, China, and France are the three largest issuers of green bonds.
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – Geography
Context: Recently, five asylum seekers died while crossing the English Channel from France to Britain in an overcrowded small boat.
Background:
- In recent years, the English Channel has become a focal point for migrants and asylum seekers attempting to reach the UK. Many undertake dangerous journeys in small boats, hoping to find safety and better opportunities.
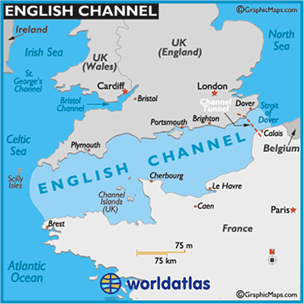
About English Channel:
- The English Channel, also known as “La Manche,” is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France.
- It links to the southern part of the North Sea via the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end.
- Notably, it is the busiest shipping area in the world.
- Historically, the channel played a pivotal role in Britain’s naval supremacy and served as a natural defence mechanism against invasions during significant events like the Napoleonic Wars and World War II.
Source: Reuters
Syllabus
- Prelims – Science
Context: NASA Voyager 1 spacecraft has begun sending readable communications again after months of transmitting gibberish back to Earth.
Background:
- NASA’s Voyager flight team detected a glitch in November and worked to fix the problem via code, leading to the successful return of readable data.
About VOYAGER 1 SPACECRAFT :
- Voyager 1 was launched by NASA on September 5, 1977.
- Voyager 1 is part of the Voyager program, which also includes Voyager 2.
Mission Objective:
- To study the outer Solar System and beyond, including flybys of Jupiter and Saturn.
Discoveries:
- It discovered a thin ring around Jupiter and two new Jovian moons: Thebe and Metis.
- At Saturn, it found five new moons and a new ring called the G-ring.
Interstellar Achievement:
- Voyager 1 was the first human-made object to cross the heliosphere and enter interstellar space in August 2012.
Current Status:
- It is the most distant human-made object from Earth and is expected to send data until at least 2025.
Golden Record:
- Carries a golden record with sounds and images representing life and culture on Earth.
Source: Live Science
Syllabus
- Prelims – GS 2 & GS 3
Context: The Supreme Court of India acknowledged the right to protection from climate change impacts as part of the fundamental rights to life (Article 21) and equality (Article 19) enshrined in the Indian Constitution.
Background:
- The arguments were a part of a verdict by a three-judge bench headed by the Chief Justice of India DY Chandrachud hearing a case on the conservation of the great India bustard and the lesser florican.
The intersection of climate change and human rights:
- Climate change can directly affect people’s right to life by causing extreme weather events like hurricanes or floods, which can lead to loss of life and property. For example, in low-lying coastal areas, rising sea levels due to climate change can threaten people’s homes and livelihoods, forcing them to relocate.
- Climate change can impact water sources, leading to water scarcity or contamination. This affects people’s right to clean water and sanitation. In regions where droughts are becoming more frequent due to climate change, communities may struggle to access safe drinking water, leading to health issues.
- Climate change can exacerbate health problems, especially for vulnerable populations. For instance, increased heat waves can lead to heat-related illnesses and deaths, affecting the right to health.
- Climate change-induced events such as sea-level rise, extreme weather events, or desertification can force people to migrate or be displaced from their homes. This intersects with human rights, particularly the right to residence and the right to seek asylum.
- Climate change can disproportionately affect indigenous communities that rely heavily on natural resources for their livelihoods and cultural practices. For instance, changes in ecosystems due to climate change can threaten traditional livelihoods like farming or fishing, impacting indigenous peoples’ rights to land, resources, and cultural heritage.
The Supreme Court’s interpretation of constitutional provisions concerning climate change:
- Article 48A which mandates environmental protection and Article 51A(g) which promotes wildlife conservation, implicitly guarantee a right to be safeguarded from climate change.
- Article 21 recognises the right to life and personal liberty while Article 14 indicates that all persons shall have equality before the law and the equal protection of laws. These articles are important sources of the right to a clean environment and the right against the adverse effects of climate change.
- In MC Mehta vs Kamal Nath Case, 2000, the Supreme Court stated that the right to a clean environment is an extension of the right to life.
Issues/Challenges in balancing climate change mitigation with human rights protection:
- Some climate mitigation measures may conflict with human rights, such as restrictions on land use for conservation projects or displacement due to renewable energy infrastructure development. Finding solutions that minimise negative impacts while maximising benefits is challenging.
- Climate actions like transitioning to renewable energy or implementing carbon pricing can impact access to essential resources like energy, water, and food, especially for marginalised communities.
- Climate-induced migration can strain social systems and lead to conflicts over resources and rights in host communities. Managing migration flows in a way that respects the rights of both migrants and host populations is a multifaceted challenge.
- Balancing efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (mitigation) with investments in adaptation to climate impacts can be challenging. Prioritising one over the other can have implications for human rights, particularly for communities already facing climate-related risks.
- Climate change is a global issue requiring international cooperation. Balancing national climate goals with global responsibilities and ensuring that climate actions do not undermine the rights of vulnerable communities across borders is a complex task.
Source: Down To Earth
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to the Voyager 1 spacecraft, consider the following statements:
- Voyager 1 was launched by ISRO.
- The primary mission of Voyager 1 was to explore the outer planets of solar system.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2.) English Channel separates England from
- Spain
- France
- Germany
- Poland
Q3.) With reference to the Green Financing, consider the following statements:
- Green financing aims to align financial activities with environmental goals.
- It encompasses a variety of debt mechanisms and investments aimed at promoting the development of green projects.
- Green bonds are a common green finance instrument.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 25th April 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs.st
ANSWERS FOR 24th April – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d
