Archives
(PRELIMS Focus)
Category: International Organisations
Context:
- The International Monetary Fund’s annual review has given India’s national accounts statistics, a grade of ‘C’, the second-lowest rating.
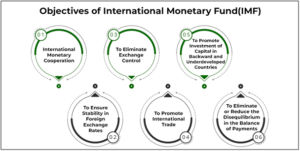
About International Monetary Fund (IMF):
-
- Nature: The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an organization of 191 member countries, each of which has representation on the IMF’s executive board in proportion to its financial importance.
- Establishment: The IMF, also known as the Fund, was conceived at a UN conference in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States, in July 1944.
- Reason behind its foundation: The 44 countries at that conference sought to build a framework for economic cooperation to avoid a repetition of the competitive devaluations that had contributed to the Great Depression of the 1930s.
- Major objectives:
-
-
- To foster global monetary cooperation
- To secure financial stability and facilitate international trade
- To promote high employment and sustainable economic growth
- To reduce poverty around the world and ensure macro-economic growth
- To promote exchange rate stability, and an international payment system
-
- Governance setup:
-
- Board of Governors: It consists of one governor and one alternate governor for each member country. Each member country appoints its two governors.
- Ministerial Committees: The Board of Governors is advised by two ministerial committees- International Monetary and Financial Committee (IMFC) and Development Committee.
- Executive Board: It is 24-member Executive Board elected by the Board of Governors.
- Management: IMF’s Managing Director is both chairman of the IMF’s Executive Board and head of IMF staff. The Managing Director is appointed by the Executive Board by voting or consensus.
- Membership: Any other state, whether or not a member of the UN, may become a member of the IMF in accordance with IMF Articles of Agreement and terms prescribed by the Board of Governors. Membership in the IMF is a prerequisite to membership in the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD).
- Quota system: On joining the IMF, each member country contributes a certain sum of money, called a quota subscription, which is based on the country’s wealth and economic performance. Members’ voting power is related directly to their quotas (the amount of money they contribute to the institution).
- Use of SDRs: Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) is the IMF’s unit of account and not a currency. The currency value of the SDR is determined by summing the values in U.S. dollars, based on market exchange rates, of a SDR basket of currencies (U.S. dollar, Euro, Japanese yen, pound sterling and the Chinese renminbi).
- Capacity Development: It provides technical assistance and training to central banks, finance ministries, tax authorities, and other economic institutions.
Source:
Category: Defence and Security
Context:
- Recently, the Indian Navy commissioned INS Mahe, during a ceremony held at the Naval Dockyard, Mumbai.

About INS Mahe:
- Nature: It is the first of the eight anti-submarine warfare shallow water craft (ASW-SWC) of the Indian Navy.
- Construction: It is indigenously designed and built by the Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL).
- Nomenclature: The ship takes her name from the historic coastal town of Mahe on the Malabar Coast. The town’s maritime heritage and tranquil estuary mirror the ship’s balance of elegance and strength.
- Mascot: Its mascot, the Cheetah, embodies speed and focus.
- Motto: Its motto “Silent Hunters” reflects the ship’s stealth, vigilance, and unyielding readiness.
- Capability: Designed for a wide range of coastal defence missions, Mahe is equipped for underwater surveillance, search and rescue duties, Low Intensity Maritime Operations (LIMO), and complex mine-laying tasks.
- Uniqueness: The 78-meter-long vessel is the largest Indian naval warship powered by a diesel engine-waterjet propulsion system. This advanced propulsion system ensures superior manoeuvrability and a reduced acoustic signature, crucial in anti-submarine operations carried out in littoral waters.
- Step towards Aatmanirbhar Bharat: With over 80% indigenous content, the ship underscores the Indian Navy’s sustained efforts to promote indigenisation through homegrown solutions and innovative technologies.
- Embodies spirit of Kalaripayattu: The ship’s crest features the Urumi, the flexible sword of Kalaripayattu, rising from stylised blue waves – a symbol of agility, precision, and lethal grace.
- Design: Its compact design and high agility make it ideal for operations in shallow waters where conventional destroyers and frigates face navigational constraints. These ships are equipped with one RBU-6000 anti-submarine rocket launcher and two sets of light-weight torpedo-tube launchers for launching anti-submarine torpedoes.
Source:
Category: Government Schemes
Context:
- Union Minister of State for Science & Technology recently said that the EIR initiative is successfully cultivating a new generation of scientist-entrepreneurs.

About Entrepreneur-in-Residence (EIR) Programme:
- Nature: It is one of the programs introduced under National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI).
- Objective: It aims to encourage graduate students to take to entrepreneurship as a prospective career option by providing financial and non-financial support in the form of a fellowship.
- Implementation: It is implemented by the Dept. of Science and Technology, Govt. of India in association with NCL Venture Centre, Pune.
- Financial Support: The recipient is eligible to get financial support of up to INR 30,000/- monthly. It is offered to graduate students for a maximum period of 12 months.
- Mentorship: The Programme includes mentoring support and guidance, technical and financial advice, industry connections etc.
- Connects lab to market: It helps innovators convert scientific discoveries into market-ready solutions through mentoring, incubation and industry linkages.
- Promotes scientist-entrepreneurs: It cultivates a new generation of scientist-entrepreneurs, where researchers are encouraged to innovate, patent and commercialise their ideas.
- Mitigates risk: A primary goal is to minimize the risk involved in pursuing technology-based startups, thereby creating a stronger pipeline of entrepreneurs for incubators.
Source:
Category: Science and Technology
Context:
- The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has approved the name of a 3.5 billion-year-old crater on Mars, after M.S. Krishnan, the pioneering Indian geologist.

About International Astronomical Union (IAU):
-
- Nature: It is a global organization of professional astronomers, at the PhD level and beyond who are active in professional education and research in astronomy.
- Establishment: It was founded in 1919 as a senior body governing international professional astronomical activities worldwide.
- Objective: Its mission is to promote and safeguard the science of astronomy in all its aspects, including research, communication, education, and development, through international cooperation.
- Activities undertaken:
-
- Defining fundamental astronomical and dynamical constants and unambiguous astronomical nomenclature
- Rapid dissemination of new discoveries and organization of international observing campaigns
- Promotion of educational activities in astronomy to early informal discussions of possible future international large-scale facilities.
- Uniqueness: It is the only organization recognized professionally for the naming of astronomical bodies, which it does solely on the basis of merit, history, or discoverer’s privilege.
- Headquarters: Its headquarters is located in Paris, France.
- Membership: IAU membership spans 92 countries. Out of those countries, 85 are National Members.
- Governance: The IAU holds a general assembly every three years in varying parts of the world. The long-term policy of the IAU is defined by the General Assembly.
Source:
Category: Miscellaneous
Context:
- Recently, Commonwealth Sport’s General Assembly in Glasgow formally confirmed Ahmedabad as the venue of centenary edition of the Commonwealth Games 2030.

About Commonwealth Games:
- Nature: It is the world’s 2nd largest multi-sports event (after Olympic Games), bringing together athletes from 71 nations and territories and celebrating the diversity and unity of the Commonwealth.
- First edition: It was first held in 1930 in Hamilton, Canada as the British Empire Games.
- Nomenclature: The event was known as the British Empire and Commonwealth Games in 1954, before being renamed the Commonwealth Games from 1978 onwards.
- Governing Body: Commonwealth Games Federation (CGF) is responsible for the direction and control of the Games.
- Frequency: It is held once every 4 years and is often referred to as the Friendly Games, reflecting the core values of Humanity, Equality, and Destiny.
- Promotes diversity: It promotes sports, education, and recreation while celebrating the Commonwealth’s cultural and linguistic diversity.
About Commonwealth Nations:
-
- Nature: It is a voluntary association of several countries, mostly formerly British colonies, with shared goals of development, democracy, and peace.
- Historical Genesis:
-
- Imperial Conference (1926): UK and Dominions agreed to be equal members within the British Empire, owing allegiance to the monarch but retaining autonomy.
- London Declaration (1949): Established the Modern Commonwealth of Nations, allowing republics and non-British monarchies to join.
- Membership: It is composed of 56 independent countries, most formerly British colonies. Membership is voluntary, and any country can join.
- Governance: It is guided by the Commonwealth Charter, promoting development, democracy, and peace, with the Commonwealth Secretariat in London supporting member states in achieving these goals.
- India and the Commonwealth: India is the largest Commonwealth member by population and the 4th largest financial contributor. It has hosted the Commonwealth Summit (1983) and the Commonwealth Games (2010) in New Delhi.
Source:
(MAINS Focus)
(UPSC GS Paper III – “Inclusive Growth; Employment; Labour Reforms”)
Context (Introduction)
With the Four Labour Codes becoming effective on November 21, 2025, India has initiated one of its most significant structural reforms since GST, aiming to modernise labour regulation, extend social protection, formalise employment, and create a competitive, future-ready labour ecosystem.
Main Arguments
- Historical Consolidation: The Codes streamline decades of fragmented labour laws into four functional statutes, as recommended by the Second National Commission on Labour, improving clarity and coherence.
- Demographic Advantage: With 643 million workers and two-thirds of future global entrants expected from India, a simplified labour framework is vital for harnessing demographic potential.
- Worker Protections: Provisions such as universal minimum wages, national floor wage, 48-hour work week, mandatory appointment letters, and stronger OSH norms enhance fairness and safety.
- Expanded Social Security: The Social Security Code extends ESIC coverage nationwide, strengthens EPFO processes, sets up a National Social Security Fund, and includes construction workers.
- Compliance Simplification: Single registration, licence, and return, along with digital inspections and decriminalisation, reduce compliance burdens, benefiting particularly the MSME sector.
Challenges / Criticisms
- Implementation Gaps: Effective rollout requires States to align rules with central guidelines, risking uneven application if coordination falters.
- Informal Sector Coverage: Extending protections to 90% informal workforce remains difficult despite expanded definitions and social security provisions.
- Gig Worker Integration: Operationalising social security for gig and platform workers—expected to reach 2.35 crore by 2029-30—requires administrative preparedness and financing models.
- Industrial Relations Concerns: While flexibility aids industry, trade unions fear dilution of collective bargaining and increased thresholds for layoffs and closures.
- Awareness Deficit: Workers and small enterprises often lack awareness of new rules, hampering effective utilisation of protections and compliance mechanisms.
Way Forward
- State–Centre Coordination: Strengthen cooperative mechanisms to ensure uniformity in thresholds, definitions, and grievance systems across all States.
- Digital Implementation: Build robust digital platforms for ESI, EPF, gig-worker registration, and compliance to improve coverage and transparency.
- Formalisation Drive: Incentivise enterprises—especially MSMEs—to formalise through credit benefits, simplified taxation, and awareness programmes.
- Gender-Inclusive Policies: Expand safe transport, night-shift safeguards, childcare support, and equal remuneration enforcement to raise women’s LFPR beyond 32.8%.
- Continuous Social Dialogue: Foster collaboration among industry, labour unions, and government to ensure balanced industrial relations and minimise disputes.
Conclusion
The Four Labour Codes signal India’s transition toward a simplified, protective, and investment-friendly labour regime suited to a diversifying workforce. Their success, however, hinges on coordinated implementation, digital capacity, and sustained reform momentum to generate employment and enhance global competitiveness.
Mains Question
- The Four Labour Codes mark a major shift toward a simplified, modern labour framework. Critically examine (250 words, 15 marks)
Source: The Hindu
(UPSC GS Paper II – “International Groupings; Global Governance; India and Major Powers”)
Context
The absence of the U.S., China, and Russia from the 2025 Johannesburg G20 summit signals a deeper erosion of the platform’s authority, highlighting how geopolitical realignments, unilateralism, and shifting power balances are undermining multilateral economic governance.
Main Arguments
- Great-Power Absence: The absence of Trump, Xi, and Putin reduces the G20 to a “middle-power gathering,” diminishing its capacity to influence global economic outcomes.
- Origins of the Platform: The G20’s elevation in 2008 addressed a trans-Atlantic financial crisis, driven by the need to include rising powers like China, India, Saudi Arabia, and Indonesia in crisis response.
- Post-Crisis Drift: After the initial three summits (2008–09), the G20 failed to make meaningful progress on global challenges such as climate change, trade reform, and sustainable development.
- Geopolitical Shocks: Trump’s tariff wars, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, and worsening U.S.–China ties fractured consensus, making joint communiqués impossible since 2022.
- Unilateral U.S. Turn: Trump’s push for a G2 with China and call to readmit Russia to the G8 has relegated the G20 to the sidelines, making plurilateral platforms less attractive.
Challenges / Criticisms
- Erosion of Collective Legitimacy: Without great-power participation, G20 decisions lack weight and global acceptance.
- Middle-Power Limitations: With only middle powers attending Johannesburg, the forum loses its unique ability to bridge major economies and emerging powers.
- Failure to Address Core Issues: Persistent inaction on climate finance, mercantilist trade disruptions, and migration challenges diminishes credibility.
- Fragmented Global Order: Competing blocs (G2, G8, BRICS+) challenge the G20’s role as the premier economic coordination platform.
- India’s Dilemma: India’s enthusiasm for the G20 as a “UN economic security council” substitute weakens as the grouping drifts, complicating India’s multilateral strategy.
Way Forward
- Great-Power Re-engagement: Revive strategic dialogue among the U.S., China, and Russia to restore G20’s centrality in global governance.
- Substantive Agenda Setting: Refocus the G20 on actionable issues — climate finance, supply-chain resilience, global tax reform, and digital trade.
- Institutional Credibility: Strengthen follow-up mechanisms, task forces, and peer review to ensure implementation of commitments.
- Alternative Platforms: Bolster India’s engagement with dynamic forums like the East Asia Summit, which retain major-power participation.
- Reform Multilateral Architecture: Advocate expansion of global governance structures like the UNSC and IMF to reflect contemporary power realities.
Conclusion
The G20 risks becoming a ceremonial forum unless it reclaims its role as the world’s premier economic steering committee through great-power participation and coherent agenda-setting. Without such renewal, middle-power diplomacy alone cannot prevent strategic drift or restore global confidence.
Mains Question
- “The G20 is becoming a middle-power forum without the participation of major powers.” Examine. (250 words, 15 marks)
Source: Indian Express
