Archives
(PRELIMS Focus)
Category: Government Schemes
Context:
- The Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), in collaboration with the ICMR and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, has launched the Maha MedTech Mission to boost India’s medical technology ecosystem.

About Maha MedTech Mission:
- Nature: The Mission for Advancement in High-Impact Areas (MAHA)–MedTech is a national initiative to accelerate innovation, manufacturing, and commercialization of cutting-edge medical technologies in India, enhancing access and affordability in healthcare.
- Launch: It is jointly launched by the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF), the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
- Objective: It aims to reduce India’s dependence on high-cost medical imports, strengthen domestic capacity, and ensure equitable access to affordable and high-quality medical devices and diagnostics aligned with national health priorities such as tuberculosis, cancer, and neonatal care.
- Funding: It provides Rs. 5–25 crore per project (up to ₹50 crore for exceptional cases) for startups, MSMEs, academic, hospital, and industry collaborations.
- Coverage: It covers devices, diagnostics, implants, AI/ML-based tools, robotics, and assistive technologies.
- Enabling Frameworks: It includes Patent Mitra for IP protection, MedTech Mitra for regulatory clearances, and a Clinical Trial Network for validation.
Source:
Category: Environment and Ecology
Context:
- Home minister Amit Shah said that India’s maritime global trade will get a boost with proposed Great Nicobar Island Project.
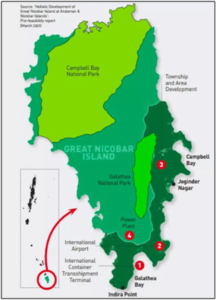
About Great Nicobar Island (GNI) Project:
- Launch: The Great Nicobar Island (GNI) Project was conceived by NITI Aayog and it was launched in 2021.
- Objective: It aims to build an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), a greenfield international airport, a township, and a gas–solar power plant.
- Implementation: It is implemented by Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- In sync with Vision 20147: It aligns with India’s Maritime Vision 2030 and is one of the key projects under the Amrit Kaal Vision 2047.
- Tribal Safeguards: Large-scale development in GNI is permitted only after consultations with the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Directorate of Tribal Welfare and Andaman Adim Janjati VikasSamiti (AAJVS), as mandated by the Jarawa Policy (2004) and Shompen Policy (2015).
- Environmental Safeguards: The Project incorporates strict environmental safeguards, following the Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification, 2006, and based on detailed EIAs and an Environmental Management Plan (EMP).
Source:
Category: History and Culture
Context:
- PM Modi acknowledged 150 years of ‘Vande Mataram’ in Mann ki Baat episode.

About Vande Mataram:
- Meaning: Vande Mataram (meaning “I bow to thee, Mother”) is India’s national song, symbolizing reverence to the motherland and evoking patriotism and unity among citizens.
- Composition: It was composed in Sanskritised Bengali by Bankim Chandra Chattopadhyay in the 1870s and it was first published in his novel Anandamath (1882).
- First public rendition: The song’s first public rendition was by Rabindranath Tagore at the 1896 Congress Session. It became the anthem of India’s freedom struggle, sung in protests and revolutionary gatherings despite being banned by the British.
- Adoption as national song: The Indian National Congress in 1937 adopted its first two stanzas as the National Song, balancing inclusivity and secular appeal.
- Comparison to national anthem: On January 24, 1950, the Constituent Assembly accorded Vande Mataram equal honour to the National Anthem “Jana Gana Mana.”
- Current Status: It is recognized by the Government of India as equal in stature to the National Anthem and its instrumental version is played at the closing of every Parliament session.
Source:
Category: Science and Technology
Context:
- In a breakthrough, scientists have developed a ready-to-use, egg yolk-free solution, CRYODIL with shelf life of 18 months, at refrigeration temperature, for cryopreserving buffalo semen.

About CRYODIL:
- Nature: CRYODIL is a ready-to-use, egg yolk-free semen extender designed to preserve buffalo semen for long durations while maintaining fertility and motility.
- Development: It is developed by scientists at the National Institute of Animal Nutrition and Physiology (NIANP) under the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), Bengaluru.
- Objective: It aims to provide a safe, efficient, and affordable alternative to traditional egg-yolk-based semen extenders and enhance buffalo breeding efficiency in India.
- Long Shelf Life: It has the ability to preserve semen for up to 18 months without contamination or loss of motility.
- No risk of microbial defilement: It eliminates risk of microbial contamination associated with egg yolks and uses purified whey proteins instead of egg yolk, ensuring consistent semen quality.
- Cost-Effective: It is cheaper and easier to produce compared to imported commercial extenders.
Source:
Category: Government Schemes
Context:
- While 19,220 hectares of land under MISTHI scheme has been taken up in Gujarat, only 10 hectares of mangrove plantation has been taken up in West Bengal which accounts for about 42% of mangrove cover in country.

About MISHTI Scheme:
- Nature: The Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI) scheme is a government-led initiative aimed at increasing the mangrove cover along the coastline and on salt pan lands.
- Launch: It was launched after India joined the ‘Mangrove Alliance for Climate’ launched during the 27th Conference of Parties (COP27) to the UNFCCC held in November 2022.
- Objective: It aims to restore mangrove forests by undertaking mangrove reforestation/afforestation measures along the coast of India across various states.
- Nodal Ministry: It comes under the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change.
- Focus areas: It is primarily focused on the Sundarbans delta, Hooghly Estuary in West Bengal and other bay parts of the country, but also includes other wetlands in the country.
- Financial assistance: Under this scheme the government is providing financial assistance to local communities to undertake mangrove plantation activities.
- Leverage of other schemes: It leverages the strengths and provisions of different government schemes and initiatives such as the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS), the Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) Fund and other relevant sources.
- Participatory mechanism: The plantation activities are carried out in a participatory manner, involving local communities and NGOs, to ensure sustainability and community ownership of the initiative.
Source:
(MAINS Focus)
(GS Paper 3: Major Crops – Cropping Patterns in Various Parts of the Country)
Context (Introduction)
India, the world’s largest producer and consumer of pulses, faces a persistent demand–supply gap due to low yields and climatic risks. The Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses (2025–31) aims to enhance productivity, reduce imports, and ensure farmer profitability.
Main Objectives and Features of the Mission
- Launched in 2025 with a financial outlay of ₹11,440 crore, the mission targets self-reliance in pulses by 2030–31.
- Production goal: Increase pulses output by 45%, from 242 lakh MT (2023–24) to 350 lakh MT (2030–31).
- Area expansion: From 275 to 310 lakh ha (+13%); yield increase from 881 to 1130 kg/ha (+28%).
- Focus crops: Tur (Arhar), Urad, and Masoor, covering 34% of total pulses area.
- Key interventions:
- Climate-resilient seed varieties and improved genetics.
- Protein enhancement and yield improvement through R&D.
- Post-harvest management and storage upgrades to reduce losses.
- Remunerative pricing via assured procurement under PM-AASHA.
- Cluster-based approach: Each cluster (≥10 ha) to serve as a model value-chain node.
Current Status and Challenges in Pulses Sector
- Production pattern: Rabi pulses dominate (60% of production).
- Top states: Madhya Pradesh (59.74 LMT), Maharashtra (40 LMT), Rajasthan (33 LMT), Uttar Pradesh (31 LMT).
- Major crops: Gram, Moong, Tur, Urad, Masoor.
- Low productivity: India’s yield (881 kg/ha) is far below Canada (2200 kg/ha) and China (1815 kg/ha) due to rainfed cultivation, fragmented holdings, and poor technology adoption.
- Import dependence: Despite being the largest producer, India imports 2–3 million tonnes annually from Myanmar, Tanzania, Mozambique, Australia, and Canada to meet consumption needs.
- Rising demand: NITI Aayog projects demand at 268 LMT by 2030 and 293 LMT by 2047, highlighting the need for sustained domestic growth.
Significance of the Mission
- Nutritional Security: Pulses are a key protein source for India’s largely vegetarian population.
- Economic Security: Reduces import bills and improves farm incomes via assured procurement.
- Climate Resilience: Encourages crop diversification and optimises use of rice fallow lands in states like Bihar, West Bengal, and Chhattisgarh.
- Regional Balance: Focus on aspirational, LWE, border, and NE districts promotes inclusive agricultural growth.
- Value Chain Development: Integration of production, storage, and market linkages fosters agri-entrepreneurship and reduces post-harvest losses.
Criticisms and Challenges
- Implementation hurdles: Cluster-based approach requires strong institutional coordination across states.
- Procurement inefficiencies: Past experiences with PM-AASHA show delays and coverage gaps.
- Market volatility: Dependence on MSP procurement may distort prices if not matched by demand.
- Technology adoption: Small farmers may find it difficult to access high-yield seeds and mechanisation.
- Climate variability: Pulses are sensitive to erratic monsoons, drought, and pest attacks.
Reforms and Way Forward
- R&D investment: Strengthen ICAR and IIPR-led research for high-yield, drought-tolerant, and pest-resistant varieties.
- Digital integration: Use Aadhaar-enabled procurement and geo-tagged clusters for transparency.
- Private participation: Incentivise agritech startups, FPOs, and cooperatives for storage, processing, and marketing.
- Crop insurance and irrigation: Expand PMFBY and micro-irrigation coverage in pulses regions.
- Nutrition-sensitive agriculture: Link pulses production with Mid-Day Meal and ICDS programmes to stabilise demand and ensure nutritional impact.
Conclusion
The Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses marks a strategic step toward food and nutritional sovereignty. Its success hinges on bridging the yield gap, ensuring market assurance, and promoting technology-driven inclusivity. A resilient pulses ecosystem would not only achieve self-reliance but also strengthen India’s rural economy and environmental sustainability.
Mains Question
- India’s Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses seeks to bridge the demand–supply gap and reduce import dependence. Examine the structural challenges in India’s pulses sector and suggest reforms needed for sustainable self-reliance.(250 words, 15 marks)
Source: The Hindu
(GS Paper 3: Conservation, Environmental Pollution and Degradation, Environmental Impact Assessment)
Context (Introduction)
As the world prepares for COP30 in Belém, Brazil, global climate leadership appears weakened due to Western reluctance and U.S. withdrawal from the Paris Agreement. This vacuum offers India both a challenge and an opportunity to assert climate leadership.
India’s Emerging Role and Strengths
- Steady and Credible Actor: Unlike many developed nations, India’s climate action has remained bipartisan and consistent, with a focus on implementation rather than rhetoric.
- ‘Axis of Good’: Growing partnerships with Europe and Brazil reflect India’s position as a dependable player in areas like climate technology and forest conservation.
- Implementation Focus: India’s credibility rests on fulfilling commitments—achieving its Paris goals ahead of time and aiming for 50% electricity from non-fossil sources by 2030.
- Energy–Emission Decoupling: India’s power sector emissions have plateaued, despite economic growth, signaling a structural shift toward renewable energy dominance.
Major Arguments for India’s Leadership
- Moral and Developmental Imperative: India represents the Global South’s concerns—balancing development needs with climate action, emphasizing equity and common but differentiated responsibilities (CBDR).
- Pragmatic Diplomacy: International cooperation succeeds when driven by strategic and security interests, not charity. India’s approach aligns climate goals with energy security and industrial competitiveness.
- Economic and Technological Leverage: Corporate giants like Adani and Reliance are heavily investing in green hydrogen, renewables, and storage, positioning India as a low-cost clean-tech hub.
- Adaptation as Opportunity: Large-scale schemes like PM-KUSUM and solar-powered cold chains combine mitigation and adaptation, showing scalable models for developing nations.
- Institutional Innovation: India can champion new financing frameworks, integrating multilateral banks, private capital, and philanthropy to mobilize the $1.3 trillion annual climate finance target by 2035.
Challenges and Criticisms
- Finance and Technology Deficit: Domestic funding alone cannot sustain large-scale adaptation. India needs global financial commitments and technology transfer mechanisms.
- Hard-to-Abate Sectors: Industrial emissions from steel and cement remain major hurdles, requiring innovation beyond fuel-switching.
- Fragmented Global Will: Western reluctance and geopolitical divides undermine collective ambition, limiting room for new global frameworks.
- Domestic Implementation Gaps: Despite ambitious policies, project-level execution often faces bureaucratic and capacity-related delays.
- Risk of Overstretch: Overemphasizing leadership could divert focus from internal resilience-building and adaptation to local climate shocks.
Reforms and Strategic Path Ahead
- National Adaptation Plan (NAP): Prioritise sector-wise resilience in agriculture, water, and coastal zones with state-level customisation.
- NDC Upgradation: Include green hydrogen linkage, solar-plus-storage systems, and industry-specific emission reduction pathways.
- Blended Finance Models: Encourage joint public-private funding to leverage concessional capital and risk guarantees.
- Carbon Market Development: Operationalise a robust domestic carbon trading system aligned with international markets.
- Technology Partnerships: Promote India–EU–Brazil trilateral initiatives on forests, carbon sinks, and climate-smart agriculture.
- South–South Cooperation: Lead by example—share India’s solar, adaptation, and digital monitoring models with other developing nations.
Conclusion
India’s leadership in climate action must be rooted in pragmatism, inclusivity, and implementation. Rather than assuming symbolic leadership, India should shape coalitions of credible doers, exemplifying how economic growth, equity, and ecological sustainability can coexist. In a fragmented world, India’s steady hand and scalable models can redefine global climate cooperation.
UPSC Mains Question
- Critically examine India’s efforts till date and potential to emerge as a global leader in climate action. (250 words, 15 marks)
Source: The Hindu
