Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 3
Context: On August 24, NASA announced that Boeing’s Starliner crew capsule, which took astronauts Sunita Williams and Barry Wilmore to the International Space Station (ISS) on its first crewed test flight, was deemed unsafe for their return.
Background: –
- Williams and Wilmore will stay on the ISS until February 2025 and return in a SpaceX crew capsule launching in September 2024. The Starliner meanwhile will undock and return uncrewed.
What is Space?
- Defining Space: Space is easier to identify far from Earth than near it due to the gradual transition from ‘earth-like’ to ‘space-like’ conditions. In aeronautics, space begins at the Karman line, 100 km above sea level.
- Gravity in Space: While gravity diminishes over distance, it never entirely disappears. Astronauts on the ISS experience microgravity, not zero gravity.
- Varying Conditions: Different parts of space expose astronauts to different conditions. For example, the Van Allen radiation belts, located from 640 km to 58,000 km above Earth, contain charged particles trapped by Earth’s magnetic field.
Effects of Space on the Human Body:
- Research Limitations: Although hundreds of astronauts have flown to space, their numbers are too small to fully understand all the effects of spaceflight on the human body. However, broad trends have been observed.
- Bone and Muscle Loss: In microgravity, bones weaken, which might force the body to deposit the ‘excess’ mineral content in the kidneys leading to kidney stones. Because of the body’s weightless experience, the heart is required to do less work and could shrink. Similarly, other parts of the musculature could shed muscle mass and strength.
- Digestive Changes: Food may move more slowly through the gut, leading to weight gain.
- Vision Issues: Around 20% of astronauts, and 70% of those on long missions, develop spaceflight-associated neuro-ocular syndrome (SANS), where fluids build up in the head and affect eyesight.
- Blood Changes: Astronauts lose more red blood cells in space, requiring dietary adjustments to produce more cells.
- Balance and Orientation: The brain works harder in space to maintain balance and orientation due to altered signals from the body.
Causes and Countermeasures:
- Key Causes: Radiation, confined environments, distance from Earth, and microgravity are major factors affecting astronauts’ health.
- Exercise and Routines: Astronauts follow strict exercise regimes and routines to maintain physical health and reduce stress.
- Technological Solutions: Proposals include portable devices to monitor SANS and countermeasures like lower body negative pressure and artificial gravity.
Human Time in Space:
- Increased Duration: The average time an astronaut spends in space has increased from one month in the 1960s to six months in the 2020s.
- Future Challenges: With plans for permanent lunar stations and missions to Mars, new long-duration missions will bring additional safety challenges.
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – POLITY
Context: The issue of granting sanction to prosecute a public servant has resurfaced after the Karnataka Governors approval to open an investigation and to prosecute Chief Minister Siddaramaiah over alleged irregularities in allotting compensatory plots to his wife, following the acquisition of her land by the Mysore Urban Development Authority.
Background: –
- The law relating to a Governor granting sanction for a serving CM’s prosecution is governed not by statutory provisions alone, but also a string of court judgments.
Why is Sanction Required to Prosecute a Public Servant?
- Sanction for prosecuting a public servant has been a mandatory feature of anti-corruption law.
- Protection from Vexatious Prosecution: It is required to protect them from malicious or vexatious prosecutions for actions taken during official duties.
Legal Provisions:
- Section 197, CrPC: No court can take cognisance of a case against a public servant without sanction from an authority competent to remove them. Applies to those currently or formerly public servants. Similar to CrPC, Prevention of Corruption Act, 1947, has provision for sanction.
- Under both the CrPC and the Prevention of Corruption Act (PCA), the State and Central governments had the authority to sanction prosecution of their respective employees.
Latest Provisions on Granting Sanction
- Section 218 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), the procedure code that has replaced the CrPC, retains the sanction provisions.
Prevention of Corruption Act (2018 Amendment):
- Section 17A: Government approval is required even to begin an investigation.
- Section 19: Sanction is a prerequisite for any court to take cognisance of a charge sheet or complaint of corruption.
- Applies to Current and Former Public Servants: The amendment covers those who are and were public servants.
Governor’s Role in Cases Against a Chief Minister
- Authority to Grant Sanction: The Governor, who has the power to dismiss a Chief Minister, is considered the authority to grant sanction for prosecuting a Chief Minister.
- Governor’s Discretion: According to the Supreme Court (A.R. Antulay case), the Governor should act in his discretion and not on the advice of the Council of Ministers when granting sanction to prosecute a Chief Minister.
Court Rulings on Sanction
- Madhya Pradesh Special Police Establishment vs. State of MP and others (2004): The Supreme Court upheld the Governor’s decision to grant sanction against two Ministers despite the Council of Ministers’ decision to the contrary. The Court found the Council’s decision irrational and emphasized that the Governor can act in his discretion when there is apparent bias or irrationality in the Council’s decision.
Source: Hindu
Syllabus
- Prelims – GEOGRAPHY
Context: On a three-day visit to India, Chile’s Foreign Minister held a meeting with External Affairs minister S Jaishankar on Wednesday and discussed bilateral cooperation in trade and investment, agriculture, critical minerals, defence and space among other issues.
Background: Chile is a key partner of India in the Latin American region.
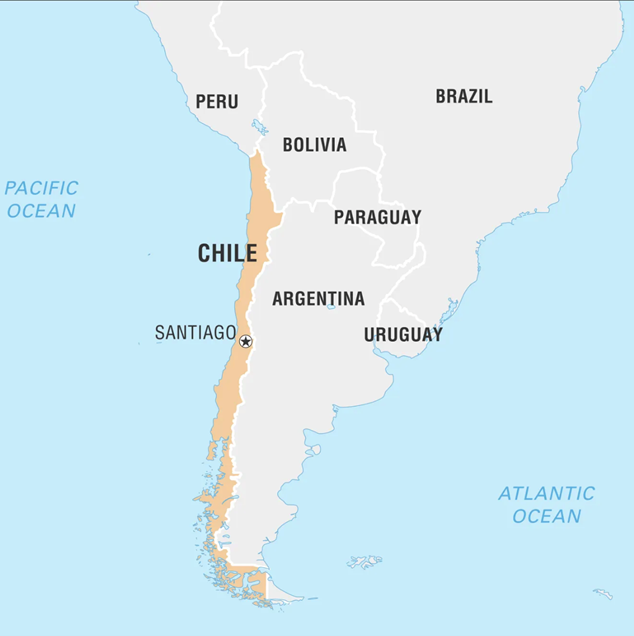
About Chile
- Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in western South America.
- It is the southernmost country in the world and the closest to Antarctica.
- The capital and largest city of Chile is Santiago.
Geography
- Location: Chile stretches over 4,300 km (2,700 miles) from north to south, making it one of the longest countries in the world. It is bordered by Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west.
- Landscape: The country is known for its diverse landscapes, including the Atacama Desert in the north, the fertile Central Valley, and the rugged Andes mountains. It also includes Easter Island and several other Pacific islands.
Climate
- Variety: Due to its length, Chile experiences a wide range of climates, from the arid desert in the north to a Mediterranean climate in the central region, and a temperate climate in the south.
- Natural Events: Chile is prone to natural events such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis due to its location along the Pacific Ring of Fire.
Population and Culture
- Population: As of 2024, Chile has an estimated population of around 20 million people.
- Language: Spanish is the official language.
- Culture: Chilean culture is a blend of indigenous and European influences. The country is also known for its wine production and cuisine.
Government and Economy
- Government: Chile is a multiparty republic with a president as the head of state and government. The current president is Gabriel Boric.
- Economy: Chile has a mixed economy with a strong emphasis on mining, particularly copper, which is a major export. Other important sectors include agriculture, fishing, and manufacturing.
- Natural Beauty: The country is home to stunning natural landscapes, including the Torres del Paine National Park, the Lake District, and the fjords of Patagonia
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – ECONOMY
Context: Canara Bank issued India’s first Additional Tier I perpetual bonds since recent rule changes, attracting strong investor interest with a lower-than-expected coupon of 8.27%.
Background: This marks a revival in demand for these bonds, which had declined due to regulatory challenges. The Securities and Exchange Board of India’s (SEBI) recent valuation tweak, allowing mutual funds to value these bonds based on the call option, has made them more attractive.
About Perpetual Bonds
- Perpetual bonds, also known as perpetual notes or perps, are a type of bond that has no maturity date.
- They are issued by companies or organizations to raise capital, and the issuer is not required to repay the principal amount.
Characteristics:
- No maturity date: Perpetual bonds do not have a fixed maturity date, and the issuer is not obligated to repay the principal.
- Interest payments: Investors receive regular interest payments, usually semi-annually or annually, but the principal amount remains outstanding.
- High credit risk: Perpetual bonds are considered high-risk investments since the issuer may not repay the principal, and the investor may face credit risk.
- Subordinated debt: Perpetual bonds are often subordinated to other debt obligations, meaning they have a lower claim on assets and earnings.
- Callable: Some perpetual bonds may be callable, allowing the issuer to redeem the bonds at a specified price.
Types of perpetual bonds:
- Fixed-Rate Perpetual Bonds: Offer a fixed interest rate throughout their existence.
- Floating-Rate Perpetual Bonds: Interest rates adjust periodically based on a reference rate (e.g., LIBOR).
- Convertible Perpetual Bonds: Can be converted into equity shares after a specified period.
- Hybrid Perpetual Bonds: Combine features of different bond types.
Common Issuers:
- Financial Institutions: Banks and other financial entities use perps for capital management.
- Corporations: Especially those seeking long-term financing.
- Governments: To fund infrastructure projects or manage debt.
- Infrastructure Projects: Funding large-scale developments.
Source: Business Standard
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: Monthly Economic Review of the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) for August acknowledges that the domestic economy remains resilient.
Background: However, it highlighted moderation in certain high-frequency indicators, such as industrial output and core sectors’ performance in June.
Key takeaways
- The National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) is India’s oldest and largest independent, non-profit economic policy research think tank.
- NCAER was established in 1956 in New Delhi.
- Its mission is to provide research-based policy solutions that help understand India’s rapid economic and social transformation as new and complex challenges emerge.
Research Themes:
- National Growth and Macroeconomic Center: Analyzing growth trends and macro policies.
- Human Development and Data Innovation: Focusing on education, health, and data-driven insights.
- Investor Education and Protection Fund Chair Unit: Enhancing financial literacy and investor protection.
- Trade, Technology, and Skills: Addressing trade dynamics and skill development.
- Agriculture and Rural Development: Supporting sustainable rural growth.
- Centre for Health Policy and Systems: Advancing health policy research.
NCAER’s contributions to Indian Economy:
- Rich Data and Evidence:
- NCAER gathers evidence through scientific surveys, panel surveys, and data collection.
- This rich data serves as a foundation for informed policy decisions, enabling evidence-based reforms and targeted interventions.
- Economic Analysis and Modelling:
- NCAER estimates demand, supply, income, investment, savings, and conducts macroeconomic modelling and forecasting.
- These analyses provide insights into economic trends, growth drivers, and potential policy impacts.
- Policy Research and Forums:
- NCAER hosts unique platforms for discussions, bringing together policymakers, industry leaders, and experts.
- These forums facilitate dialogue on critical economic issues, fostering evidence-based decision-making.
Source: Money Control
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains : POLITY
Context: The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D) recently celebrated its 54th Foundation Day at its headquarters in New Delhi.
Background: BPR&D plays a pivotal role in shaping policing practices and law enforcement strategies in India.
About Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D)
- The Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D) is a premier research and development organization in the field of policing and law enforcement in India.
- It was established in 1970 under the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India.
- It was established with a mandate to:
- Identify the needs and problems of the police in the country.
- Undertake research projects and studies, and suggest modalities to overcome problems and challenges and meet the needs and requirements of the police.
- Objectives:
- To promote excellence in policing and law enforcement
- To identify areas of improvement and develop strategies for modernization
- To conduct research and studies on policing and related issues
- To develop and disseminate best practices and standards
- To provide training and capacity-building programs for police personnel
- Functions:
- Research and studies on policing, crime, and law enforcement
- Development of training programs and materials
- Modernization of police forces and equipment
- International cooperation and collaboration
- Publication of journals, reports, and other resources
- Key areas of focus:
- Police reforms and modernization
- Crime prevention and control
- Cybercrime and digital forensics
- Counter-terrorism and internal security
- Human rights and police accountability
Source: PIB
Practice MCQs
Q1.) With reference to the Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D), consider the following statements:
- The Bureau of Police Research and Development is a premier research and development organization in the field of policing and law enforcement in India.
- It was established under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q2.) With reference to the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER), consider the following statements?
- The National Council of Applied Economic Research is a statutory body.
- Its mission is to provide research-based policy solutions that help understand India’s rapid economic and social transformation
- NCAER estimates demand, supply, income, investment, savings, and conducts macroeconomic modelling and forecasting.
Which of the statements given above is/are not correct?
- 1 only
- 1 and 2 only
- 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q3.) With reference to the Perpetual bonds, consider the following statements:
- Perpetual bonds are a type of bond that has no maturity date.
- They are issued by companies or organizations to raise capital.
- The issuers of perpetual bond are not required to repay the principal amount.
How many of the above given statements are correct?
- Only one
- Only two
- All three
- None
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 30th August 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 29th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – d
