Archives
(PRELIMS Focus)
Category: Environment and Ecology
Context:
- Amazonian stingless bees have become the first insect in the world to be granted legal rights, after two municipalities Satipo and Nauta in Peru passed an ordinance recently.

About Stingless Bees:
- Nature: Stingless Bees are a class of bees which either do not have stingers or have stingers that cannot cause much pain.
- Genera: Common genera of stingless bees include Austroplebeia, Melipona, and Tetragonula
- Possess small stingers: They do possess stingers, but they are too small to be useful in defense. Instead of stinging, stingless bees use their mandibles to bite their attackers.
- Uniqueness: They are among the planet’s oldest pollinators, with a remarkable concentration of species in the Amazon rainforest.
- Global spread: They are found in tropical regions across the world, and about half of the 500 known species live in the Amazon. Africa, Australia, Southeast Asia, and parts of the Americas are the main areas where the stingless bee is found.
- Distribution in India: In India, these bees are reported primarily from the northeastern, eastern, and southern Indian States.
- Significance: Stingless bees can be used for pollination without fear of being stung. They are known for their popular medicinal honey and pollination potential.
- Keystone species: They pollinate over 80% of Amazonian flora and are vital for crops like coffee, cocoa, avocados, and blueberries.
- Medicinal Honey: Their honey, often called “pot honey,” is prized for high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. It is more liquid and has a tangy/sour taste compared to standard honey.
- Threats: Deforestation has reduced nesting sites, while pesticide use, climate change and competition from invasive honeybees have further weakened populations.
Source:
Category: Defence and Security
Context:
- The National Investigation Agency (NIA) said that a series of milestone achievements marked the year 2025, key among them being an over 92% conviction rate.

About National Investigation Agency (NIA):
- Nature: The National Investigation Agency (NIA) is India’s premier federal counter-terrorism agency.
- Nodal ministry: It functions under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Formation: Established in 2009 under the National Investigation Agency Act, 2008, it was created in the aftermath of the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks to handle terror-related crimes with a unified national approach.
- Legal status: It is a statutory body empowered to investigate and prosecute “Scheduled Offences” affecting the sovereignty and integrity of India.
- Suo-motu powers: Unlike the CBI, the NIA can take up investigations across any state without state government permission if directed by the Central Government.
- Special courts: Trials for NIA cases are conducted in specially designated NIA Special Courts to ensure speedy justice.
- Jurisdiction: The NIA investigates crimes listed in the Schedule of the NIA Act, including:
- Terrorism and terror financing (UAPA).
- Offences against atomic and nuclear facilities.
- Hijacking of aircraft and ships
- Amendment: NIA (Amendment) Act, 2019 significantly strengthened the agency by:
- Widening Scope: Adding new categories of crime (human trafficking, cyber-terrorism, etc.).
- Extending Reach: Empowering the NIA to probe terror attacks targeting Indians abroad.
- Special Courts: Allowing the Central and State Governments to designate Sessions Courts as Special Courts for NIA trials.
Source:
Context: Geography
Context:
- Recently, a powerful “bomb cyclone” barreled across the northern United States, triggering severe winter weather in the Midwest and the East Coast.
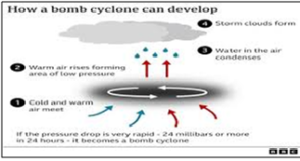
About Bomb Cyclone:
- Nature: It is a large midlatitude storm resulting from explosive cyclogenesis (or, informally, bombogenesis), a type of accelerated extratropical cyclone development.
- Classification: To be classified as a bomb cyclone, the central atmospheric pressure must drop by at least 24 millibars within 24 hours.
- Structure: In structure, a bomb cyclone is indistinguishable from any other intense midlatitude storm.
- Differentiation: The centre of the storm is a low-pressure cell (or cyclone) that draws winds near the surface inward. However, a bomb cyclone is set apart by its rapid rate of intensification.
- Associated phenomena: Bomb cyclones are often associated with atmospheric rivers and typically form in winter when cold and warm air masses collide.
- Type of precipitation: The precipitation associated with a bomb cyclone is intense, ranging from heavy downpours to strong thunderstorms to blizzards and heavy snowfalls, along with strong winds.
- Active regions: The four most active regions where extra-tropical explosive cyclogenesis occurs in the world are the Northwest Pacific, the North Atlantic, the Southwest Pacific, and the South Atlantic.
Source:
Category: Polity and Governance
Context:
- According to a gazette notification issued by the Bureau of Energy Efficiency, energy-efficiency star labelling became mandatory for a range of appliances, from January 1.

About Bureau of Energy Efficiency:
-
- Establishment: It was established in 2002 under the provisions of the Energy Conservation Act, 2001.
- Objective: The primary objective of Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) is to reduce energy intensity in the Indian economy.
- Nodal ministry: It comes under Ministry of Power.
- International cooperation: India, through BEE, is a member of the International Energy Efficiency Hub, which succeeded the IPEEC in 2020 to foster global collaboration on energy efficiency.
- Annual recognition: National Energy Conservation Day is observed every December 14th, where the National Energy Conservation Awards (NECA) are presented to industries and institutions for exemplary energy savings.
- Key functions:
-
-
- Standards and Labelling (S&L): Launched in 2006, this program provides consumers with an “informed choice” via Star Ratings (1 to 5 stars) for appliances. As of early 2026, the program has expanded to include a wider range of mandatory appliances to further reduce carbon emissions.
- Energy Conservation Building Code (ECBC): Sets minimum energy standards for new commercial buildings. A specialized code for residential buildings, Eco Niwas Samhita, was also introduced.
- Certification: BEE is the nodal agency for certifying Energy Managers and Energy Auditors.
- Designated Consumers: Prescribes energy consumption norms for energy-intensive industries.
-
- Major programs:
-
- Perform, Achieve, and Trade (PAT) Scheme: A market-based mechanism where energy-intensive industries receive energy-saving targets. Those exceeding targets earn Energy Saving Certificates (ESCerts), which can be traded.
- State Energy Efficiency Index (SEEI): Released annually to track state-level progress. The SEEI 2024 (released in late 2025) categorized states like Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh as “Front Runners”.
- ADEETIE Scheme: Launched for the FY 2025-26 to 2027-28 period, this flagship initiative provides financial and technical assistance to MSMEs to adopt advanced energy-efficient technologies.
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency (NMEEE): One of the eight missions under the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC).
Source:
Category: Science and Technology
Context:
- Recently BSNL announced the nationwide rollout of Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi), also known as Wi-Fi Calling.
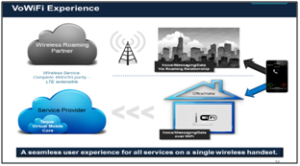
About Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi) Services:
-
- Nature: Voice over WiFi (VoWiFi) is a technology that allows users to make and receive voice calls and SMS over a Wi-Fi network instead of a mobile tower.
- Operation: It works using IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) and uses the same mobile number and phone dialer, without any third-party app.
- Key features:
-
-
- IMS-based service: Uses IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) to manage calls, enabling smooth handover between Wi-Fi and cellular networks.
- Existing mobile number and dialer: Users make and receive calls using their regular phone number and default dialer, without installing any additional apps.
- No additional charges: Wi-Fi calls are treated like normal voice calls and are provided free of extra cost to subscribers.
- Indoor and low-signal support: Ensures reliable connectivity in basements, offices, high-rise buildings, and remote areas with poor mobile coverage.
- Wide smartphone compatibility: Supported on most modern VoWiFi-enabled smartphones, requiring only a settings toggle.
- Network congestion reduction: Offloads voice traffic from mobile towers to Wi-Fi, improving overall network efficiency and call quality.
-
- Mechanism:
-
-
- The smartphone uses an available home, office, or public Wi-Fi network to connect to the telecom network, instead of relying on a nearby mobile tower.
- The user is authenticated through the SIM card, ensuring the same level of security and identity verification as regular mobile calls.
- Voice is converted into digital data packets and transmitted over the internet, allowing calls even where mobile signals cannot reach.
- When Wi-Fi becomes weak or unavailable, the call automatically shifts to the mobile network (VoLTE) without interruption or call drop.
-
- Advantages:
-
- Reliable calling without mobile signal: Enables uninterrupted communication in signal-dark zones, particularly useful in rural and indoor environments.
- Better call quality: Provides clearer and more stable voice calls compared to weak or fluctuating cellular networks.
- Enhanced security: Maintains strong protection using SIM-based encryption and authentication, similar to VoLTE services.
Source:
(MAINS Focus)
(GS Paper III – Environment, Climate Change, Urbanisation)
Context (Introduction)
Urban waste management has moved from a municipal service issue to a climate, health, and governance challenge. At COP30 (2025), waste—particularly organic waste and methane emissions—was recognised as central to climate action, with global consensus on circularity as a pathway to inclusive growth and public health. India’s Mission LiFE and Swachh Bharat Mission reflect this thinking, but recent urban tragedies highlight persistent gaps between intent and outcomes.
Solid Waste Management in Indian Cities: Current Status
- Rising waste burden: Indian cities generate nearly 62 million tonnes of municipal solid waste annually, projected to rise to 165 million tonnes by 2030 and 436 million tonnes by 2050, as urban population expands to over 800 million.
- Climate implications: Urban waste is expected to emit over 41 million tonnes of greenhouse gases by 2030, largely methane from untreated organic waste, making waste management a climate imperative.
- Partial success under SBM: Under SBM–Urban 2.0, around 1,100 cities have been declared dumpsite-free, but most are not fully garbage-free or circular.
- Waste composition reality: Over 50% of municipal waste is organic, suitable for composting or bio-methanation, while over one-third is dry waste, including plastics and recyclables.
- Construction-driven stress: Rapid urban construction generates around 12 million tonnes of construction and demolition (C&D) waste annually, much of it dumped illegally.
- Water–waste linkage: Poor solid waste management directly contaminates water sources, aggravating urban water stress and public health risks.
Key Challenges in Solid Waste Management
- Weak segregation at source: Despite policy mandates, household-level segregation remains inconsistent, breaking the entire recycling and recovery chain.
- Plastic waste bottleneck: Plastics pose the toughest challenge due to low recyclability, incomplete Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) coverage, and weak market demand for recycled plastic.
- C&D waste mismanagement: Despite the C&D Waste Management Rules, 2016, and upcoming Environment (C&D) Waste Management Rules, 2025, enforcement remains weak and accountability diffused.
- Curtailment of circularity markets: Refuse-derived fuel (RDF), recycled aggregates, and compost face quality perception issues, weak procurement mandates, and poor price discovery.
- Municipal capacity constraints: Urban Local Bodies face chronic shortages of finance, skilled manpower, testing infrastructure, and monitoring systems.
- Fragmented governance: Waste management involves multiple agencies, leading to coordination failures and regulatory gaps.
Government Efforts and Policy Framework
- Swachh Bharat Mission–Urban 2.0: Focus on Garbage Free Cities, dumpsite remediation, source segregation, and scientific waste processing.
- Circular economy shift: Policy emphasis on moving from linear “collect–dump” systems to reduce–reuse–recycle–recover, recognising waste as a resource.
- Bio-energy initiatives: Expansion of Compressed Biogas (CBG) plants converting wet waste into green fuel and power, supporting both energy transition and waste reduction.
- Plastic & EPR framework: Gradual strengthening of producer responsibility, though coverage remains uneven across dry waste categories.
- Water and wastewater reuse: Integration with AMRUT and SBM to promote recycling and reuse of wastewater for agriculture, industry, and horticulture, crucial for urban water security.
- Global and regional leadership: India-led Cities Coalition for Circularity (C-3) to promote best practices and knowledge sharing across Asia-Pacific cities.
Way Forward: Making Indian Cities Truly Circular
- Universal source segregation: Combine behavioural change campaigns with strict enforcement, incentives, and penalties for households and bulk waste generators.
- Scale up processing capacity: Expand composting, biomethanation, recycling, RDF, and C&D recycling plants in line with projected waste growth.
- Strengthen EPR and markets: Extend EPR to all dry waste streams and mandate procurement of recycled materials in public works to stabilise demand.
- Integrate urban regulations: Align building approvals, construction permits, and municipal laws with C&D waste tracking and accountability.
- Empower municipalities: Enhance financial autonomy, technical capacity, and inter-departmental coordination of Urban Local Bodies.
- Citizen-centric circularity: Make waste reduction and recycling economically rewarding through buy-back systems, user-fee rationalisation, and visible local benefits.
Conclusion
India’s urban future will be shaped by how decisively its cities transition from waste accumulation to resource recovery and circularity. Solid waste management is no longer about cleanliness alone—it is central to climate mitigation, water security, public health, and urban governance. With sustained policy enforcement, empowered municipalities, and active citizen participation, Indian cities can move away from landfills and become engines of sustainable and inclusive growth.
Mains Question
- “Solid waste management has emerged as a critical pillar of India’s urban sustainability and climate strategy.”
Discuss the challenges faced by Indian cities in adopting a circular waste economy and evaluate the effectiveness of government initiatives in this regard.(250 words,15 marks)
Source: The Hindu
(GS Paper II – Indian Constitution: Equality, Reservation, Judiciary)
Context (Introduction)
A recent Supreme Court ruling clarified that the general (open) category is not reserved for any social group, but is a merit-based pool open to all candidates. The judgment arose from exclusion of meritorious reserved-category candidates during recruitment shortlisting, raising concerns that affirmative action was being misapplied to create new forms of exclusion, contrary to Articles 14 and 16.
Reservation in India: Constitutional Basis and Rationale
- Article 16(1): Guarantees equality of opportunity in public employment for all citizens.
- Article 16(4): Permits reservation for backward classes inadequately represented in services—an exception, not the rule.
- Article 14: Prohibits arbitrary classification; reservation must further substantive equality, not reverse discrimination.
- Rationale: Address historical exclusion, structural disadvantage, and lack of representation—not to penalise merit.
- Nature of reservation: Reservation applies only to earmarked posts, not to open competition posts.
Judicial Evolution on Merit and Reservation
- Supreme Court of India – Indra Sawhney (1992): Open category posts are available to all; reserved candidates qualifying on merit cannot be excluded.
- Saurav Yadav (2021): Reaffirmed that meritorious reserved candidates must be counted in the open category, not forced into reserved slots.
- Core principle: Reservation cannot be applied in a manner that undermines merit-based equality under Article 16(1).
The Latest Judgment: Key Constitutional Clarifications
- Open category is not a quota:
- The Court held that treating the general category as exclusive to non-reserved candidates converts it into “communal reservation,” violating Articles 14 and 16.
- Merit over social identity:
- A reserved-category candidate crossing the general cut-off does so on merit, not by availing reservation.
- No “double benefit”:
- Reservation is availed only when relaxations (age, marks, standards) are used. Mere social identity does not amount to benefit.
- Shortlisting stage matters:
- Since written exam marks formed a substantial part of final selection, exclusion at this stage caused irreversible harm.
- Merit-induced shift, not migration:
- The Court clarified this is not “migration” at a later stage, but competing in the open category from the outset.
- Corrective directions:
- First prepare a common merit list, then fill reserved posts from remaining candidates.
- Protection against disadvantage:
- A meritorious reserved candidate cannot be forced into an open slot if it results in losing a better post available under reservation.
Significance of the Ruling
- Reinforces that reservation is a tool of inclusion, not exclusion.
- Prevents penalisation of merit among disadvantaged groups.
- Ensures consistency between affirmative action and equality of opportunity.
- Provides clarity to recruitment agencies on constitutionally compliant selection processes.
Way Forward
- Standardised recruitment guidelines: Mandate merit-first preparation of open category lists across all public recruitments.
- Administrative training: Sensitise recruiting authorities on constitutional limits of reservation.
- Judicial consistency: Apply the principle uniformly across multi-stage examinations.
- Policy clarity: Avoid mechanical category-wise segregation at intermediate stages.
- Balance equality goals: Ensure reservation continues to correct disadvantage without creating new inequities.
Conclusion
The judgment restores the constitutional balance between merit and social justice, reaffirming that equality of opportunity remains the rule and reservation its carefully limited exception. By clarifying that the general category is open to all, the Court ensures that affirmative action remains a means of empowerment, not a mechanism of unintended exclusion.
UPSC Mains Practice Question
“Reservation in India is a means to achieve substantive equality, not a departure from merit.”
In light of recent Supreme Court judgments, critically examine how the constitutional balance between merit and reservation is maintained. (250 words)
