Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims: CURRENT EVENT
Context: Namibia plans to cull hundreds of wild animals, including dozens of elephants and hippopotamuses, to provide meat for its 1.4 million people who are reeling under the worst drought in a century.
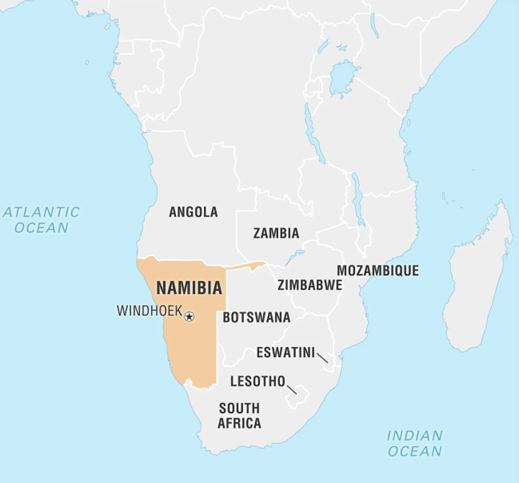
Background: –
- Namibia, located in drought-prone southern Africa, frequently experiences severe droughts, having declared national emergencies in 2013, 2016, and 2019.
Key takeaways
- The drought, which began in Botswana in October 2023, has spread and intensified across Angola, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and Namibia, affecting most of southern Africa.
- The severity of the situation is largely attributed to El Niño. Numerous studies have shown that rising global temperatures due to climate change are making extreme weather events, such as droughts and floods, more frequent and intense.
- Food availability in Namibia, typically low from July through September, has been further strained by the drought. Staple crops like maize have withered, large numbers of livestock have perished, and nearly 84% of the country’s food reserves are depleted.
- As food stocks dwindle, prices have soared, severely limiting access to food for many people.
- The Namibian government is considering culling wild animals, not just for meat, but to prevent them from migrating in search of food and water, which could lead to conflicts with humans.
- Namibia is home to a significant number of wild animals, including approximately 24,000 elephants, one of the largest populations in the world.
About Namibia: Namibia is located on the southwestern coast of Africa.
Geography
- Bordered by Angola to the north, Zambia to the northeast, Botswana to the east, South Africa to the southeast and south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the west.
- Known for its diverse landscapes, including the Namib Desert along the coast, the Kalahari Desert in the east, and savannas and mountains.
- Climate: Mostly arid to semi-arid, with the coastal areas being cooler due to the Benguela Current.
Additional Information
- Colonial Era: Formerly known as South West Africa, it was colonized by Germany in the late 19th century and later administered by South Africa after World War .
- Independence: Gained independence from South Africa on March 21, 1990.
- Government Type: Republic with a semi-presidential system.
- Capital: Windhoek.
- Main Industries: Mining (diamonds, uranium, gold), agriculture, and tourism2.
Source: Down To Earth
Syllabus
- Prelims : Polity
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi set out Tuesday on a three-day visit to Brunei Darussalam and Singapore in a bid to boost ties and celebrate diplomatic milestones. The Prime Minister’s visit aims to strengthen these relationships and expand India’s engagement with the broader ASEAN region.
Background: –
- ASEAN is central to India’s Act East policy, which focuses on the extended neighbourhood in the Asia-Pacific region.
About ASEAN
- The Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) is a regional intergovernmental organization comprising ten Southeast Asian countries.
Formation and Purpose
- Established: August 8, 1967, with the signing of the Bangkok Declaration by Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, and Thailand.
- Purpose: To promote economic growth, social progress, cultural development, regional peace, and stability.
- Its official motto is “One Vision, One Identity, One Community”.
Member States
- ASEAN currently has ten member states: Brunei Darussalam, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, Vietnam.
Structure and Leadership
- Secretariat: Located in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- Chairmanship: Rotates annually among member states. Laos holds the chairmanship for 2024.
Key Pillars
- ASEAN operates through three main pillars:
- Political-Security Community: Aims to ensure regional peace and stability.
- Economic Community: Focuses on creating a single market and production base, enhancing economic integration.
- Socio-Cultural Community: Promotes social development and cultural exchange.
- Economic Impact
- Population: Over 683 million people.
- GDP: Combined GDP (PPP) of approximately $12 trillion in 2024.
- Trade: ASEAN is a significant global trading bloc, engaging in numerous free trade agreements with countries and regions worldwide.
- Initiatives and Partnerships
- ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA): Established to increase ASEAN’s competitive edge as a production base in the global market.
- ASEAN Plus Three: Includes China, Japan, and South Korea, focusing on East Asian cooperation.
- ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF): A platform for security dialogue in the Asia-Pacific region.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims: POLITY
Context: The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) recently approved an important proposal to procure 240 aero-engines for the Su-30 MKI aircraft of the Indian Air Force (IAF) at a cost of over Rs 26,000 crore.
Background:
- The engines will be sourced from Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), furthering the nation’s self-reliance in military technology.
About Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS)
- The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) is led by the Prime Minister and includes the Ministers for Finance, Defence, Home Affairs, and External Affairs.
- The CCS is tasked with making major decisions regarding national security, significant appointments in security bodies, and defence expenditure.
- In addition to defence matters, the CCS addresses issues related to law and order, internal security, and security-related foreign policy matters. It also considers matters concerning atomic energy.
About Cabinet committees
- After the Union Cabinet is sworn in and ministerial portfolios are allocated, the Prime Minister forms various high-profile Cabinet committees with selected Cabinet members, assigning specific functions to each.
- The Prime Minister has the authority to create, modify, or dissolve committees and adjust their functions. Membership typically ranges from three to eight members, predominantly Cabinet ministers, though non-Cabinet ministers or special invitees may also be included.
- When the Prime Minister is a member of a committee, he serves as the committee’s head. These committees resolve issues, propose solutions for Cabinet consideration, and make decisions on assigned matters, with the Cabinet having the power to review these decisions.
- During the Manmohan Singh government, there were 12 Cabinet committees, in addition to numerous Groups of Ministers (GoMs) and Empowered Groups of Ministers (EGoMs).
- Currently, there are eight Cabinet committees:
- Appointments Committee of the Cabinet
- Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs
- Cabinet Committee on Political Affairs
- Cabinet Committee on Investment and Growth
- Cabinet Committee on Security
- Cabinet Committee on Parliamentary Affairs
- Cabinet Committee on Employment & Skill Development
- Cabinet Committee on Accommodation
- The Modi government introduced the Cabinet Committee on Investment and the Cabinet Committee on Employment & Skill Development in 2019. All committees, except the Cabinet Committee on Accommodation and the Cabinet Committee on Parliamentary Affairs, are headed by the Prime Minister.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains: POLITY
Context: Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs has granted “in-principle approval” for the creation of five new districts in Ladakh.
Background: –
- This will increase the total number of districts in the Union Territory from two to seven. The move is aimed at improving governance and development in the region.
About Ladakh
- Ladakh is a Union Territory in northern India, situated between the Karakoram Mountain range in the north and the main Himalayas to the south.
- It is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region to the east, the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh to the south, the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir to the west, and the southwest corner of Xinjiang across the Karakoram Pass in the far north.
New Districts in Ladakh:
- The Ministry of Home Affairs has granted “in-principle approval” for the creation of five new districts in Ladakh. The new districts are: Zanskar, Drass, Sham, Nubra and Changthang.
Who has the Authority to Declare New Districts?
- The authority to declare new districts in a state or Union Territory in India lies with the respective state government or the central government, depending on the region:
- States: The state government has the authority to create new districts. This is typically done through a notification in the official gazette after approval from the state legislature.
- Union Territories: The central government, specifically the Ministry of Home Affairs, has the authority to create new districts in Union Territories. This is done through an official notification after considering various administrative and logistical factors.
How will the creation of new districts impact the local governance and administration?
- Improved Accessibility
- Closer Administrative Services: With more districts, administrative offices and services will be closer to the residents, reducing travel time and making it easier for people to access government services.
- Better Implementation of Schemes: Localized administration can ensure more effective implementation of government schemes and programs, tailored to the specific needs of each district.
- Enhanced Governance
- Focused Development: Each district can focus on its unique developmental needs, leading to more balanced and inclusive growth across the Union Territory.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Resources can be allocated more efficiently, addressing the specific challenges and opportunities of each district.
- Increased Representation
- Local Representation: More districts mean better representation of local communities in governance, ensuring that their voices and concerns are heard and addressed.
- Community Engagement: Smaller administrative units can foster greater community engagement and participation in local governance.
- Economic and Social Benefits
- Economic Growth: Improved infrastructure and services can stimulate local economies, creating jobs and boosting economic activities.
- Social Development: Enhanced access to education, healthcare, and other essential services can improve the overall quality of life for residents.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims : CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Indian Army recently launched the first phase of Project NAMAN.
Background: –
- In the first phase, 14 Common Service Centres (CSCs) have been established in key locations across India, including New Delhi, Jalandhar, Leh, Dehradun, Lucknow, Jodhpur, Bengdubi, Gorakhpur, Jhansi, Secunderabad, Saugor, Guntur, Ahmedabad, and Bangalore.
About Project NAMAN
- Project NAMAN is an initiative under the Ministry of Defence.
- It aimed at providing dedicated support and services to Defence Pensioners, Veterans, and their families.
- It focuses on implementing the SPARSH (System for Pension Administration Raksha) digital pension system to streamline pension-related processes.
Components:
- SPARSH Digital Pension System: Streamlines pension-related processes for Defence Pensioners.
- Common Service Centres (CSCs): Established at key locations to offer various services.
- Tripartite MoU: Between the Indian Army’s Directorate of Indian Army Veterans, CSC e-Governance India Limited, and HDFC Bank Limited.
- Village Level Entrepreneurs (VLEs): Manage the CSCs, selected from veterans or Next of Kin (NOKs).
Purpose:
- Streamline Pension Processes: Implement the SPARSH system to make pension-related processes more efficient and accessible.
- Provide Accessible Facilitation Points: Establish CSCs to offer SPARSH-enabled pension services, Government to Citizen (G2C) services, and Business to Consumer (B2C) services.
- Support Veterans and Families: Offer essential care and support to veterans, pensioners, war widows, and NOKs.
Benefits:
- Convenience: All services are available at a single, convenient location.
- Financial Assistance: HDFC Bank provides a monthly grant of ₹20,000 for the first 12 months to VLEs to help stabilize and sustain the centres.
- Comprehensive Training: VLEs receive training to deliver the required services effectively.
- Community Support: Extends services to the entire resident population of military stations and surrounding localities.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims: CURRENT EVENT
Context: The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) recently endorsed the Australia-funded Pacific Policing Initiative (PPI).
Background: –
- The PPI represents a significant investment in the security and stability of the Pacific region, reflecting Australia’s commitment to supporting its Pacific neighbours.
About Pacific Policing Initiative (PPI)
- The Pacific Policing Initiative (PPI) is a comprehensive program funded by Australia.
- It aimed at enhancing policing capabilities across the Pacific region.
- This initiative, with a budget of approximately AU$400 million over five years, aims to reshape policing across the Pacific region.
The PPI focuses on three main areas:
- Regional Training Centres of Excellence: These will be located throughout the Pacific to enhance police training.
- Pacific Police Support Group: A multinational force that can respond to regional emergencies, such as natural disasters and transnational crime.
- Central Coordination Hub: Based in Brisbane, Australia, this hub will support the regional centres and the Pacific Police Support Group.
Objectives:
- Strengthen Regional Security: By enhancing the capabilities of local police forces, the PPI aims to improve overall security in the Pacific region.
- Promote Cooperation: The initiative encourages collaboration among Pacific nations, fostering a united approach to common security challenges.
- Build Resilience: Through training and support, the PPI seeks to build resilience against various threats, including natural disasters, transnational crime, and geopolitical tensions.
Pacific Islands Forum (PIF)
- The Pacific Islands Forum (PIF) is an inter-governmental organization that aims to enhance cooperation among countries and territories in the Pacific region.
- It was established in 1971 (originally as the South Pacific Forum, renamed in 1999 to be more inclusive of all Pacific nations).
- PIF members include 18 countries and territories, including Australia, New Zealand, Fiji, Papua New Guinea, and several smaller island nations.
- PIF Headquarters is in Suva, Fiji.
Source: News on AIR
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Pacific Policing Initiative (PPI), recently seen in news is funded by
- USA
- UN
- IMF
- Australia
Q2.) With reference to the Project NAMAN, consider the following statements:
- Project NAMAN is an initiative under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- It aimed at providing dedicated support and services to Defence Pensioners, Veterans, and their families.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Q3.) Who has the Authority to declare new districts in a state of India?
- State government
- Governor of the state
- Central government
- President of India
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 3rd September 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 2nd September – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – b
Q.2) – b
Q.3) – d
