Archives
(PRELIMS & MAINS Focus)
Syllabus
- Prelims & Mains – GEOGRAPHY
Context: Intense wildfires in the United States and Canada have sparked the formation of pyrocumulonimbus clouds.
Background:-
- The occurrence of these clouds has increased in recent years. Typically, about 102 pyrocumulonimbus clouds were recorded globally in a year, with 50 of them in Canada. However, during last year’s extreme wildfire season, Canada alone witnessed 140 pyrocumulonimbus clouds.
About pyrocumulonimbus clouds
- The cumulonimbus flammagenitus cloud (CbFg), also known as the pyrocumulonimbus cloud, is a type of cumulonimbus cloud that forms above a source of heat, such as a wildfire, nuclear explosion, or volcanic eruption.
Formation of Pyrocumulonimbus Clouds:
- Not all wildfires produce pyrocumulonimbus clouds; they form during extremely hot fires or volcanic eruptions. For example, the Australian bushfires of 2019-2020, with temperatures exceeding 800°C, led to their formation.
- Process: Intense heat from fires causes surrounding air to rise, carrying water vapour, smoke, and ash. As this air ascends and cools, water vapour condenses on ash particles, forming pyrocumulus or “fire clouds.” But if there is sufficient water vapour available and the upward movement of hot air intensifies, pyrocumulus clouds can evolve into a pyrocumulonimbus cloud, reaching up to 50,000 feet and generating their own thunderstorms.
- Impacts: While they can produce lightning, they yield little rain, potentially igniting new fires far from the original source. Additionally, they can induce strong winds, accelerating and complicating wildfire spread.
Increasing Frequency:
- The exact cause of the rise in pyrocumulonimbus events is not fully understood, as research in this area is emerging. However, climate change, leading to higher global temperatures and more intense wildfires, is believed to contribute to their increased occurrence.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – ENVIRONMENT
Context: Chhattisgarh recently cleared a long-pending proposal to notify a new tiger reserve – the third largest in the country. This comes amid the dwindling tiger population in the state.
Background:
- Chhattisgarh’s tiger population fell from 46 in 2014 to 17 in 2022, according to a National Tiger Conservation Authority report.
About Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve
- The Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve, which integrates an existing national park with a wildlife sanctuary, is Chhattisgarh’s fourth reserve for tigers.
- The decision to establish the reserve comes after Chhattisgarh High Court, while hearing a PIL on July 15, granted four weeks to the state government to clear its stand on declaring that area a tiger reserve.
- In 2019, wildlife activist filed a PIL in the high court highlighting the decline in the big cat population in the state. The PIL accused the government of inaction in notifying and establishing the reserve, despite approval from the National Tiger Conservation Authority and the Union Environment Ministry since 2012.
- On 7th August, the state cabinet merged the regions of the Guru Ghasidas National Park and the Tamor Pingla Sanctuary, located in the districts of Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur, Koriya, Surajpur and Balrampur, to create the new reserve.
- Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve will be the third largest tiger reserve in the country. It spans 2,829 square kilometres across four northern districts of Chhattisgarh.
- Andhra Pradesh’s Nagarjunasagar Srisailam Tiger Reserve is the country’s largest tiger reserve, covering 3,296.31 sq km. Manas Tiger Reserve in Assam is the second largest with an area of 2,837.1 sq km.
Source: Indian Express
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: Union Minister of State for Textiles, Shri Pabitra Margherita in a written reply to Lok Sabha mentioned about the progress in Kasturi cotton initiative.
Background:
- In order to attain the objective of building image of Indian cotton at Global level, making India Aatmanirbhar and vocal for local in the field of cotton, Ministry of Textiles had announced the “Kasturi Cotton India” Brand of cotton on the eve of World Cotton Day on 7th October 2020.
About Kasturi cotton
- Kasturi Cottonis a premium cotton brand from India, launched by the Government of India to promote the country’s cotton and textile industry globally.
Key Features
- High Quality: Kasturi Cotton is known for its long staple length, typically 30 mm and 29 mm, which ensures superior quality.The cotton must meet specific benchmarked parameters, including micronaire value, RD (degrees of reflectance) value, fiber strength, uniformity index, trash, and moisture content.
- Traceability: One of the standout features of Kasturi Cotton is its blockchain traceability and barcode validation.This ensures transparency and quality control throughout the supply chain.
- Sustainability: The brand emphasizes sustainable practices in cotton production, which helps in earning premium prices and enhancing credibility.
Objectives
- Global Recognition: Kasturi Cotton aims to create a unique identity for Indian cotton in the global market, reinforcing India’s position as a cotton powerhouse
- Value Addition: It seeks to add value to the entire cotton chain, from farmers to end users, by ensuring high standards and traceability.
Additional Information
- The Cotton Textiles Export Promotion Council (TEXPROCIL) the apex body to promote exports of Indian Cotton textile products including raw cotton across the world, has been designated as the implementing agency for Traceability, Certification and Branding of “KASTURI Cotton India”.
Source: PIB
Syllabus
- Prelims – SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Context: Astronomers recently discovered ten strange dead stars, or “neutron stars,” lurking near the heart of the Milky Way.
Background:
- Neutron stars are one of the most extreme and exotic objects in the known universe.
About Neutron stars :
- Neutron stars are the collapsed cores of massive stars that have undergone a supernova explosion.
- They are among the densest objects in the universe, second only to black holes.
- Typically, neutron stars have a diameter of about 20 kilometers (12 miles) and a mass between 1.18 and 1.97 times that of the Sun.
How Are Neutron Stars Formed?
- Supernova Explosion: When a massive star (usually 10-25 times the mass of the Sun) exhausts its nuclear fuel, it can no longer support itself against gravitational collapse. This leads to a supernova explosion.
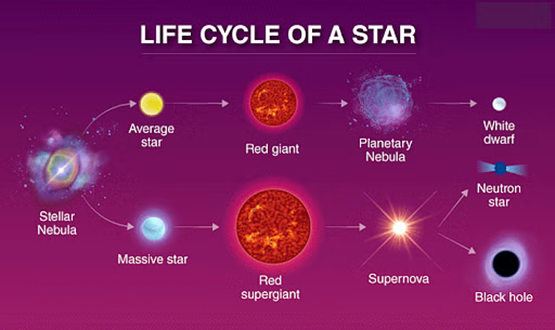
- Core Collapse: The core of the star collapses under gravity, causing protons and electrons to combine into neutrons. This process results in an incredibly dense core composed almost entirely of neutrons.
- Formation of Neutron Star: If the core’s mass is between about 1 and 3 solar masses, the newly-created neutrons can halt further collapse, resulting in a neutron star. If the core’s mass exceeds this limit, it will continue to collapse into a black hole.
Characteristics of Neutron Stars
- Density: Neutron stars are extremely dense. A sugar-cube-sized amount of neutron star material would weigh about a billion tons on Earth.
- Magnetic Fields: They have very strong magnetic fields, which can be billions of times stronger than Earth’s magnetic field.
- Rotation: Neutron stars can rotate very rapidly, sometimes hundreds of times per second. These rapidly rotating neutron stars are known as pulsars.
- Temperature: Newly formed neutron stars can have surface temperatures of around 10 million K. Over time, they cool down, but even older neutron stars can still be quite hot.
Source: Space
Syllabus
- Prelims – CURRENT EVENT
Context: The central government recently announced the full list of the first-ever Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (RVP) 2024 awardees.
Background:
- The award ceremony is scheduled to take place on August 23 at the Rashtrapati Bhavan Cultural Centre, coinciding with the first National Space Day.
About Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar
- The Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar is a prestigious set of awards introduced by the Government of India to recognize outstanding contributions in the fields of science, technology, and innovation.
- These awards are on par with other national honours like the Padma awards.
Categories of Awards:
- Vigyan Ratna Awards: Recognizes lifetime achievements and contributions in any field of science and technology.
- Vigyan Shri Awards: Honors distinguished contributions in any field of science and technology.
- Vigyan Team Awards: Given to teams of three or more scientists/researchers/innovators for exceptional collaborative contributions.
- Vigyan Yuva-Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (VY-SSB) Awards: The highest multidisciplinary science awards for young scientists (up to 45 years old), named after Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar.
Eligibility:
- Open to scientists, technologists, and innovators from government, private sector organizations, or individuals working independently.
- The awards also recognize contributions from Persons of Indian Origin abroad.
Domains:
- Covers 13 domains including Physics, Chemistry, Biological Sciences, Mathematics & Computer Science, Earth Science, Medicine, Engineering Sciences, Agricultural Science, Environmental Science, Technology & Innovation, Atomic Energy, Space Science and Technology.
Nomination and Announcement:
- Nominations are invited annually from January 14th to February 28th, with awards announced on May 11th (National Technology Day) and the ceremony held on August 23rd (National Space Day).
- All nominations received for the RVP awards are placed before the Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar Committee (RVPC), headed by the Principal Scientific Adviser (PSA) to the Government of India.
Source: Hindustan Times
Syllabus
- Mains – GS 4
Context: Artificial Intelligence is on the rise, with new developments and products making headlines almost daily.
Background:
- The future of Artificial Intelligence (AI) will not be secured by regulation alone. To ensure safe and trustworthy AI for all, we must balance regulation with policies that promote high-quality data as a public good.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- It refers to the capability of a computer or robot controlled by a computer to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence and judgment.
Ethical AI:
- It refers to the development and deployment of AI systems in a manner that aligns with ethical principles, societal values, and human rights.
- It is also known as Moral or Responsible AI.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Ethical Issues:
- AI-generated content may raise concerns about preserving the authenticity and integrity of artistic expression, particularly when it is difficult to discern between human-created and AI-generated works.
- There are questions regarding the rights of artists, creators, and participants involved in AI-driven projects, including issues related to intellectual property, ownership, and consent for using personal data or creative contributions.
- AI can revive historical voices or artistic styles, but ethical considerations arise concerning whether such efforts aim to preserve cultural heritage or exploit the identities and legacies of individuals for commercial gain.
- The widespread adoption of AI in creative industries may have implications for human creativity and innovation, potentially leading to homogenization, loss of diversity, or reliance on formulaic approaches.
- The lack of regulatory measures presents challenges in safeguarding privacy and preventing discrimination, necessitating compliance, enforcement, and adaptation to evolving technologies.
Way Forward:
- AI-driven creative processes should ensure transparency and disclosure including clear attribution of AI-generated content and obtaining informed consent from all involved parties.
- The authenticity and integrity of artistic expression should be upheld by acknowledging the contributions of human creators and respecting their rights to control and be properly credited for their work.
- The ethical guidelines and best practices for the ethical use of AI in creative endeavours should be developed by addressing issues such as consent, ownership, fairness, and accountability.
- The regulatory oversight and governance mechanisms should advocate compliance with ethical standards and protect the rights and interests of individuals involved in AI-driven creative projects.
Source: The Hindu
Practice MCQs
Q1.) Which among the following is the largest tiger reserve of India ?
- Nagarjunasagar Srisailam Tiger Reserve
- Manas Tiger reserve
- Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla Tiger Reserve
- Sariska Tiger reserve
Q2.) With reference to the Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar, consider the following statements:
- The Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar is a prestigious set of awards introduced by the Government of India to recognize outstanding contributions in the fields of science, technology, and innovation.
- These awards are on par with other national honours like the Padma awards.
- The awards also recognize contributions from Persons of Indian Origin abroad.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1,2 and 3
Q3.) Consider the following statements:
- Neutron stars are the collapsed cores of massive stars that have undergone a supernova explosion.
- They are among the densest objects in the universe, second only to black holes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
- 1 only
- 2 only
- Both 1 and 2
- Neither 1 nor 2
Comment the answers to the above questions in the comment section below!!
ANSWERS FOR ’ 9th August 2024 – Daily Practice MCQs’ will be updated along with tomorrow’s Daily Current Affairs
ANSWERS FOR 8th August – Daily Practice MCQs
Q.1) – c
Q.2) – c
Q.3) – c
