Archives
Hello Friends
The 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series is IASbaba’s Flagship Initiative recommended by Toppers and loved by the aspirants’ community every year.
It is the most comprehensive program which will help you complete the syllabus, revise and practice tests on a daily basis. The Programme on a daily basis includes
Daily Prelims MCQs from Static (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily Static Quiz will cover all the topics of static subjects – Polity, History, Geography, Economics, Environment and Science and technology.
- 20 questions will be posted daily and these questions are framed from the topics mentioned in the schedule.
- It will ensure timely and streamlined revision of your static subjects.
Daily Current Affairs MCQs (Monday – Saturday)
- Daily 5 Current Affairs questions, based on sources like ‘The Hindu’, ‘Indian Express’ and ‘PIB’, would be published from Monday to Saturday according to the schedule.
Daily CSAT Quiz (Monday – Friday)
- CSAT has been an Achilles heel for many aspirants.
- Daily 5 CSAT Questions will be published.
Note – Daily Test of 20 static questions, 10 current affairs, and 5 CSAT questions. (35 Prelims Questions) in QUIZ FORMAT will be updated on a daily basis.
To Know More about 60 Days Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series – CLICK HERE
60 Day Rapid Revision (RaRe) Series Schedule – CLICK HERE
Important Note
- Comment your Scores in the Comment Section. This will keep you accountable, responsible and sincere in days to come.
- It will help us come out with the Cut-Off on a Daily Basis.
- Let us know if you enjoyed today’s test 🙂
- You can post your comments in the given format
- (1) Your Score
- (2) Matrix Meter
- (3) New Learning from the Test
Test-summary
0 of 35 questions completed
Questions:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
Information
The following Test is based on the syllabus of 60 Days Plan-2023 for UPSC IAS Prelims 2022.
To view Solutions, follow these instructions:
- Click on – ‘Start Test’ button
- Solve Questions
- Click on ‘Test Summary’ button
- Click on ‘Finish Test’ button
- Now click on ‘View Questions’ button – here you will see solutions and links.
You have already completed the test before. Hence you can not start it again.
Test is loading...
You must sign in or sign up to start the test.
You have to finish following test, to start this test:
Results
0 of 35 questions answered correctly
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have scored 0 points out of 0 points, (0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- Answered
- Review
-
Question 1 of 35
1. Question
Consider the following statements:
- All the interacting organisms in an area excluding the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem.
- Both biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors constitute an ecosystem.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Ecosystem: All organisms such as plants, animals, microorganisms and human beings as well as the physical surroundings interact with each other and maintain a balance in nature. All the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem An ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals. Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Ecosystem: All organisms such as plants, animals, microorganisms and human beings as well as the physical surroundings interact with each other and maintain a balance in nature. All the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem An ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals. -
Question 2 of 35
2. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Food Chain:
- Each level of food chain forms a trophic level.
- The food chain may consist of any number of trophic levels.
- The flow of energy in a food chain is always unidirectional.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Correct Food chain is a series of organisms taking part in feeding at various biotic levels. Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level. The autotrophs or the producers are at the first trophic level. They fix up the solar energy and make it available for heterotrophs or the consumers. The herbivores or the primary consumers come at the second, small carnivores or the secondary consumers at the third and larger carnivores or the tertiary consumers form the fourth trophic level. There is a loss of energy as we go from one trophic level to the next, this limits the number of trophic levels in a food-chain. Thus, food chains generally consist of only three or four levels. The loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy remains after four trophic levels. The flow of energy in food chain in unidirectional because the sun is the only source of energy for all ecosystems on earth. Then the energy is captured by the autotrophs does not revert back to the sun. Therefore, in the food chain, the energy moves progressively through various trophic levels. Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Correct Incorrect Correct Food chain is a series of organisms taking part in feeding at various biotic levels. Each step or level of the food chain forms a trophic level. The autotrophs or the producers are at the first trophic level. They fix up the solar energy and make it available for heterotrophs or the consumers. The herbivores or the primary consumers come at the second, small carnivores or the secondary consumers at the third and larger carnivores or the tertiary consumers form the fourth trophic level. There is a loss of energy as we go from one trophic level to the next, this limits the number of trophic levels in a food-chain. Thus, food chains generally consist of only three or four levels. The loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy remains after four trophic levels. The flow of energy in food chain in unidirectional because the sun is the only source of energy for all ecosystems on earth. Then the energy is captured by the autotrophs does not revert back to the sun. Therefore, in the food chain, the energy moves progressively through various trophic levels. -
Question 3 of 35
3. Question
‘Ten Percent Law’ is associated with which of the following?
Correct
Solution (a)
Ten per cent law was given by Lindeman which states that only 10% of energy contained in a lower trophic level is available to next higher tropic level, the remaining 90% being lost as heat to the environment, into digestion and in doing work and the rest goes towards growth and reproduction. Therefore, 10% can be taken as the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaches the next level of consumers.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Ten per cent law was given by Lindeman which states that only 10% of energy contained in a lower trophic level is available to next higher tropic level, the remaining 90% being lost as heat to the environment, into digestion and in doing work and the rest goes towards growth and reproduction. Therefore, 10% can be taken as the average value for the amount of organic matter that is present at each step and reaches the next level of consumers.
-
Question 4 of 35
4. Question
Which of the given term describes not only the physical space occupied by an organism but also its functional role in the community of organisms?
Correct
Solution (b)
Ecological niche can be defined as the functional role and position (micro-habitat) of species in its ecosystem, including what resources it uses, how and when it uses the resources, and how it interacts with other species.
Each organism has an invariably defined range of conditions that it can tolerate, diversity in the resources it utilises and a distinct functional role in the ecological system, all these together comprise its niche.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Ecological niche can be defined as the functional role and position (micro-habitat) of species in its ecosystem, including what resources it uses, how and when it uses the resources, and how it interacts with other species.
Each organism has an invariably defined range of conditions that it can tolerate, diversity in the resources it utilises and a distinct functional role in the ecological system, all these together comprise its niche.
-
Question 5 of 35
5. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Homeostasis:
- The ability of an organism to maintain its internal environment is called as Homeostasis.
- In a homeostatic system, positive feedback mechanism is responsible for maintaining stability in an ecosystem.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Homeostasis refers to maintenance of a constant internal environment by the organisms. This contributes to optimal performance of organisms In a homeostatic system, negative feedback mechanism is responsible for maintaining stability in an ecosystem. Only some organisms (regulators) are capable of homeostasis in the face of changing external environment. Others either partially regulate their internal environment or simply conform.
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Homeostasis refers to maintenance of a constant internal environment by the organisms. This contributes to optimal performance of organisms In a homeostatic system, negative feedback mechanism is responsible for maintaining stability in an ecosystem. Only some organisms (regulators) are capable of homeostasis in the face of changing external environment. Others either partially regulate their internal environment or simply conform.
-
Question 6 of 35
6. Question
What is the meaning of term ‘Diapause’?
Correct
Solution (c)
Diapause is the ability of an organism to suspend its development owing to extreme environmental conditions. In this state, developmental arrest or dormancy is seen that signifies shutting down of most life processes. This kind of physiological state is found mostly in arthropods. During the life cycle of an insect, diapause can happen at any stage such as embryonic, larval, pupal, and adult. This developmental arrest is a spontaneous response amongst these animals to survive unfavourable environmental conditions.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Diapause is the ability of an organism to suspend its development owing to extreme environmental conditions. In this state, developmental arrest or dormancy is seen that signifies shutting down of most life processes. This kind of physiological state is found mostly in arthropods. During the life cycle of an insect, diapause can happen at any stage such as embryonic, larval, pupal, and adult. This developmental arrest is a spontaneous response amongst these animals to survive unfavourable environmental conditions.
-
Question 7 of 35
7. Question
“Mammals from colder climates generally have shorter ears and limbs to minimise heat loss”, This rule is known as?
Correct
Solution (b)
Allen’s Rule says that mammals from colder climates generally have shorter ears and limbs to minimise heat loss. In the polar seas aquatic mammals like seals have a thick layer of fat (blubber) below their skin that acts as an insulator and reduces loss of body heat.
Bergmann’s rule says that animals or organisms residing at a higher altitude should be larger and have a thicker coat than those that are living at lower altitudes and found close to the equator.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Allen’s Rule says that mammals from colder climates generally have shorter ears and limbs to minimise heat loss. In the polar seas aquatic mammals like seals have a thick layer of fat (blubber) below their skin that acts as an insulator and reduces loss of body heat.
Bergmann’s rule says that animals or organisms residing at a higher altitude should be larger and have a thicker coat than those that are living at lower altitudes and found close to the equator.
-
Question 8 of 35
8. Question
Consider the following statements regarding ‘Insectivorous Plants’:
- Insectivorous plants are a specialized group of plants that grow in dry, alkaline soils.
- These plants are usually associated with leached and nutrient-poor soils.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Insectivorous plants are a specialized group of plants that grow in wet, acidic soils. · One of the most critical plant nutrients is nitrogen which is usually taken up by plants as nitrates. Nitrogen is a nutrient that is easily leached out of soils. · For this reason, the plants that live in these soils have evolved into carnivorous plants that capture and digest insects as a means of obtaining nitrates. These plants are usually associated with leached, nutrient-poor soils, or wet and acidic areas that are ill-drained.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Correct Insectivorous plants are a specialized group of plants that grow in wet, acidic soils. · One of the most critical plant nutrients is nitrogen which is usually taken up by plants as nitrates. Nitrogen is a nutrient that is easily leached out of soils. · For this reason, the plants that live in these soils have evolved into carnivorous plants that capture and digest insects as a means of obtaining nitrates. These plants are usually associated with leached, nutrient-poor soils, or wet and acidic areas that are ill-drained.
-
Question 9 of 35
9. Question
Which of the following statement is correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
The important steps in the process of decomposition are: fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification and mineralisation.
- Detritivores (e.g., earthworm) break down detritus into smaller particles. This process is called fragmentation.
- In the process of leaching, water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
- Bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. This process is called as catabolism.
- Humification leads to accumulation of a dark-coloured amorphous substance called humus that is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate. Being colloidal in nature it serves as a reservoir of nutrients.
- The humus is further degraded by some microbes and release of inorganic nutrients occur by the process known as mineralization.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
The important steps in the process of decomposition are: fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification and mineralisation.
- Detritivores (e.g., earthworm) break down detritus into smaller particles. This process is called fragmentation.
- In the process of leaching, water-soluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts.
- Bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. This process is called as catabolism.
- Humification leads to accumulation of a dark-coloured amorphous substance called humus that is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate. Being colloidal in nature it serves as a reservoir of nutrients.
- The humus is further degraded by some microbes and release of inorganic nutrients occur by the process known as mineralization.
-
Question 10 of 35
10. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Decomposition:
- Decomposition is largely an oxygen-requiring process.
- Warm and moist environment slows down the decomposition
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Decomposition is largely an oxygen-requiring process. The rate of decomposition is controlled by chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors. In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is slower if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin, and quicker, if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water-soluble substances like sugars.
Temperature and soil moisture are the most important climatic factors that regulate decomposition through their effects on the activities of soil microbes. Warm and moist environment favour decomposition whereas low temperature and anaerobiosis inhibit decomposition resulting in buildup of organic materials.Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Decomposition is largely an oxygen-requiring process. The rate of decomposition is controlled by chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors. In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is slower if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin, and quicker, if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water-soluble substances like sugars.
Temperature and soil moisture are the most important climatic factors that regulate decomposition through their effects on the activities of soil microbes. Warm and moist environment favour decomposition whereas low temperature and anaerobiosis inhibit decomposition resulting in buildup of organic materials. -
Question 11 of 35
11. Question
Consider the following statements:
- In a terrestrial ecosystem, grazing food chain is the major conduit for energy flow.
- The detritus food chain has no connection with the grazing food chain at any level.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (d)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Incorrect In an aquatic ecosystem, the grazing food chain (GFC) is the major conduit for energy flow. As against this, in a terrestrial ecosystem, a much larger fraction of energy flows through the detritus food chain (DFC) than through the GFC. Detritus food chain may be connected with the grazing food chain at some levels: some of the organisms of DFC are prey to the GFC animals, and in a natural ecosystem, some animals like cockroaches, crows, etc., are omnivores. These natural interconnection of food chains make it a food web. Incorrect
Solution (d)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Incorrect Incorrect In an aquatic ecosystem, the grazing food chain (GFC) is the major conduit for energy flow. As against this, in a terrestrial ecosystem, a much larger fraction of energy flows through the detritus food chain (DFC) than through the GFC. Detritus food chain may be connected with the grazing food chain at some levels: some of the organisms of DFC are prey to the GFC animals, and in a natural ecosystem, some animals like cockroaches, crows, etc., are omnivores. These natural interconnection of food chains make it a food web. -
Question 12 of 35
12. Question
Consider the following pairs
- Aerobic Azotobacter – Fix atmospheric Nitrogen to ammonium ion.
- Nitrosomonas bacteria – Nitrite to nitrate
- Nitrobacter Bacteria – Ammonium Ion to Nitrite
- Pseudosomanas – Denitrifying Bacteria.
How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
Correct
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Statement 4 Correct Incorrect Incorrect Correct Certain organisms are capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium ions. These include free living nitrifying bacteria (e.g. aerobic Azotobacter and anaerobic Clostridium) and symbiotic nitrifying bacteria living in association with leguminous plants and symbiotic bacteria living in non-leguminous root nodule plants (e.g. Rhizobium) as well as blue green algae (e.g. Anabaena, Spirulina).
Ammonium ions can be directly taken up as a source of nitrogen by some plants, or are oxidized to nitrites or nitrates by two groups of specialized bacteria: Nitrosomonas bacteria promote transformation of ammonia into nitrite. Nitrite is then further transformed into nitrate by the Nitrobacter bacteria. In the soil as well as oceans there are special denitrifying bacteria (e.g. Pseudomonas), which convert the nitrates/nitrites to elemental nitrogen Incorrect
Solution (b)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Statement 3 Statement 4 Correct Incorrect Incorrect Correct Certain organisms are capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen into ammonium ions. These include free living nitrifying bacteria (e.g. aerobic Azotobacter and anaerobic Clostridium) and symbiotic nitrifying bacteria living in association with leguminous plants and symbiotic bacteria living in non-leguminous root nodule plants (e.g. Rhizobium) as well as blue green algae (e.g. Anabaena, Spirulina).
Ammonium ions can be directly taken up as a source of nitrogen by some plants, or are oxidized to nitrites or nitrates by two groups of specialized bacteria: Nitrosomonas bacteria promote transformation of ammonia into nitrite. Nitrite is then further transformed into nitrate by the Nitrobacter bacteria. In the soil as well as oceans there are special denitrifying bacteria (e.g. Pseudomonas), which convert the nitrates/nitrites to elemental nitrogen -
Question 13 of 35
13. Question
Consider the following statements regarding ‘Ecosystem Services’:
- Provisioning includes obtaining products such as food, fodder and fuel form the ecosystem.
- Supporting services are photosynthesis, nutrient recycling and soil formation.
- Maintaining air quality, climate and pollution control forms Regulating services.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
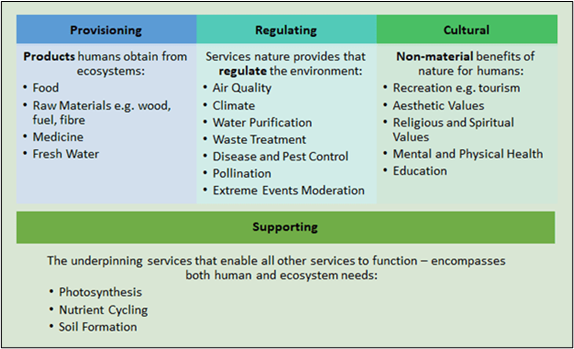 Incorrect
Incorrect
Solution (c)

-
Question 14 of 35
14. Question
Consider the following statements
- More than 70 percent of all the species recorded on earth are animals, while plants comprise around 22 percent of the total.
- Among animals, mammals are the most species-rich taxonomic group, making up more than 70 per cent of the total
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect With respect to earth’s biodiversity, More than 70 per cent of all the species recorded are animals, while plants (including algae, fungi, bryophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms) comprise no more than 22 per cent of the total. Among animals, insects are the most species-rich taxonomic group, making up more than 70 per cent of the total. Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect With respect to earth’s biodiversity, More than 70 per cent of all the species recorded are animals, while plants (including algae, fungi, bryophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms) comprise no more than 22 per cent of the total. Among animals, insects are the most species-rich taxonomic group, making up more than 70 per cent of the total. -
Question 15 of 35
15. Question
Which of the following countries is not a Mega diversity country?
Correct
Solution (c)
The 17 Mega-diverse countries are:
- Australia
- Brazil
- China
- Colombia
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Ecuador
- India
- Indonesia
- Madagascar
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- Papua New Guinea
- Peru
- Philippines
- South Africa
- United States
- Venezuela
Incorrect
Solution (c)
The 17 Mega-diverse countries are:
- Australia
- Brazil
- China
- Colombia
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Ecuador
- India
- Indonesia
- Madagascar
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- Papua New Guinea
- Peru
- Philippines
- South Africa
- United States
- Venezuela
-
Question 16 of 35
16. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Species diversity decreases towards poles from equator.
- High seasonal variation is the cause for high species diversity in tropical regions.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Correct
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Latitudinal gradients: The diversity of plants and animals is not uniform throughout the world but shows a rather uneven distribution. For many group of animals or plants, there are interesting patterns in diversity, the most well- known being the latitudinal gradient in diversity. In general, species diversity decreases as we move away from the equator towards the poles. Speciation is generally a function of time, unlike temperate regions subjected to frequent glaciations in the past, tropical latitudes have remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years and thus, had a long evolutionary time for species diversification. Tropical environments, unlike temperate ones, are less seasonal, relatively more constant and predictable. Such constant environments promote niche specialisation and lead to a greater species diversity.
There is more solar energy available in the tropics, which contributes to higher productivity; this in turn might contribute indirectly to greater diversity
Incorrect
Solution (a)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Incorrect Latitudinal gradients: The diversity of plants and animals is not uniform throughout the world but shows a rather uneven distribution. For many group of animals or plants, there are interesting patterns in diversity, the most well- known being the latitudinal gradient in diversity. In general, species diversity decreases as we move away from the equator towards the poles. Speciation is generally a function of time, unlike temperate regions subjected to frequent glaciations in the past, tropical latitudes have remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years and thus, had a long evolutionary time for species diversification. Tropical environments, unlike temperate ones, are less seasonal, relatively more constant and predictable. Such constant environments promote niche specialisation and lead to a greater species diversity.
There is more solar energy available in the tropics, which contributes to higher productivity; this in turn might contribute indirectly to greater diversity
-
Question 17 of 35
17. Question
Consider the following statements:
- No high variation in productivity from year to year.
- Resistant to occasional disturbances, be it natural or man-made.
- Sensitive to invasive species.
Which of the above statements are features of stable community?
Correct
Solution (b)
A Stable community should not show too much variation in productivity from year to year; it must be either resistant or resilient to occasional disturbances (natural or man-made), and it must also be resistant to invasions by alien species.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
A Stable community should not show too much variation in productivity from year to year; it must be either resistant or resilient to occasional disturbances (natural or man-made), and it must also be resistant to invasions by alien species.
-
Question 18 of 35
18. Question
It is an area of uniform environmental conditions providing a living place for a specific assemblage of plants and animals. Which of the following term is being referred to here?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Biome: A large terrestrial ecosystem characterized by specific plant communities and formations; usually named after the predominant vegetation in the region.
- Biosphere: The totality of life on or near Earth’s surface.
- Biota: The entire complement of species of organisms, plants, and animals, found within a given region.
- Biotype: A biotope is an area of uniform environmental conditions providing a living place for a specific assemblage of plants and animals. Biotope is almost synonymous with the term habitat.
- In ecology, a community is an assemblage or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area and in a particular time, also known as a biocoenosis.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Biome: A large terrestrial ecosystem characterized by specific plant communities and formations; usually named after the predominant vegetation in the region.
- Biosphere: The totality of life on or near Earth’s surface.
- Biota: The entire complement of species of organisms, plants, and animals, found within a given region.
- Biotype: A biotope is an area of uniform environmental conditions providing a living place for a specific assemblage of plants and animals. Biotope is almost synonymous with the term habitat.
- In ecology, a community is an assemblage or association of populations of two or more different species occupying the same geographical area and in a particular time, also known as a biocoenosis.
-
Question 19 of 35
19. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Consumption of Fossil Fuels
- Microbial Respiration in Oceans
- Zooplankton Grazing in Oceans
- Auto and Factory emissions.
Which of the above add carbon dioxide to the carbon cycle on Earth?
Correct
Solution (d)
1. 2. 3. 4. Consumption of Fossil Fuels Microbial Respiration in Oceans Zooplankton Grazing in Oceans Auto and Factory emissions Correct Correct Correct Correct Consumption of Fossil Fuels adds CO2 from the carbon cycle. Microbial Respiration in Oceans adds CO2 to the carbon cycle on Earth. Zooplankton Grazing in Oceans adds CO2 to the carbon cycle on Earth. Auto and Factory emissions adds CO2 to the carbon cycle on Earth. Notes:
Carbon cycle-
- Carbon is a minor constituent of the atmosphere as compared to oxygen and nitrogen.
- However, without carbon dioxide life could not exist because it is vital for the production of carbohydrates through photosynthesis by plants.
- t is the element that anchors all organic substances from coal and oil to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid: the compound that carries genetic information).
- Carbon is present in the atmosphere, mainly in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Carbon cycle involves a continuous exchange of carbon between the atmosphere and organisms.
- Carbon from the atmosphere moves to green plants by the process of photosynthesis, and then to animals.
- By process of respiration and decomposition of dead organic matter, it returns to the atmosphere. It is usually a short-term cycle.
- Some carbon also enters a long-term cycle. It accumulates as un-decomposed organic matter in the peaty layers of marshy soil or as insoluble carbonates in bottom sediments of aquatic systems which take a long time to be released.
- In deep oceans, such carbon can remain buried for millions of years till geological movement may lift these rocks above sea level.
- These rocks may be exposed to erosion, releasing their carbon dioxide, carbonates and bicarbonates into streams and rivers.
- Fossil fuels such as coals, oil and natural gas etc. are organic compounds that were buried before they could be decomposed and were subsequently transformed by time and geological processes into fossil fuels. When they are burned the carbon stored in them is released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
1. 2. 3. 4. Consumption of Fossil Fuels Microbial Respiration in Oceans Zooplankton Grazing in Oceans Auto and Factory emissions Correct Correct Correct Correct Consumption of Fossil Fuels adds CO2 from the carbon cycle. Microbial Respiration in Oceans adds CO2 to the carbon cycle on Earth. Zooplankton Grazing in Oceans adds CO2 to the carbon cycle on Earth. Auto and Factory emissions adds CO2 to the carbon cycle on Earth. Notes:
Carbon cycle-
- Carbon is a minor constituent of the atmosphere as compared to oxygen and nitrogen.
- However, without carbon dioxide life could not exist because it is vital for the production of carbohydrates through photosynthesis by plants.
- t is the element that anchors all organic substances from coal and oil to DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid: the compound that carries genetic information).
- Carbon is present in the atmosphere, mainly in the form of carbon dioxide (CO2).
- Carbon cycle involves a continuous exchange of carbon between the atmosphere and organisms.
- Carbon from the atmosphere moves to green plants by the process of photosynthesis, and then to animals.
- By process of respiration and decomposition of dead organic matter, it returns to the atmosphere. It is usually a short-term cycle.
- Some carbon also enters a long-term cycle. It accumulates as un-decomposed organic matter in the peaty layers of marshy soil or as insoluble carbonates in bottom sediments of aquatic systems which take a long time to be released.
- In deep oceans, such carbon can remain buried for millions of years till geological movement may lift these rocks above sea level.
- These rocks may be exposed to erosion, releasing their carbon dioxide, carbonates and bicarbonates into streams and rivers.
- Fossil fuels such as coals, oil and natural gas etc. are organic compounds that were buried before they could be decomposed and were subsequently transformed by time and geological processes into fossil fuels. When they are burned the carbon stored in them is released back into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
-
Question 20 of 35
20. Question
With reference to ‘Carrying Capacity’ of an environment, consider the following statements:
- It is the maximum population size of biological species that can be sustained in that specific environment.
- The carrying capacity is different for each species in a given habitat.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Correct It is the maximum population size of biological species that can be sustained in that specific environment. The carrying capacity is different for each species in a given habitat. Notes:
The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained in that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available.
The carrying capacity is different for each species in a habitat because of that species’ particular food, shelter, and social requirements. Disease, competition, predator-prey interaction, resource use and the number of populations in an ecosystem all affect carrying capacity. It does not relate to the diversity of species. Important direct drivers affecting biodiversity are habitat change, climate change, invasive species, overexploitation, and pollution.
Populations grow through births and immigration and decline through deaths and emigration. When resources are unlimited, the growth is usually exponential but when resources become progressively limiting, the growth pattern turns logistic. The intrinsic rate of natural increase (r) is a measure of the inherent potential of a population to grow. The ‘intrinsic rate of natural increase’ is a very important parameter chosen for assessing impacts of any biotic or abiotic factor on population growth.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
Statement 1 Statement 2 Correct Correct It is the maximum population size of biological species that can be sustained in that specific environment. The carrying capacity is different for each species in a given habitat. Notes:
The carrying capacity of an environment is the maximum population size of a biological species that can be sustained in that specific environment, given the food, habitat, water, and other resources available.
The carrying capacity is different for each species in a habitat because of that species’ particular food, shelter, and social requirements. Disease, competition, predator-prey interaction, resource use and the number of populations in an ecosystem all affect carrying capacity. It does not relate to the diversity of species. Important direct drivers affecting biodiversity are habitat change, climate change, invasive species, overexploitation, and pollution.
Populations grow through births and immigration and decline through deaths and emigration. When resources are unlimited, the growth is usually exponential but when resources become progressively limiting, the growth pattern turns logistic. The intrinsic rate of natural increase (r) is a measure of the inherent potential of a population to grow. The ‘intrinsic rate of natural increase’ is a very important parameter chosen for assessing impacts of any biotic or abiotic factor on population growth.
-
Question 21 of 35
21. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Bosporus Strait connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara.
- The Strait of the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara to the Aegean Sea.
- Kerch Strait connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Azov.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- Bosporus Strait connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The Strait of the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara to the Aegean Sea. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Kerch Strait connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Azov. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- Bosporus Strait connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- The Strait of the Dardanelles connects the Sea of Marmara to the Aegean Sea. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Kerch Strait connects the Black Sea to the Sea of Azov. Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 22 of 35
22. Question
Consider the following statements about the Index of Industrial Production (IIP):
- It is published annually by the National Statistical Office (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- It indicates the relative change over time in the volume of production in the industrial sector.
- Refinery products constitute the highest percentage among the eight core industries.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is published monthly by the National Statistical Office (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- It indicates the relative change over time in the volume of production in the industrial sector. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It is an effective tool to measure the trend of current industrial production that is used by government agencies including the Ministry of Finance, the Reserve Bank of India, etc., for policy-making purposes.
- The eight core sector industries in decreasing order of their weightage: Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilizers.
- Refinery products constitute the highest percentage among the eight core industries. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is published monthly by the National Statistical Office (NSO) under the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- It indicates the relative change over time in the volume of production in the industrial sector. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It is an effective tool to measure the trend of current industrial production that is used by government agencies including the Ministry of Finance, the Reserve Bank of India, etc., for policy-making purposes.
- The eight core sector industries in decreasing order of their weightage: Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilizers.
- Refinery products constitute the highest percentage among the eight core industries. Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 23 of 35
23. Question
Consider the following statements about Gharials:
- They are an indicator species found in the tributaries of River Ganga.
- They are listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List.
- They are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- Gharials are an indicator species found in the tributaries of River Ganga.
- They are an indicator of clean water. They are found in three tributaries of the Ganga River – the Chambal and the Girwa Rivers in India and the Rapti-Naryani River in Nepal. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- They are listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List and in Appendix I of the CITES. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- They are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- Gharials are an indicator species found in the tributaries of River Ganga.
- They are an indicator of clean water. They are found in three tributaries of the Ganga River – the Chambal and the Girwa Rivers in India and the Rapti-Naryani River in Nepal. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- They are listed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List and in Appendix I of the CITES. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- They are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972. Hence statement 3 is correct.
-
Question 24 of 35
24. Question
Consider the following statements regarding Rudragiri Hillock:
- It has prehistoric rock paintings from the Mesolithic period located in Karnataka.
- It is the first cave representing murals of battle between the Vanara brothers, Vali, and Sugriva.
- It has a sketch of Hanuman, accompanied by sacred symbols of the conch and the fire altar.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Rudragiri Hillock has prehistoric rock paintings from the Mesolithic period and art from the Kakatiya dynasty is located in Andhra Pradesh. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- It is nestled amidst the Eastern Ghats and features five naturally formed rock shelters at its foothills, facing westward.
- These shelters served as living quarters for people during the Mesolithic age around 5000 B.C.
- It is the first cave representing murals of battle between the Vanara brothers, Vali, and Sugriva. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Ganapati Deva Maharaja (1199-1262 AD) who was built the Muppavaram temple and a prominent figure of the Kakatiya dynasty is likely to be the patron of the rich ancient mural heritage found at Rudragiri.
- It has a sketch of Hanuman, accompanied by sacred symbols of the conch and the fire altar. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Note:
Kakatiya kingdom was a south Indian dynasty that ruled most of the eastern Deccan region comprising present-day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, and parts of eastern Karnataka and southern Odisha. They ruled between the 12th and 14th centuries.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Rudragiri Hillock has prehistoric rock paintings from the Mesolithic period and art from the Kakatiya dynasty is located in Andhra Pradesh. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- It is nestled amidst the Eastern Ghats and features five naturally formed rock shelters at its foothills, facing westward.
- These shelters served as living quarters for people during the Mesolithic age around 5000 B.C.
- It is the first cave representing murals of battle between the Vanara brothers, Vali, and Sugriva. Hence statement 2 is correct.
- Ganapati Deva Maharaja (1199-1262 AD) who was built the Muppavaram temple and a prominent figure of the Kakatiya dynasty is likely to be the patron of the rich ancient mural heritage found at Rudragiri.
- It has a sketch of Hanuman, accompanied by sacred symbols of the conch and the fire altar. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Note:
Kakatiya kingdom was a south Indian dynasty that ruled most of the eastern Deccan region comprising present-day Telangana and Andhra Pradesh, and parts of eastern Karnataka and southern Odisha. They ruled between the 12th and 14th centuries.
-
Question 25 of 35
25. Question
Consider the following statements about PM SVANidhi Scheme:
- It provides collateral-free loans up to INR 1,00,000/- to street vendors for one year tenure.
- It is implemented by the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI).
- An interest subsidy of 7% per annum is provided on timely/ early repayment of the loan.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme provides collateral-free working capital loans up to INR 10,000/- to street vendors for one year tenure. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- Street vendors with a Certificate of Vending/Identity Card issued by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) are eligible for the scheme.
- It is implemented by the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI). Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It encourages entrepreneurship and creates employment opportunities.
- An interest subsidy of 7% per annum is provided on timely/ early repayment of the loan. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- There is no processing fee to apply for the scheme, making it cost-effective for street vendors.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- The Prime Minister Street Vendor’s AtmaNirbhar Nidhi (PM SVANidhi) Scheme provides collateral-free working capital loans up to INR 10,000/- to street vendors for one year tenure. Hence statement 1 is incorrect.
- Street vendors with a Certificate of Vending/Identity Card issued by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) are eligible for the scheme.
- It is implemented by the Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI). Hence statement 2 is correct.
- It encourages entrepreneurship and creates employment opportunities.
- An interest subsidy of 7% per annum is provided on timely/ early repayment of the loan. Hence statement 3 is correct.
- There is no processing fee to apply for the scheme, making it cost-effective for street vendors.
-
Question 26 of 35
26. Question
Consider the following statements about picolinic acid:
- It is a pyridinemonocarboxylic acid.
- It helps in the absorption of zinc from our gut.
- It disrupts the entry of enveloped viruses into the host’s cell and prevents infection.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (c)
- Picolinic acid is a pyridinemonocarboxylic acid i.e., the carboxy group is located at position 2. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- It is an intermediate in the metabolism of tryptophan, an essential amino acid used to make proteins.
- It helps in the absorption of zinc from our gut. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- It stays inside the body only for a short duration and is usually excreted out quickly.
- It disrupts the entry of enveloped viruses into the host’s cell and prevents infection. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- It leads to an increase in the number of immune cells in the animals and is effective against a variety of enveloped viruses, including flaviviruses like the Zika virus and the Japanese encephalitis virus.
Incorrect
Solution (c)
- Picolinic acid is a pyridinemonocarboxylic acid i.e., the carboxy group is located at position 2. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- It is an intermediate in the metabolism of tryptophan, an essential amino acid used to make proteins.
- It helps in the absorption of zinc from our gut. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- It stays inside the body only for a short duration and is usually excreted out quickly.
- It disrupts the entry of enveloped viruses into the host’s cell and prevents infection. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- It leads to an increase in the number of immune cells in the animals and is effective against a variety of enveloped viruses, including flaviviruses like the Zika virus and the Japanese encephalitis virus.
-
Question 27 of 35
27. Question
Which of the following activities are eligible for benefits under the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF)?
- Dairy Processing
- Meat Processing
- Animal Feed Manufacturing
- Breed Improvement Technology
- Veterinary Vaccine and Drugs Production
- Animal Waste to Wealth Management
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (d)
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) was launched in 2021 by the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying. It is implemented by the Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying. Its objectives are:
- To help increasing of milk and meat processing capacity and product diversification thereby providing greater access for unorganized rural milk and meat producers to organized milk and meat market.
- To make available increased price realization for the producer.
- To make available quality milk and meat products for the domestic consumer.
- To fulfill the objective of protein-enriched quality food requirement of the growing population of the country and prevent malnutrition in one of the highest malnourished children population in the world.
- Develop entrepreneurship and generate employment.
- To promote exports and increase the export contribution in the milk and meat sector.
- To make available quality concentrated animals feed to the cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry to provide balanced ration at affordable prices.
The activities are eligible for benefits under the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) are:
- Dairy Processing
- Meat Processing
- Animal Feed Manufacturing
- Breed Improvement Technology
- Veterinary Vaccine and Drugs Production
- Animal Waste to Wealth Management
Hence, option d is correct.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) was launched in 2021 by the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying. It is implemented by the Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying. Its objectives are:
- To help increasing of milk and meat processing capacity and product diversification thereby providing greater access for unorganized rural milk and meat producers to organized milk and meat market.
- To make available increased price realization for the producer.
- To make available quality milk and meat products for the domestic consumer.
- To fulfill the objective of protein-enriched quality food requirement of the growing population of the country and prevent malnutrition in one of the highest malnourished children population in the world.
- Develop entrepreneurship and generate employment.
- To promote exports and increase the export contribution in the milk and meat sector.
- To make available quality concentrated animals feed to the cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, and poultry to provide balanced ration at affordable prices.
The activities are eligible for benefits under the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) are:
- Dairy Processing
- Meat Processing
- Animal Feed Manufacturing
- Breed Improvement Technology
- Veterinary Vaccine and Drugs Production
- Animal Waste to Wealth Management
Hence, option d is correct.
-
Question 28 of 35
28. Question
Consider the following statements about Bacteriophages:
- They are viruses that infect and replicate only in bacterial cells.
- They are vectors for horizontal gene transfer.
- They are found only in soil.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Bacteriophages are viruses that infect and replicate only in bacterial cells. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- These viruses kill bacteria in our microbiomes.
- They only attack bacteria and are harmless to people, animals, and plants.
- They are classified in a number of virus families some examples include Inoviridae, Microviridae, Rudiviridae, and Tectiviridae.
- They are clinically relevant for their ability to distinguish strains of the same bacterial species.
- They are vectors for horizontal gene transfer, including antimicrobial resistance genes. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- They are found in soil, water, and sewage. Hence, statement 3 is incorrect.
- Like all viruses, phages are simple organisms that consist of a core of genetic material (nucleic acid) surrounded by a protein capsid.
- Capsid of a bacteriophage can be icosahedral, filamentous, or head-tail in shape.
- The head-tail structure seems to be unique to phages and their close relatives.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Bacteriophages are viruses that infect and replicate only in bacterial cells. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- These viruses kill bacteria in our microbiomes.
- They only attack bacteria and are harmless to people, animals, and plants.
- They are classified in a number of virus families some examples include Inoviridae, Microviridae, Rudiviridae, and Tectiviridae.
- They are clinically relevant for their ability to distinguish strains of the same bacterial species.
- They are vectors for horizontal gene transfer, including antimicrobial resistance genes. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- They are found in soil, water, and sewage. Hence, statement 3 is incorrect.
- Like all viruses, phages are simple organisms that consist of a core of genetic material (nucleic acid) surrounded by a protein capsid.
- Capsid of a bacteriophage can be icosahedral, filamentous, or head-tail in shape.
- The head-tail structure seems to be unique to phages and their close relatives.
-
Question 29 of 35
29. Question
Consider the following statements about DPT3 Vaccine:
- It provides protection against three severe viral diseases – Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis.
- All children should get five doses of the DTP vaccine at 6 weeks, 10 weeks, 14 weeks, 16-18 months, and 5 years.
- A child who had a life-threatening allergic reaction after a dose of DTP vaccination should not get another dose.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- DPT3 Vaccine provides protection against three severe bacterial diseases – Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis. Hence, statement 1 is incorrect.
- Diphtheria causes a thick covering in the back of the throat. It can lead to breathing problems, paralysis, heart failure, and even death in severe cases.
- Tetanus causes painful tightening of the muscles usually all over the body. It can lead to locking of the jaw as a result the victim cannot open his mouth or swallow. Deaths because of Tetanus are around 10%.
- Pertussis (whooping cough or black cough) causes severe coughing spells that it is hard for infants to eat, drink or even breathe. These spells can last for weeks. It can lead to pneumonia, convulsions, brain damage, and death.
- All children should get five doses of the DTP vaccine at 6 weeks, 10 weeks, 14 weeks, 16-18 months, and 5 years. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- A child who had a life-threatening allergic reaction after a dose of DTP vaccination should not get another dose. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- A child who had encephalopathy (brain illness) or nervous system disease within 7 days after a dose of DTP should not get another dose.
- A child who had a temperature of 105oF within 48 hours after a dose of DTP should probably not get another dose of the Pertussis-containing vaccine.
- A child who collapses or goes into a “shock-like” state within 48 hours after a dose of DTP should probably not get another dose of the Pertussis-containing vaccine.
- A child who cries continuously for 3 or more hours within 48 hours after a dose of DTP should probably not get another dose of the Pertussis-containing vaccine.
- A child who has convulsions within 3 days after a dose of DTP should probably not get another dose of the Pertussis-containing vaccine.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- DPT3 Vaccine provides protection against three severe bacterial diseases – Diphtheria, Tetanus, and Pertussis. Hence, statement 1 is incorrect.
- Diphtheria causes a thick covering in the back of the throat. It can lead to breathing problems, paralysis, heart failure, and even death in severe cases.
- Tetanus causes painful tightening of the muscles usually all over the body. It can lead to locking of the jaw as a result the victim cannot open his mouth or swallow. Deaths because of Tetanus are around 10%.
- Pertussis (whooping cough or black cough) causes severe coughing spells that it is hard for infants to eat, drink or even breathe. These spells can last for weeks. It can lead to pneumonia, convulsions, brain damage, and death.
- All children should get five doses of the DTP vaccine at 6 weeks, 10 weeks, 14 weeks, 16-18 months, and 5 years. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- A child who had a life-threatening allergic reaction after a dose of DTP vaccination should not get another dose. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- A child who had encephalopathy (brain illness) or nervous system disease within 7 days after a dose of DTP should not get another dose.
- A child who had a temperature of 105oF within 48 hours after a dose of DTP should probably not get another dose of the Pertussis-containing vaccine.
- A child who collapses or goes into a “shock-like” state within 48 hours after a dose of DTP should probably not get another dose of the Pertussis-containing vaccine.
- A child who cries continuously for 3 or more hours within 48 hours after a dose of DTP should probably not get another dose of the Pertussis-containing vaccine.
- A child who has convulsions within 3 days after a dose of DTP should probably not get another dose of the Pertussis-containing vaccine.
-
Question 30 of 35
30. Question
Consider the following statements:
- Malware is any kind of software that is designed to cause damage to a single computer, server, or computer network.
- Denial of Service involves impersonating a bank’s URL with a website that is quite similar to the original one and has similar functions as well.
- Spoofing is an attack meant to shut down a machine or network, making it inaccessible to its intended users.
- Phishing is attempting to obtain sensitive information for fraudulent activities, by disguising oneself as an authentic entity via electronic communication.
How many of the above statements are correct?
Correct
Solution (b)
- Malware is any kind of software that is designed to cause damage to a single computer, server, or computer network. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Spoofing involves impersonating a bank’s URL with a website that is quite similar to the original one and has similar functions as well. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- Phishing is attempting to obtain sensitive information for fraudulent activities, by disguising oneself as an authentic entity via electronic communication. Hence statement 4 is correct.
- Denial of Service is an attack meant to shut down a machine or network, making it inaccessible to its intended users. Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks occur when attackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction. Once the attackers interrupt the traffic, they can filter and steal data.
- Structured Query Language (SQL) Injection is a programming language used to communicate with databases. Many of the servers that store critical data for websites and services use SQL to manage the data in their databases. A SQL injection attack specifically targets such kinds of servers, using malicious code to get the server to divulge information it normally would not
Incorrect
Solution (b)
- Malware is any kind of software that is designed to cause damage to a single computer, server, or computer network. Hence statement 1 is correct.
- Spoofing involves impersonating a bank’s URL with a website that is quite similar to the original one and has similar functions as well. Hence statement 2 is incorrect.
- Phishing is attempting to obtain sensitive information for fraudulent activities, by disguising oneself as an authentic entity via electronic communication. Hence statement 4 is correct.
- Denial of Service is an attack meant to shut down a machine or network, making it inaccessible to its intended users. Hence statement 3 is incorrect.
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks occur when attackers insert themselves into a two-party transaction. Once the attackers interrupt the traffic, they can filter and steal data.
- Structured Query Language (SQL) Injection is a programming language used to communicate with databases. Many of the servers that store critical data for websites and services use SQL to manage the data in their databases. A SQL injection attack specifically targets such kinds of servers, using malicious code to get the server to divulge information it normally would not
-
Question 31 of 35
31. Question
The product of all integers from 1 to 200 will have the following numbers of zeros at the end:
Correct
Solution (b)
Method I
The product of all integers from 1 to 200 = 200!
In case of ‘n!’ (n = a natural number): (number of 2’s) ≥ (number of 5’s).
The number of zeros at the end = Lowest of the (number of 2’s, number of 5’s) = Number of 5’s.
[As 10 = 2× 5, so one 2 and one 5 is needed for a zero at the end].
So, we have to find only number of 5’s in ‘n!’.
Calculation of number of 5’s in ‘200!’:
Step 1: 200/5 = 40
Step 2: 40/5 = 8
Step 3: 8/5 = 1 (ignore the fractional part)
Total number of 5’s in ‘200!’ = 40 + 8 + 1 = 49.
Method ІІ
Number of 2’s in the product of all integers from 1 to 200 (i.e. 200!) = *200/2+ + *200/22] + [200/23] + [200/24] + [200/25] + [200/26] + [200/27] + [200/28]
([.] denotes the greatest integer; i.e. take only integral part, ignore the fractional part if the number is non – negative, e.g. [200/24] = [12.5] = 12)
= 100 + 50 + 25 + 12 + 6 + 3 + 1 + 0 = 197.
Number of 5’s in the product of all integers from 1 to 200 (i.e. 200!) = *200/5+ + *200/52] + [200/53] + [200/54] = 40 + 8 + 1 + 0 = 49.
Hence, the number of zeros at the end = Lowest of the (number of 2’s, number of 5’s) = 49.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Method I
The product of all integers from 1 to 200 = 200!
In case of ‘n!’ (n = a natural number): (number of 2’s) ≥ (number of 5’s).
The number of zeros at the end = Lowest of the (number of 2’s, number of 5’s) = Number of 5’s.
[As 10 = 2× 5, so one 2 and one 5 is needed for a zero at the end].
So, we have to find only number of 5’s in ‘n!’.
Calculation of number of 5’s in ‘200!’:
Step 1: 200/5 = 40
Step 2: 40/5 = 8
Step 3: 8/5 = 1 (ignore the fractional part)
Total number of 5’s in ‘200!’ = 40 + 8 + 1 = 49.
Method ІІ
Number of 2’s in the product of all integers from 1 to 200 (i.e. 200!) = *200/2+ + *200/22] + [200/23] + [200/24] + [200/25] + [200/26] + [200/27] + [200/28]
([.] denotes the greatest integer; i.e. take only integral part, ignore the fractional part if the number is non – negative, e.g. [200/24] = [12.5] = 12)
= 100 + 50 + 25 + 12 + 6 + 3 + 1 + 0 = 197.
Number of 5’s in the product of all integers from 1 to 200 (i.e. 200!) = *200/5+ + *200/52] + [200/53] + [200/54] = 40 + 8 + 1 + 0 = 49.
Hence, the number of zeros at the end = Lowest of the (number of 2’s, number of 5’s) = 49.
-
Question 32 of 35
32. Question
A kid has been given 4 consonants and 3 vowels. How many words can the kid form with these if he has to use only 3 consonants and 2 vowels in one word?
Correct
Solution (b)
Number of ways of selecting 3 consonants from a set of 4 consonants = 4C3 = 4
Number of ways of selecting 2 vowels from a set of 3 vowels = 3C2 = 3
Number of ways of selecting 3 consonants and 2 vowels = 4 × 3 =12
So, number of ways of forming a five lettered word = 12 × 5!
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Number of ways of selecting 3 consonants from a set of 4 consonants = 4C3 = 4
Number of ways of selecting 2 vowels from a set of 3 vowels = 3C2 = 3
Number of ways of selecting 3 consonants and 2 vowels = 4 × 3 =12
So, number of ways of forming a five lettered word = 12 × 5!
-
Question 33 of 35
33. Question
X is the set of positive integers such that when divided by 24, 32 and 36 these integers leave the remainders 19, 27 and 31 respectively. How many integers between 1 and 1000 belong to set X?
Correct
Solution (b)
Note that the difference between the divisors and the remainders is constant.
24 – 19 = 5; 32 – 27 = 5; 36 – 31 = 5
In such a case, the required number will always be [a multiple of LCM (24, 32, 36) – (The constant difference)], i.e. [n× LCM (24, 32, 36) – 5]
(n= natural number)
Now, 24 = 23 × 3; 32 = 25; 36 = 22 × 32
So, LCM (24, 32, 36) = 25×32 = 288.
Hence, the required number = n×288 – 5
For n=1, X1 = 1 × 288 – 5 = 283
For n=2, X2 = 2 × 288 – 5 = 571
For n=3, X3 = 3 × 288 – 5 = 859.
So, between 1 and 1000, there are three such numbers, viz. 283, 571 and 859.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Note that the difference between the divisors and the remainders is constant.
24 – 19 = 5; 32 – 27 = 5; 36 – 31 = 5
In such a case, the required number will always be [a multiple of LCM (24, 32, 36) – (The constant difference)], i.e. [n× LCM (24, 32, 36) – 5]
(n= natural number)
Now, 24 = 23 × 3; 32 = 25; 36 = 22 × 32
So, LCM (24, 32, 36) = 25×32 = 288.
Hence, the required number = n×288 – 5
For n=1, X1 = 1 × 288 – 5 = 283
For n=2, X2 = 2 × 288 – 5 = 571
For n=3, X3 = 3 × 288 – 5 = 859.
So, between 1 and 1000, there are three such numbers, viz. 283, 571 and 859.
-
Question 34 of 35
34. Question
A two-digit number n1 is divisible by 12, 15 and 20 and n2 is nearest perfect square to number n1. Then find n2-n1
Correct
Solution (b)
Number n1 is divisible by 12, 15 and 20 so we find its LCM of these numbers
= 2|12, 15, 20
= 2|6, 15, 10
= 3|3, 15, 5
= 5|1, 5, 5
= |1, 1, 1
So LCM of 12, 15 and 20 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 = 60
So lowest possible number divisible by 12, 15 and 20 = 60
So n1 = 60
Nearest perfect square near 60 = 64=n2
So n2 – n1= 64 – 60 = 4.
Incorrect
Solution (b)
Number n1 is divisible by 12, 15 and 20 so we find its LCM of these numbers
= 2|12, 15, 20
= 2|6, 15, 10
= 3|3, 15, 5
= 5|1, 5, 5
= |1, 1, 1
So LCM of 12, 15 and 20 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 = 60
So lowest possible number divisible by 12, 15 and 20 = 60
So n1 = 60
Nearest perfect square near 60 = 64=n2
So n2 – n1= 64 – 60 = 4.
-
Question 35 of 35
35. Question
Which of the following number(s) is/are not prime?
- 22001 + 1
- 22002 + 1
- 22003 + 1
Choose the correct code:
Correct
Solution (d)
In expression (an + bn)/ (a + b), Remainder = 0, if n is odd.
[i.e. (an + bn) is divisible by (a + b) if n is an odd number].
So, (22001 + 1) and (22003 + 1) both are divisible by (2 + 1), i.e. 3.
Now, 22002 + 1 = (22)1001 + 1 = 41001 + 1, which is divisible by (4 + 1), i.e. 5.
Hence, none of the given numbers is a prime number.
Incorrect
Solution (d)
In expression (an + bn)/ (a + b), Remainder = 0, if n is odd.
[i.e. (an + bn) is divisible by (a + b) if n is an odd number].
So, (22001 + 1) and (22003 + 1) both are divisible by (2 + 1), i.e. 3.
Now, 22002 + 1 = (22)1001 + 1 = 41001 + 1, which is divisible by (4 + 1), i.e. 5.
Hence, none of the given numbers is a prime number.
All the Best
IASbaba
