Archives
IASbaba’s Daily Current Affairs – 9th December, 2015
NATIONALTOPIC:
- General Studies 1: Social issues, urbanization, migration;
- General Studies 2: Governance issues, Municipalities and Municipal Corporations
- General Studies 3: Disaster Management, Floods, El Nino effects, Cyclones etc.
Disaster Management, Urbanization Issues and Governance – The Chennai Disaster
Reasons for the recent Chennai flooding
- A complete absence of urban planning, an inability to ensure effective compliance with development rules, a lack of enforcement of fire safety mechanisms, and an abject failure to provide safe shelter to the homeless are some of the reasons for the massive devastation in Chennai.
- The city's infrastructure was not built to face a catastrophe of this kind.
- In an effort to modernize towns and citites, transport systems are being constructed illogically over lands bounding, sometimes on top of canals and rivers etc.
- The Coastal Regulation Zones have been mercilessly broken. Multi-storied buildings have been constructed on environmentally hazardous lands. Natural drainage systems have been blocked to enable a development which has become unsustainable.
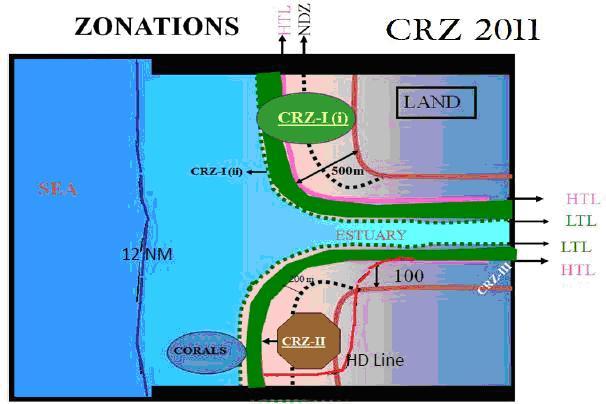
What are CRZs?
As per the official CRZ notification under Environment Protection Act, 1986, the coastal land up to 500m from the High Tide Line (HTL) and a stage of 100m along banks of creeks, estuaries, backwater and rivers subject to tidal fluctuations, is called the Coastal Regulation Zone(CRZ).
Read this government website for more information on the regulations of CRZ - http://envfor.nic.in/legis/crz/crznew.html
Urban infrastructure problems in large cities
- Violations of building rules, absurd constructions made over forbidden land and purported encroachments made on the river-beds.
- Metamorphosis from a largely rural country into an urbanising liberal democracy has led to choking of cities and towns.
- Rampant urban migration is chaotic and managed by a creaky and corrupt state infrastructure.
- Urbanisation in India has quickened because of the government's failure to boost agricultural growth and rural economic opportunities.
- The political class sitting on the top of the system shut their eyes to illegal constructions, unpaved roads and flawed flyovers. The money siphoned off through corruption is used as their election expenses.
NDMA
- National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) is an agency of the Ministry of Home Affairs whose primary purpose is to coordinate response to natural or man-made disasters and for capacity-building in disaster resiliency and crisis response.
- NDMA was established through the Disaster Management Act enacted by the Government of India in December 2005. The Prime Minister is the de facto chairperson of NDMA.
- The agency is responsible for framing policies, laying down guidelines and best-practices and coordinating with the State Disaster Management Authorities (SDMAs) to ensure a holistic and distributed approach to disaster management.
IASBaba's Views:
- Enough economic activity must be generated in the rural sector to slow down the rampant migration.
- For this, the government must focus on employment generation, improving agricultural productivity and must reduce intra-regional inequalities.
- Once the unnecessary urbanisation deteriorates, growing cities will be less choked and then the urban planning needs to be taken care of.
- Environmental rules and regulations to be followed during rampant construction. A regeneration of lost lakes and aquifers is necessary for the rebirth of the natural drainage systems.
Some Questions to Ask Ourselves:
- Are the missing drainages and shrinking water-bodies of Chennai a creation of our corrupt masters?
- Has Chennai's misery been accentuated by the failure of the state to manage its urbanisation?
- Will the Chennai disaster repeat itself in the coming days for the rest of the country?
Connecting the Dots:
- A link between global warming, climate change and frequent adverse environmental disasters are inter-related.
- Greenhouse gases emissions rooted in the aftermath of the industrial revolution can be the cause for the rampant sociological issues emerged out of intense geographical hazards and advanced by social issues such as urbanisation and corrupt state infrastructure.
- A nexus of politicians-bureaucrats-construction companies can be blamed partly for the devastation in Chennai.
- Critically comment on the need for governmental infrastructure towards disaster management and resilience.
- Analyze the social phenomena, such as migration, on the effects of urban deterioration.
NATIONAL
TOPIC:
- General Studies 2: Indian Constitution- historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
- Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries.
Fundamental Duties—What the Citizens must do
- As citizens of independent India, we are fully aware of our guaranteed fundamental rights exhibiting much significance due to its nature that portrays:
- Reassertion of the oppressed with a rare zeal from the ‘colonial oppression and a state of absence of basic rights’
- Extension of rights to the domain of freedom of religion as well
- With the much highlighted significance of the fundamental rights of the citizens, the due importance of ‘what the citizen must know’ or ‘how the citizen must be’ reached a state of perpetual ignorance wherein the concept of an organized society was subjected to be viewed only one-dimensionally ad the second dimension highlighting the citizen’s ‘high sense of duty’ stayed— shadowed.
- Fundamental Duties and Fundamental Rights need to exist together; as in a democracy like India there should absolutely be no space left for any element of ‘anarchy’ to creep in. They act as a disciplinarian force— reminding citizens of their commitment and their role as not just a mere spectator but an active citizen in the realisation of national goals.
Swaran Singh Committee:
This Committee was set up to fulfil the need and the necessity that was felt during the operation of the internal emergency in the years 1975-1977
Actions undertaken:
- Acceptance of the recommendations and enactment of 42ndConstitutional Amendment Act in the year 1976
- Addition of Part IVA to the Constitution consisting of only one Article i.e., Article 51A specifying ten duties of the citizens
Recommendations Rejected:
- Imposition of penalty or punishment for non-compliance or refusal to observe mentioned duties
- The law imposing penalty cannot be called in question to any court on the ground of infringement of any Fundamental Rights
- Duty to pay taxes
Nature of Fundamental Duties: A balanced mix of civic as well as moral duties incorporating also, our traditional values; forms the core of Fundamental Duties suiting the Indian way of living
Interventions till date:
- 43rd Amendment Act (1977) and the 44th Amendment Act (1978)
- Verma Committee was set up in 1999 to identify the existence of legal provisions for the implementation of some of the Fundamental Duties
- 86th Amendment Act—Duty of every citizen of India to provide opportunities for education to his/her child/ward between the age of 6-14 (Right to Education)
Note:
- Fundamental Duties are inspired by the Constitution of the erstwhile USSR
- The only democratic country Constitution in the world containing a list of duties of citizens— Japan
- Fundamental Duties, in India, are confined to citizens only
IASbaba’s Views:
- There are number of schemes that have been implemented and the one’s which are being implemented; but the crucial gap remains between the expected awareness amongst the citizens and the ignorance that perpetuates in their consciousness.
- The perspective ‘ekam sat viprabahudhavadanti’ highlighting the fact—‘ultimately there is one truth, but wise men say it differently’ should form the core of citizen’s duties
- There is a need for increased awareness and this should be taken care of since the childhood by making the new generation aware of their duties and by also including the essential aspects in the oaths and pledges.
- These duties should be made binding, the ‘non-justiciable’ aspect attached with it should be done away with and legal sanctions should also be established against their violation.
Connecting the Dots:
- Has the inclusion of Fundamental Duties in the Constitution contributed effectively in strengthening democracy? Discuss
- Trace the evolution of fundamental duties and put up a defending case upon its inclusion in the Constitution
MUST READ
Securing the pace of India-Pakistan talks
Tobacco farmers rally against pictorial warning
A line in the water- Curbs on construction on the Ganga must be part of a larger effort to keep alive the river ecosystem.
The right forum- Apex court does well to emphasise primacy of the legislature, and the political process, in deciding on a uniform civil code.
For Detailed Analysis ‘uniform civil code’ refer the below links-
http://iasbaba.com/2015/10/iasbabas-daily-current-affairs-13th-october-2015/
Prelude to GST
Report of a key panel lays out the middle ground for resolving political differences.
For Detailed Analysis ‘GST’ refer the below links-
http://iasbaba.com/2015/07/iasbabas-daily-current-affairs-18th-july-2015/
India to sign deal with Japan to get its first bullet train
MIND MAPS
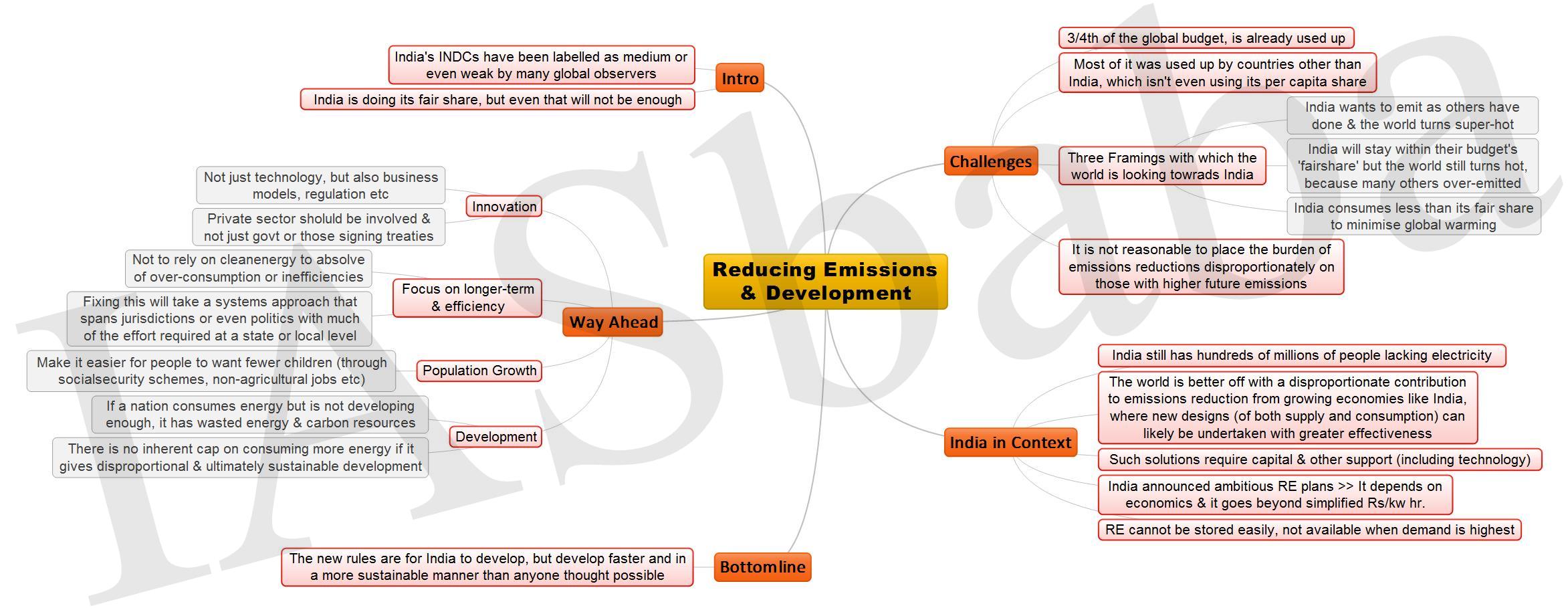
1. Duties & Polity- The Indian Express Link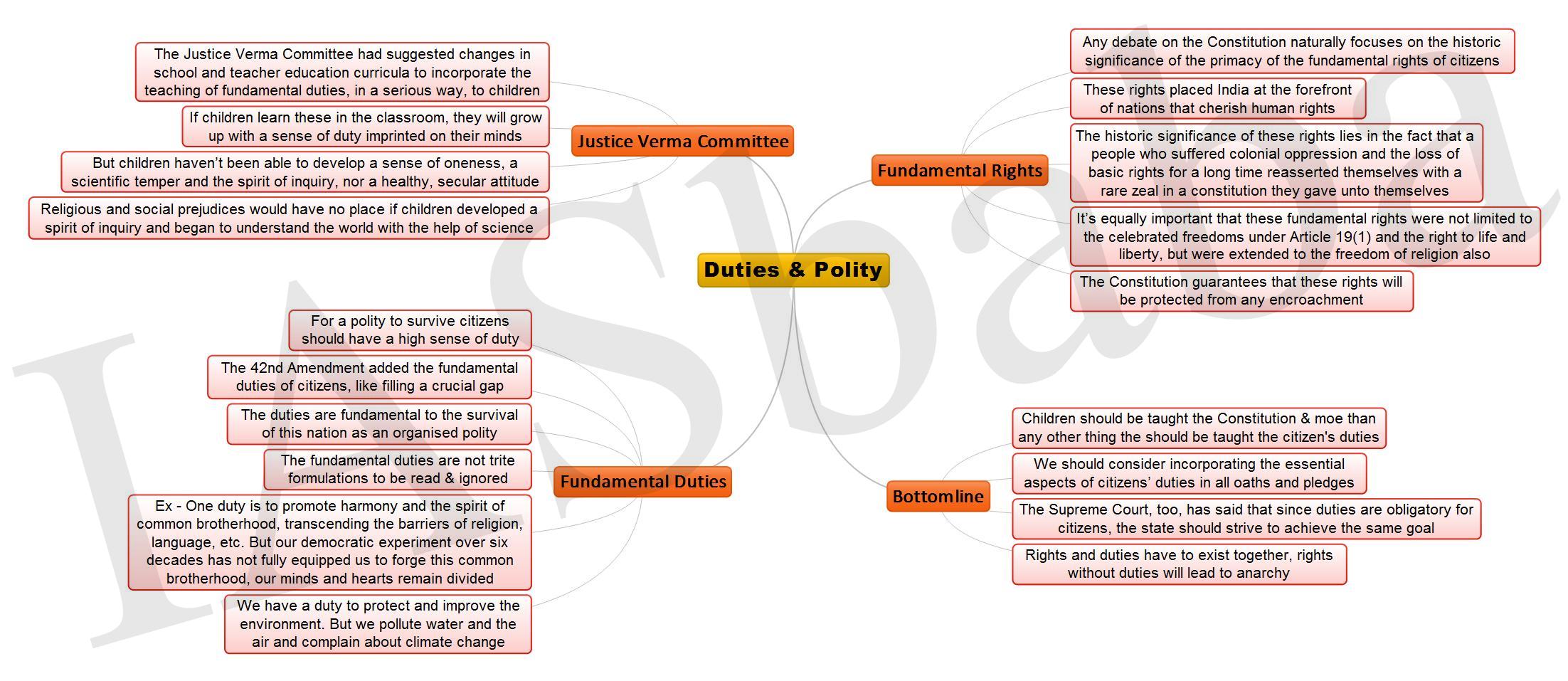 2. Reducing Emissions and Development- The Hindu
Link
2. Reducing Emissions and Development- The Hindu
Link