IASbaba's Daily Current Affairs (Prelims + Mains Focus)- 23rd June 2018
Archives
(PRELIMS+MAINS FOCUS)
Plastic Waste Management (PWM) Rules
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains – Environment and ecology; Pollution
In news:
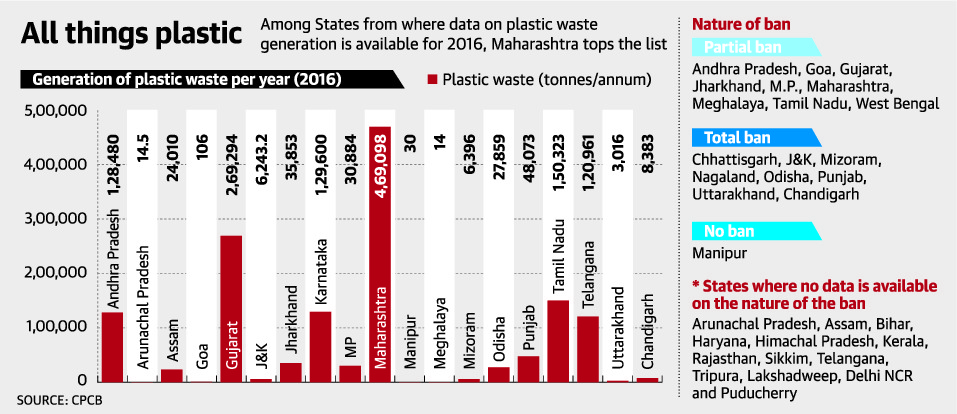
- India generates an estimated 32 million metric tonnes of packaging waste each year, of which plastic waste constitutes 16%. But only 60% of the collected plastic waste is recycled.
- According to the Plastic Waste Management (PWM) Rules, 2016, all States have to annually apprise the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) on the steps taken to reign in plastic use, whether a ban is in force, and the strength and performance of a recycler and waste-processing network.
We know that,
- The theme for the World Environment Day 2018, “Beat Plastic Pollution”.
- The theme of Earth Day 2018 is “End Plastic Pollution”.
Important Value Additions:
The Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016 aim to:
- Increase minimum thickness of plastic carry bags from 40 to 50 microns.
- Expand the jurisdiction of applicability from the municipal area to rural areas, because plastic has reached rural areas also.
- Responsibility of local bodies and Gram Panchayat.
- Collect back system of plastic waste.
- To bring in the responsibilities of producers and generators, both in plastic waste management system and to introduce collect back system of plastic waste.
- Phasing out of manufacture and use of non- recyclable multilayered plastic: to be phased out in two years’ time.
- To promote use of plastic waste for road construction as per Indian Road Congress guidelines or energy recovery, or waste to oil etc. for gainful utilization of waste and also address the waste disposal issue;
Performance (according to latest CPCB report)
- States’ claim on fighting plastic only strong on paper.
- Only 24 States and Union Territories have complied with some of the above directions.
- Most states’ have imposed ban only in specific towns or cities.
- Delhi, which reportedly generates the largest quantity of plastic waste in the country, has not provided information on its plastic management initiatives to the CPCB.
- The law requires that all plastic waste recyclers register themselves but there were around 312 unregistered plastic manufacturing/recycling units across India.
- Most of the States/UTs have not set up proper monitoring system for use of carry bags as per the specified guidelines.
- Maharashtra tops the list on plastic waste generation
Pic link: https://d39gegkjaqduz9.cloudfront.net/TH/2018/06/23/DEL/Delhi/TH/5_05/41ffb33f_2193050_101_mr.jpg
Article link: States' claim on fighting plastic only strong on paper - The Hindu
India- Seychelles: Assumption island naval base project stalled
Part of: GS Mains II – International Relations; India and the World
In news:
- Seychelles National Assembly will not ratify India’s plans to build a naval base in the western Indian Ocean region.
- India had proposed to build a naval base on the strategically located Assumption island.
- Assumption Island is a small island in the Outer Islands of Seychelles north of Madagascar.
- Seychelles believe allowing Indian Naval base would infringe on the country’s sovereignty.
Coast guard facility :
- Seychelles has indicated that instead of allowing India to run the base, it would like to develop a coast guard facility at the Assumption.
- The Indian project was to include a facility for Indian ships and an airstrip that would allow New Delhi to guard the energy lanes vital to India’s economy.
Ambubachi Mela: Festival to mark the menstrual period of the goddess
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains I – Culture and Indian society
In news:
- Ambubachi Mela, a four-day fair to mark the annual menstruation of the goddess at Kamakhya temple, Assam.
- Kamakhya, atop Nilachal Hills in Guwahati, is one of 51 shaktipeeths or seat of Shakti followers, each representing a body part of Sati, Lord Shiva’s companion. The temple’s sanctum sanctorum houses the yoni — female genital — symbolised by a rock.
- Temple priests said the ritualistic fair celebrating the goddess’ period is one of the reasons why the taboo associated with menstruation is less in Assam compared to other parts of India. The attainment of womanhood of girls in Assam is celebrated with a ritual called ‘Tuloni Biya’, meaning small wedding.
Indo-UN Small Satellites Programme (UNSSP):
Part of: GS Prelims and Mains III – Science and Tech; Space programmes
Key pointers:
- India to teach satellite tech to students from abroad
- India has thrown open its satellite-building expertise to engineering graduates chosen from other countries.
- ISRO’s Bengaluru-based U.R. Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) — until recently known as ISAC — will train the overseas students.
- Capacity-building programme was India’s contribution to the world in response to a request that the UN Office for Outer Space Affairs had made to space-faring nations last year.
- The countries are marking the 50th year of the first UN Conference on the Exploration and Peaceful Uses of Outer Space — called UNISPACE+50.
(MAINS FOCUS)
INTERNAL SECURITY
TOPIC:General Studies 3:
- Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security.
- Challenges to internal security through communication networks
- Security challenges and their management in border areas; linkages of organized crime with terrorism.
Tackling Vigilantism and Protecting Minorities
Background:
In our previous article [Shifting taxonomy of violence], we read that –
India is witnessing saga of violence and conflicts.
The article mainly focused on incidents which caused law and order problems due to industry versus environment concerns –
- Sterlite’s copper smelters in Thoothukudi
- tanneries spewing effluents in Kanpur
- iron mines in Goa
- Bhopal Gas Tragedy of 1984, the mother of all environmental tragedies.
Also adding to above list, were the escalating violence resulting from caste conflicts, such as –
- most recent Dalit uprising
- farmers’ woes across the country
- rape of young women and children
- issues revolving around tradition versus modernity
- outsider versus insider syndrome, especially in the Northeast
All the above issues had resulted in highly complex violence (police firings, death of over a dozen individuals, etc) and needed careful attention.
The article stressed the need for redefining the internal security landscape and for new methods to deal with the above new-era protests. (You can revise previous article by clicking this link - Shifting taxonomy of violence)
Apart from above incidents there are other episodes of mass communal violence – recurring incidents of lynching and targeted mob violence against vulnerable groups – have been reported from various parts of the country.
These recurring incidents are a direct challenge thrown by right-wing groups to political processes, especially electoral processes and the rule of law. (what we can all as ‘vigilante violence’)
**Vigilantism - law enforcement undertaken without legal authority by a self-appointed group of people.
Vigilantism, at its peak?
South Asia has a long history of communal violence, but these were primarily big episodes of mass violence.
This has now given way to a smaller-scale of conflict and vigilante violence against individuals endorsed by state inaction.
According to India Spend, a data-journalism website -
- 86% of those killed in lynching incidents in 2017 were Muslims
- Supreme Court in 2017 directed all State governments to take measures to prevent vigilantism in the name of cow protection.
- However, public lynching or vigilante violence hasn’t subsided.
- Majority of attacks are due to bovine related, anti-minority attacks and hate violence around festivals.
Are minorities under siege?
- The victims in cases of lynching are almost entirely from poor families and minorities.
- Minorities are continually kept under siege through targeted attacks.
- India has a poor record when it comes to prevention and punishment of the perpetrators of mass violence and/or lynchings.
- Each event of violence has hardened community boundaries and widened the divide between Hindus and Muslims.
According to the Citizens Against Hate (CAH), a civil society group report - 97% of cow-related lynchings had occurred since the Bharatiya Janata Party’s (BJP) rise to political dominance in 2014.
Most of these attacks were based on rumours sparked by accusations, often circulating on social media which take the shape of communal stereotypes of victims.
Most actors leading the charge are suspected to belong to right-wing parties who are backed by political protection.
Apart from the political reasons alluded to above, the rising trend is directly related to the ‘intensification of communal polarisation’ and ‘instrumentalisation of prejudice’ for political ends apparent in various government attempts to infuse religion into politics and education.
In the event, these acts seem to have acquired a certain degree of legitimacy in the public mind.
Conclusion
As hate crimes grow, so does the sense of impunity or licence/freedom enjoyed by the actual perpetrators to continue such injurious crimes increases. Lack of justice for victims further reinforces the vicious cycle of impunity.
The lack of public reaction to such incidents implies a degree of acceptability of violence as an expression of vengeance against ‘injustices’ suffered by Hindus in the past. The theory of ‘Hindu insecurity’ and ‘Hindu persecution’ comes at a time when political representation of Muslims in legislatures and administration and their presence in the public sphere is at its lowest since Independence.
Most of the incidents are not spontaneous acts of violence; there is usually systematic planning behind them.
Has active support of powerful political figures in the current establishment at the Centre and in the States has helped to build networks, gain new recruits, resources and legitimacy that right-wing groups did not have in the past?
Preventing further atrocities requires respect for the rule of law and legal institutions and strong prosecutions and expeditious punishments. Unless checked, it can cause irreversible harm to the social fabric of our society and to the tenets of democracy that have shaped and sustained the idea of India.
Connecting the dots:
Growing hate crimes and vigilante violence needs reforms in our existing laws and legal procedures. Do you agree? Critically examine.
INDIAN HERITAGE AND CULTURE
TOPIC:
General Studies 1:
- Indian culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, Literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
- Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India.
General Studies 2:
- Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate.
UNESCO's World Heritage mission and India’s World Heritage List
Introduction:
Heritage is our legacy from the past, what we live with today, and what we pass on to future generations. Our cultural and natural heritage are both irreplaceable sources of life and inspiration.
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) seeks to encourage the identification, protection and preservation of cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity. This is embodied in an international treaty called the Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage , adopted by UNESCO in 1972.
UNESCO's World Heritage mission is to
- Encourage countries to sign the World Heritage Convention and to ensure the protection of their natural and cultural heritage;
- Encourage States Parties to the Convention to nominate sites within their national territory for inclusion on the World Heritage List;
- Encourage States Parties to establish management plans and set up reporting systems on the state of conservation of their World Heritage sites;
- Help States Parties safeguard World Heritage properties by providing technical assistance and professional training;
- Provide emergency assistance for World Heritage sites in immediate danger;
- Support States Parties' public awareness-building activities for World Heritage conservation;
- Encourage participation of the local population in the preservation of their cultural and natural heritage;
- Encourage international cooperation in the conservation of our world's cultural and natural heritage.
The Criteria for Selection
To be included on the World Heritage List, sites must be of outstanding universal value and meet at least one out of ten selection criteria.
The World Heritage Committee, the main body in charge of the implementation of the Convention, has developed precise criteria for the inscription of properties on the World Heritage List and for the provision of international assistance under the World Heritage Fund.
Selection criteria
(i) to represent a masterpiece of human creative genius;
(ii) to exhibit an important interchange of human values, over a span of time or within a cultural area of the world, on developments in architecture or technology, monumental arts, town-planning or landscape design;
(iii) to bear a unique or at least exceptional testimony to a cultural tradition or to a civilization which is living or which has disappeared;
(iv) to be an outstanding example of a type of building, architectural or technological ensemble or landscape which illustrates (a) significant stage(s) in human history;
(v) to be an outstanding example of a traditional human settlement, land-use, or sea-use which is representative of a culture (or cultures), or human interaction with the environment especially when it has become vulnerable under the impact of irreversible change;
(vi) to be directly or tangibly associated with events or living traditions, with ideas, or with beliefs, with artistic and literary works of outstanding universal significance. (The Committee considers that this criterion should preferably be used in conjunction with other criteria);
(vii) to contain superlative natural phenomena or areas of exceptional natural beauty and aesthetic importance;
(viii) to be outstanding examples representing major stages of earth's history, including the record of life, significant on-going geological processes in the development of landforms, or significant geomorphic or physiographic features;
(ix) to be outstanding examples representing significant on-going ecological and biological processes in the evolution and development of terrestrial, fresh water, coastal and marine ecosystems and communities of plants and animals;
(x) to contain the most important and significant natural habitats for in-situ conservation of biological diversity, including those containing threatened species of outstanding universal value from the point of view of science or conservation.
World Heritage Convention of 1972
- The World Heritage Convention of 1972, adhered to by 192 countries, aims to protect cultural and natural heritage across the world.
- There are presently 1,052 World Heritage sites in 165 countries, of which 814 are cultural sites, 203 natural and 35 mixed; 55 more properties are on the "in danger" list.

- The WHC, however, has received flak for its bias toward Europe and North America, with these two regions being home to nearly half of all World Heritage sites.
India’s World Heritage Sites
India, which ratified the Convention in 1977, has 27 cultural World Heritage sites, seven natural sites and one mixed site. Among the cultural properties are the Taj Mahal, the monuments of Hampi, the churches and convents of Goa, Jaipur’s Jantar Mantar and the Mountain Railways of India, which include the Darjeeling, Nilgiri, and Kalka-Shimla railway networks.
Natural sites include the Sundarbans in West Bengal, the Kaziranga and Manas National Parks in Assam, and the Western Ghats. Sikkim’s Khangchendzonga National Park, which was included this year, is the sole mixed site. While there are four times as many cultural sites in India as natural, the latter are much larger in area. India has the sixth largest number of World Heritage sites. Italy is on top with 51 sites.

Connecting the dots:
- Does UNESCO inscription play a significant role in tourism destinations performance? Also discuss the UNESCO's role in relation to protecting the world heritage site.
(TEST YOUR KNOWLEDGE)
Model questions: (You can now post your answers in comment section)
Q.1) Assumption island is located in -
- Madagascar
- Seychelles
- Maldives
- Mauritius
Q.2) Ambubachi Mela, a festival to mark the menstrual period of the goddess is celebrated in –
- Tamil Nadu
- Assam
- Arunachal Pradesh
- West bengal
Q.3) Ellora caves are one of the World Heritage sites in India. Which of the following statements are correct about ‘Ellora caves’?
- Ellora caves are rock cut caves made from top to bottom.
- The most famous temple of Ellora – Kailashnath temple was made by Rashtrakutas.
- These caves are dedicated to Hinduism only.
Select the code from following:
- 1 and 2
- 2 and 3
- 1 and 3
- All of the above
Q.4) In the Constitution of India, the provision 'to value and preserve the rich heritage of the country’s composite culture' is included in the:
- Preamble to the Constitution
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Fundamental Duties
- Fundamental Rights
MUST READ
At the heart of the Silk Road
Coalition Country
Redraw the Red Line
Let the elite pay
