Pneumonia
Archives
TOPIC: General studies 2
- Public Health issues
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
Pneumonia can occur in young and healthy people, but it is most dangerous for older adults, infants, people with other diseases, and those with impaired immune systems.
[caption id="attachment_52259" align="aligncenter" width="551"]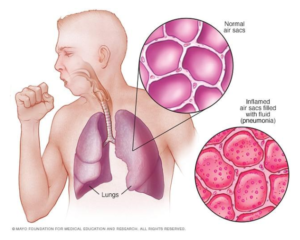 RSTV IAS UPSC – Pneumonia[/caption]
RSTV IAS UPSC – Pneumonia[/caption]
Signs and symptoms of pneumonia:
- Chest pain when you breathe or cough
- Confusion or changes in mental awareness (in adults age 65 and older)
- Cough, which may produce phlegm
- Fatigue
- Fever, sweating and shaking chills
- Lower than normal body temperature (in adults older than age 65 and people with weak immune systems)
- Nausea, vomiting or diarrhoea
- Shortness of breath
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the pneumonia.
- Bacterial types of pneumonia are usually treated with antibiotics.
- Viral types of pneumonia are usually treated with rest and plenty of fluids. Antiviral medications can be used in influenza.
- Fungal types of pneumonia are usually treated with antifungal medications.
Prevention
Along with vaccinations, physicians recommend:
- Regular hand washing
- Covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Refraining from smoking
- Eating healthfully
- Exercising 5 days a week
- Staying away from the sputum or cough particles of others with pneumonia
Is pneumonia contagious?
The germs that cause pneumonia are contagious. This means they can spread from person to person.
Both viral and bacterial pneumonia can spread to others through inhalation of airborne droplets from a sneeze or cough. One can also get these types of pneumonia by coming into contact with surfaces or objects that are contaminated with pneumonia-causing bacteria or viruses.
One can contract fungal pneumonia from the environment. However, it doesn’t spread from person to person.
Pneumonia vs. Bronchitis
Pneumonia and bronchitis are two different conditions. Pneumonia is an inflammation of the air sacs in your lungs. Bronchitis is the inflammation of your bronchial tubes. These are the tubes that lead from your windpipe into your lungs.
